It is more faster and easier to pass the Oracle 1Z0-027 exam by using Tested Oracle Oracle Exadata Database Machine Administration, Software Release 11.x questuins and answers. Immediate access to the Renewal 1Z0-027 Exam and find the same core area 1Z0-027 questions with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Online 1Z0-027 free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which three are among the software components that constitute the QoS Management framework?
- A. Cluster Health Monitor (CHM)
- B. Cluster Verification Utility (CLUVFY)
- C. O/S Resource Manager
- D. Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server
- E. Grid Infrastructure for a cluster
- F. OC4J cluster resource
Answer: AEF
Explanation:
A: In conjunction with Cluster Health Monitor, QoS Management’s Memory Guard detects nodes that are at risk of failure due to
memory over-commitment. It responds by automatically preventing new connections thus preserving existing workloads and restores connectivity once the sufficient memory is again available.
F: The ora.oc4j is for the QoS (Quality of Service Management), which is only available on
Exadata.
Incorrect:
Not B: The Cluster Verification Utility (CVU) performs system checks in preparation for installation, patch updates, or other system changes. Using CVU ensures that you have completed the required system configuration and preinstallation steps so that your Oracle grid infrastructure or Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) installation, update, or patch operation completes successfully.
NEW QUESTION 2
You plan to migrate an Oracle database that supports an online transaction processing (OLTP) workload to your Database Machine.
Following are details for the source database: Database version: 10.2.0
Byte order: Big Endian HP-UX (64-bit) Database size: 24 TB
Storage: ASM with 1 MB allocation unit size Which two are supported migration methods?
- A. Physical migration using ASM online Migration
- B. Physical migration using Transportable Database
- C. Logical migration using Oracle Streams
- D. Local migration using Oracle Streams
- E. Logical migration using logical standby
Answer: CE
Explanation:
There are several techniques for migrating data to a Database Machine. Migration can be done
using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to backup from traditional storage and restore the data
onto Exadata. Oracle Data Guard can also be used to facilitate a migration. This is done by first
creating a standby database based on Exadata storage. The standby can be using Exadata storage
and the production database can be on traditional storage. By executing a fast switchover, taking
just seconds, you can transform the standby database into the production database. This provides
a built-in safety net as you can undo the migration very gracefully if unforeseen issues arise.
Transportable Tablespaces (B) and Data Pump may also be used to migrate to Exadata.
Any
technique used to move data between Oracle Databases can be used with Exadata.
NEW QUESTION 3
You plan to monitor storage servers after configuring an I/O resource manager plan with directives for inter-database plans and intra-database plans.
Which two types if metrics would help assess the impact of the intra-database plans on I/O to the storage servers?
- A. Category I/O
- B. Database I/O
- C. Resource Consumer Group I/O
- D. Smart Flash Log I/O
- E. Smart Flash Cache I/O
Answer: BC
Explanation:
B: Database metrics provide information about the size of the I/O load from each database specified in the interdatabase plan.
C: Consumer group metrics provide information about the size of the I/O load from each consumer group specified in a database resource plan. Each database in the interdatabase plan has metrics for each of its consumer groups.
Note:
* I/O Resource Manager (IROM) Settings
* Incorrect:
Not A: Category metrics provide information about the size of the I/O load from each category specified in the current IORM category plan.
NEW QUESTION 4
Which two are true about Exadata storage server alerts?
- A. Metric alerts are never stateful.
- B. Metrics have no thresholds set on them by default.
- C. SNMP alert notifications can be sent to only one destination.
- D. Metric threshold; if set, will persist across storage server reboots.
- E. SMTP alert notifications must be sent to both ASR manager and Enterprise Manager Agents
Answer: DEExplanation:Incorrect:
Explanation:
Not A: there are both stateful and stateless alerts. Not B: Metrics have defaults.
Not C: An SNMP alert can have multiple destinations.
NEW QUESTION 5
Identify the correct sequence of commands to completely power off a Database Machine in an Orderly fashion:
1. Execute “crsctl stop cluster –all” as the grid user from one database server.
2. Execute “crsctl stop cluster –all” as the root user from one database server.
3. Power off all network switches using their power switch.
4. Execute “crsctl stop cluster –all” as the root user from one database server.
5. Execute “crsctl stop cluster –all” as the grid user from one database server.
6. Power off the rack using the power switches on the PDUs.
7. Execute “shutdown –h now” on all database servers.
8. Execute “shutdown –h now” on all Exadata storage servers.
1. 9. Execute “shutdown –h now” on all servers.
- A. 1, 9, 3 and 6
- B. 2, 9 and 6
- C. 4, 7, 8, 3 and 6
- D. 5, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- E. 2, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- F. 1, 8, 7, 3 and 6
- G. 2, 7, 8 and 6
- H. 2, 8, 7 and 6
Answer: G
NEW QUESTION 6
Consider the following list of software components:
1. DCLI
2. Management Server (MS)
3. ASM Instance
4. RDBMS instance
5. Restart Server (RS)
6. Cellcli
7. Cell Server (CELLSRV)
8. Diskmon
Identify the location where these software components may run in the standard Database machine deployment.
- A. 3, 4 and 8 run on the database servers; 1, 2, 5, 6 and 9 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
- B. 4 and 8 run on the database servers; 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
- C. 1, 3 and 4 run on the database servers; 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
- D. 3, 4 and 8 run on the database servers; 1, 2, 5, 6 and 7 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
- E. 3, 4 and 8 run on the database servers; 1, 2, 5, 7 and 8 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
- F. 1, 3, 4 and 8 run on the database servers; 1, 2, 5, 7 and 8 run on the Exadata Storage servers.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 7
Your customer wants you to partition the database and storage grids in his X3-2 full rack, creating database clusters and two storage grids.
One cluster will be used for production and should consist of 6 databases servers and 11 cells from the first storage grid.
The other cluster will be used for test and development, and should consist of 2 database servers and 3 cells from the second storage grid.
The storage must be partitioned so that the cells are visible only to the appropriate database servers based on the description above.
What must be done to achieve this?
- A. Configure Exadata realms using Oracle ASM scoped security mode.
- B. Configure Exadata realms using Database scoped security mode.
- C. Edit the CELLIP.ORA file on each database server to contain IP addresses of cells in the storage grid associated with cluster to which that database server belongs.
- D. Edit the CELLINIT.ORA file on each database server to contain IP addresses of cells in the storage grid associated with the cluster to which that database server belongs.
- E. Edit the CELLIP.ORA file on each database server to contain IP addresses of database servers which are allowed access to specific cells in the same storage grid.
- F. Edit the CELLIP.ORA file on each cell to contain IP addresses of database servers in the database server grid that are associated with the storage grid to which that cell belongs.
Answer: C
Explanation:
cellip.ora
The cellip.ora is the configuration file, on every compute node, that tells ASM instances which cells are available to this cluster.
Here is a content of a typical cellip.ora file for a quarter rack system:
$ cat /etc/oracle/cell/network-config/cellip.ora cell="192.168.10.3"
cell="192.168.10.4" cell="192.168.10.5"
Now that we see what is in the cellip.ora, the grid disk path, in the examples above, should make more sense.
Note:
* cellinit.ora decides which network takes storage traffic.
* cellip.ora - list of cells, new cells can be added dynamically without shutdown
NEW QUESTION 8
Which three storage components are available after the standard initial Database machine deployment?
- A. The DATA_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroup
- B. The RECO_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroup
- C. Mirrored system partitions on hard disk 0 and hard disk 1
- D. The DBFS_DG diskgroup with external redundancy
- E. Exadata Smart Flash Cache using all of the flashdisk space
Answer: ABC
NEW QUESTION 9
You plan to migrate a database supporting an an OLTP workload to your Database Machine
This is part of a consolidation project and several other databases already exist on the Database Machine.
Which three Exadata features may help to improve the performance of this OLTP workload?
- A. Hybrid Columnar Compression
- B. I/O Resource Manager
- C. Smart Flash Cache
- D. Smart Flash Log
- E. Smart Scan
- F. Storage Index
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
C:
OLTP performance benefits with Exadata
/ (D) Smart flash log for low latency commits
/ (C) Smart flash cache for low latency reads. KEEP in Flash for critical objects
NEW QUESTION 10
To guarantee proper cooling, you plan to place perforated floor tiles near your Database Machine.
Where, in relation to the cabinet, should they be placed?
- A. On the left side, because the air flow is from left to right
- B. At the back, because the air flow is from back to front
- C. On the right side, because the air flow is from right to left.
- D. At the front, because the air flow is from front to back
- E. Underneath the cabinet, because the air flow is from bottom to top
Answer: D
Explanation:
Airflow must be front-to-back.
Reference: Oracle White Paper, ORACLE Exadata Database Machine X3-8
NEW QUESTION 11
You are about to run the oplan utility to patch the servers on your test Database Machine before patching the production environment.
The following task might be performed:
A) Test the failback procedure
B) Run the exachk utility
C) Read the README file.
D) Automate the patch application process as appropriate.
E) Verify that the patch provides the functionality it is meant to.
F) Apply the patch.
G) Evaluate the system performance.
In which order should the tasks be performed to patch in the recommended fashion?
- A. C, B, D, F, B, E, A
- B. C, D, F, B, E, G, A, B
- C. C, B, D, F, E, G, A
- D. C, B, D, F, E, A, G
- E. C, B, D, F, B, E, G, A
Answer: E
NEW QUESTION 12
Identify two valid reasons for creating multiple griddisks on a Single celldisk.
- A. To segregate storage into multiple pools with different performance characteristics
- B. To facilitate normal or high redundancy ASM diskgroups
- C. To enable disk mirroring for the system area
- D. To segregate storage into multiple pools that can be assigned to different databases
- E. To segregate storage into multiple pools that can be assigned to different resource consumer groups in the same database.
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 13
Your database Machine has the exachk utility pre-installed and you decide to use it periodically, to validate the installation against Oracle’s recommended best practices.
Which two actions could you take to do this?
- A. Use a cron job on a database node to run it at regular intervals.
- B. Rut it once from a database node and it will then perform periodic monitoring automatically.
- C. Use a cron job on each cell to run it at regular intervals.
- D. Run it once on each cell and it will then perform periodic monitoring automatically.
- E. Create a Job in Enterprise Manager to run the exachk utility at regular intervals.
Answer: AE
NEW QUESTION 14
Yesterday, an Exadata storage server flashdisk entered the poor performance state.
This flashdisk os used by flashcache and has a griddisk which is a member of a normal redundancy diskgroup.
Identify the six steps you must perform to replace flashdisk.
- A. Identify the griddisk located on the poorly performing flashdisk and drop it from the associated ASm diskgroup.
- B. Verify that the griddisk located on the poorly performing flashdisk has been successfully dropped from the associated ASM diskgroup.
- C. Drop the flashcache on all cell.
- D. Safely power off the cell containing the poorly-performing flashdisk.
- E. Replace the poorly performing flashdisk.
- F. Power up the cell containing the replaced flashdisk and activate all griddisks.
- G. Recreate the flashcache on the cell using all flashdisks.
- H. Create a new griddisk on the replaced flashdisk.
- I. Add the griddisk back into the ASM diskgroup to which it belonged.
Answer: ADEFHI
Explanation:
Note:
* The default way to deal with the Flash Storage is to use it completely as Flash Cache. You may think of Flash Cache as a prolongation of the Database Buffer Cache. It is populated automatically by the system with objects deemed useful to cache them.
* The second possibility to deal with the Flash Storage is to take a part of it for building ASM diskgroups upon. All files on these ASM diskgroups will then reside permanently on Flash Storage:
CellCLI> drop flashcache
Flash cache exa5cel01_FLASHCACHE successfully dropped
CellCLI> create flashcache all size=100g
Flash cache exa5cel01_FLASHCACHE successfully created CellCLI> create griddisk all flashdisk prefix=flashdrive
NEW QUESTION 15
You have configured a multi-rack Database Machine with two X3-8 full racks all in a single cluster and storage grid.
Which two are true regarding the servers on which Enterprise manager agents must be deployed in order to monitor all components of the multi-rack Database Machine?
- A. On only one database server in the first rack
- B. On all storage servers in all racks
- C. On at least two storage servers in the first rack
- D. On all database servers in the first rack
- E. On only one database server in second rack
- F. On all database servers in second rack
- G. On at least two storage servers in the second rack
Answer: DF
Explanation:
Note:
* The Enterprise Manager agent must be deployed to all compute nodes of the Database Machine.
* Oracle's documentation uses the term compute node when referring to the database server tier of the platform.
* The Exadata Database Machine runs Oracle Database 11g Real Application Cluster. The cluster and the database run on the servers known as database nodes or compute nodes (or simply “nodes”).
* Cells and compute nodes are not shared between partitions.
* Compute nodes in same partition share the same Cluster.
NEW QUESTION 16
You have a partitioned database grid on an X3-2 full rack with two four-node RAC clusters called CLUSA and CLUSB. The storage grid, however, has not been partitioned.
Which files on which servers must be modified after connecting an Exadata storage full expansion rack to your X3-2 Exadata Database Machine on the InfiniBand network so that the cells on the expansion rack are added to the storage grid?
- A. The CELLINIT.ORA files on database servers in CLUSA
- B. The CELLIP.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSA
- C. The CELLINIT.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSB
- D. The CELLIP.ORA files on all existing and newly added Exadata storage servers.
- E. The CELLIP.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSB
Answer: BE
Explanation:
Note:
* cellinit.ora, cellip.ora
-- on database server
cellinit.ora - identifies the storage network interface on the database server cat /etc/oracle/cell/network-config/cellinit.ora
cellip.ora - identifies the Exadata cells that are accessible to the database server cat /etc/oracle/cell/network-config/cellip.ora
* The cellip.ora is the configuration file, on every compute node, that tells ASM instances which cells are available to this cluster.
Here is a content of a typical cellip.ora file for a quarter rack system:
$ cat /etc/oracle/cell/network-config/cellip.ora cell="192.168.10.3"
cell="192.168.10.4" cell="192.168.10.5"
NEW QUESTION 17
You are examining the existing IORM configuration on the cells of Database Machine, to see if they require my modifications based on recent changes to various workloads.
All seven cells in your X3-2 half-rack shown the following:
Which two are true about I/O to the cells using this plan?
- A. I/O requests in the batch category may use flashcache if the I/O is from the sales finance database, and these I/O requests are guaranteed to get 80% of the I/O if the interactive category I/Os use no more than 20%.
- B. I/O requests made by sessions in the marketing database may use flashing and flashcache if no other categories or database or database are using flashing and flashcache at the same time.
- C. I/O requested in the interactive category may use flashdns if the I/O is from the sales or finance databases, and these I/O requests are guaranteed to get 90% of the I/O if the enough I/Os are issued in this category.
- D. I/O requests from the sales database may use flashing regardless of the I/O category.
- E. No I/Os in any category or from any database may use flashing or flashcache because the objective is off.
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 18
Which statement is true about operating systems on database Machine multi-rack configuration consisting of two full racks and one Exadata storage rack?
- A. All Exadata storage servers and all database servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and X3-8 database server may run the Oracle Solaris O/S.
- B. All Exadata storage servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the Oracle Linux O/s.
- C. All Exadata storage servers must run the Oracle Linux O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the same O/s.
- D. All Exadata Storage Servers must run the Oracle Solaris O/S and all database servers within the same cluster must run the same O/S.
- E. All Exadata storage servers in the same cluster must run the same O/S but Exadata Storage Servers in different clusters may run a different O/S.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 19
You are evaluating the performance of a SQL statement that accesses a very large table, and have run the following query producing the output shown: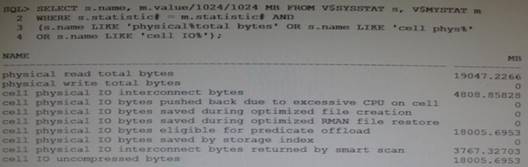
For which two reasons would the; “physical read total bytes” statistic be greater than the “cell physical IO bytes eligible for predicate offload” statistic?
- A. There is an index on the column used in the where clause, causing “cell multiblock physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O for blocks in the cells.
- B. The table is an IOT and has an overflow segment, causing “cell multiblock physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O for block in the cells.
- C. There is an uncommitted transaction that has modified some of the table blocks, causing some “cell single block physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O for block in the cells.
- D. The table is an indexed clustered table, causing “cell single block physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O for blocks in the cells.
- E. There are migrated rows in the table, causing some “cell single block physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O for blocks in the cells.
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 20
Which three statements are true about the initial storage configuration after the standard deployment of a new database Machine?
- A. The Data_<DBM_Name> and RECO_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroups are built on part of the interleaved griddisks.
- B. The Data_<DBM_Name> and RECO_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroups are built on top of the non-interleaved griddisks.
- C. There is a free space available on the hard disks inside the database servers for possible extension of the /u01 file system.
- D. There is no free disk space available on the hard disk inside the database servers for possible extensions of the /u01 file system.
- E. There is free space available on the flashdisk inside the Exadata storage servers for possible use as flash-based griddisks.
- F. There is no free disk available on the flashdisk inside the Exadata storage servers for possible use as flash-based griddisks.
Answer: BCF
Explanation:
B( not A): Griddisks are the fourth layer of abstraction, and they will be the Candidate Disks to build your ASM diskgroups from. By default (interleaving=none on the Celldisk layer), the first Griddisk that is created upon a Celldisk is placed on the outer sectors of the underlying Harddisk. It will have the best performance therefore. If we follow the recommendations, we will create 3 Diskgroups upon our Griddisks: DATA, RECO and SYSTEMDG.
Note:
* non-root partition (/u01).
* Oracle Database files: DATA disk group.
* Flashback log files, archived redo files, and backup files: RECO disk group.
NEW QUESTION 21
Which three must be true for Smart Scans to be done?
- A. Executing a query in parallel
- B. Setting _serial_direct_read=true in the session issuing the SQL statements
- C. Having direct path reads used at run time
- D. Having a 4 meg AU size for the ASM diskgroup containing the tablespace in which tables accessed by a query are stored
- E. Cell_offload_process = true for the ASM diskgroup containing the tablespace in which tables accessed by a query are stored.
- F. cell.smart_scan_capable=true for the ASM diskgroup containing the tablespace in which tables accessed by a query are stored.
Answer: BCF
NEW QUESTION 22
Which three are true regarding the use of Storage Indexes?
- A. Different storage regions may have different columns indexed for the same table.
- B. A Storage index is automatically maintained by CELLSRV based on the filter columns of the offload SQL.
- C. The use of Storage indexes for a particular database can be disabled by using an I/O Resource Manager Database Plan.
- D. Storage Indexes occupy space in the Smart Flash Cache.
- E. The use of Storage Indexes for particular categories of I/O can be disabled by using an I/O Resource Manager Category Plan.
- F. A maximum of eight table columns for any table are Indexed per storage region.
Answer: ABF
Explanation:
Note:
* Storage indexes are used during smart scans. All the limitations to smart scans apply to storage indexes. They do not work with joins. Bind variables are supported, however it’s slightly more restrictive than regular indexes/queries.
* The storage index is stored in the memory on each of the Exadata storage cells and is created and maintained transparently. However, if a storage cell is shutdown or rebooted the storage index will be lost from memory and will be recreated on subsequent accesses to the data after the cell has been brought back online.
* Storage Indexes are a very powerful capability provided in Exadata storage that helps avoid I/O operations. The Exadata Storage Server Software creates and maintains a Storage Index (that is, metadata about the database objects) in the Exadata cell. The Storage Index keeps track of minimum and maximum values of columns for tables stored on that cell. When a query specifies a WHERE clause, but before any I/O is done, the Exadata software examines the Storage Index to determine if rows with the specified column value exist in the cell by comparing the column value to the minimum and maximum values maintained in the Storage Index. If the column value is outside the minimum and maximum range, scan I/O for that query is avoided. Many SQL Operations run dramatically faster because large numbers of I/O operations are automatically replaced by a few lookups. To minimize operational overhead, Storage Indexes are created and maintained transparently and automatically by the Exadata Storage Server Software.
NEW QUESTION 23
......
P.S. Easily pass 1Z0-027 Exam with 72 Q&As DumpSolutions.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest DumpSolutions.com 1Z0-027 Dumps: https://www.dumpsolutions.com/1Z0-027-dumps/ (72 New Questions)