1z0 071 dumps for Oracle certification, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated 1z0 071 dumps. 100% PASS 1Z0-071 Oracle Database 12c SQL exam Today!
Free 1Z0-071 Demo Online For Microsoft Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
Examine the commands used to create DEPARTMENT_DETAILS and COURSE_DETAILS:
SQL>CREATE TABLE DEPARTMENT_DETAILS (DEPARTMENT_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, DEPARTMENT_NAMEVARCHAR2(50), HODVARCHAR2(50));
SQL>CREATE TABLE COURSE_DETAILS (COURSE_IDNUMBER PRIMARY KEY, COURSE_NAMEVARCHAR2(50), DEPARTMENT_IDVARCHAR2(50));
You want to generate a list of all department IDs along with any course IDs that may have been assigned to them.
Which SQL statement must you use?
- A. SELECT d.department_id, c.course_id FROM department_details d RIGHT OUTER JOIN course_details c ON (d.department_id=
- B. department_id);
- C. SELECT d.department_id, c.course_id FROM department_details d LEFT OUTER JOIN course_details c ON (d.department_id=
- D. department_id);
- E. SELECT d.department_id, c.course_id FROM course_details c LEFT OUTER JOIN department_details d ON (c.department_id=
- F. department_id);
- G. SELECT d.department_id, c.course_id FROM department_details d RIGHT OUTER JOIN course_details c ON (c.department_id=
- H. department_id);
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 2
Examine the structure of the SALES table. (Choose two.)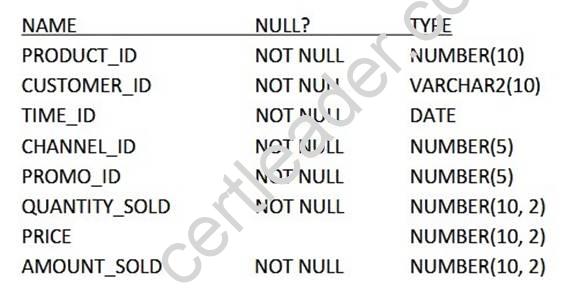
Examine this statement:
SQL > CREATE TABLE sales1 (prod_id, cust_id, quantity_sold, price) AS
SELECT product_id, customer_id, quantity_sold, price FROM sales
WHERE 1 = 2;
Which two statements are true about the SALES1 table?
- A. It will not be created because the column-specified names in the SELECT and CREATE TABLE clauses do not match.
- B. It will have NOT NULL constraints on the selected columns which had those constraints in the SALES table.
- C. It will not be created because of the invalid WHERE clause.
- D. It is created with no rows.
- E. It has PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE constraints on the selected columns which had those constraints in the SALES table.
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 3
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS and CUST_HISTORY tables.
The CUSTOMERS table contains the current location of all currently active customers.
The CUST_HISTORY table stores historical details relating to any changes in the location of all current as well as previous customers who are no longer active with the company.
You need to find those customers who have never changed their address. Which SET operator would you use to get the required output?
- A. INTERSECT
- B. UNION ALL
- C. MINUS
- D. UNION
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 4
Examine these SQL statements that are executed in the given order:
CREATE TABLE emp
(emp_no NUMBER (2) CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk PRIMARY KEY, ename VARCHAR 2 (15),
salary NUMBER (8, 2),
mgr_no NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT emp_mgr_fk REFERENCES emp (emp_no)); ALTER TABLE emp
DISABLE CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk CASCADE; ALTER TABLE emp
ENABLE CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk;
What will be the status of the foreign key EMP_MGR_FK?
- A. It will be enabled and immediate.
- B. It will be enabled and deferred.
- C. It will remain disabled and can be re-enabled manually.
- D. It will remain disabled and can be enabled only by dropping the foreign key constraint and re-creating it.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 5
View the exhibit and examine the structure of the STORES table. STORES table
NameNull?Type
---------------------- ------------- STORE_IDNUMBER NAMEVARCHAR2(100)
ADDRESSVARCHAR2(200) CITYVARCHAR2(100) COUNTRYVARCHAR2(100) START_DATEDATE END_DATEDATE PROPERTY_PRICENUMBER
You want to display the NAME of the store along with the ADDRESS, START_DATE, PROPERTY_PRICE, and the projected property price, which is 115% of property price.
The stores displayed must have START_DATE in the range of 36 months starting from 01-Jan-2000 and above.
Which SQL statement would get the desired output?
- A. SELECT name, concat (address| | ','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, '01-JAN-2000')<=36;
- B. SELECT name, concat (address| | ','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERETO_NUMBER(start_date-TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
- C. SELECT name, address||','||city||','||country AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
- D. SELECT name, concat (address||','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 6
Examine the structure of the MEMBERS table. NameNull?Type
------------------------------------------------------------ MEMBER_IDNOT NULLVARCHAR2 (6)
FIRST_NAMEVARCHAR2 (50)
LAST_NAMENOT NULLVARCHAR2 (50)
ADDRESSVARCHAR2 (50)
CITYVARCHAR2 (25)
STATENOT NULL VARCHAR2 (3)
Which query can be used to display the last names and city names only for members from the states MO and MI?
- A. SELECT last_name, city FROM members WHERE state ='MO' AND state ='MI';
- B. SELECT last_name, city FROM members WHERE state LIKE 'M%';
- C. SELECT last_name, city FROM members WHERE state IN ('MO', 'MI');
- D. SELECT DISTINCT last_name, city FROM members WHERE state ='MO' OR state ='MI';
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
Evaluate the following SQL statements that are issued in the given order:
CREATE TABLE emp
(emp_no NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk PRIMARY KEY, ename VARCHAR2(15),
salary NUMBER (8,2),
mgr_no NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT emp_mgr_fk REFERENCES emp(emp_no)); ALTER TABLE emp
DISABLE CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk CASCADE; ALTER TABLE emp
ENABLE CONSTRAINT emp_emp_no_pk;
What would be the status of the foreign key EMP_MGR_PK?
- A. It would remain disabled and can be enabled only by dropping the foreign key constraint and recreating it.
- B. It would remain disabled and has to be enabled manually using the ALTER TABLE command.
- C. It would be automatically enabled and immediate.
- D. It would be automatically enabled and deferred.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
Examine the SQL statement used to create the TRANSACTION table. (Choose the best answer.)
SQL > CREATE TABLE transaction (trn_id char(2) primary key,
Start_date date DEFAULT SYSDATE, End_date date NOT NULL);
The value 'A1' does not exist for trn_id in this table.
Which SQL statement successfully inserts a row into the table with the default value for START_DATE?
- A. INSERT INTO transaction VALUES ('A1', DEFAULT, TO_DATE(DEFAULT+10))
- B. INSERT INTO transaction VALUES ('A1', DEFAULT, TO_DATE('SYSDATE+10'))
- C. INSERT INTO transaction (trn_id, end_date) VALUES ('A1', '10-DEC-2014')
- D. INSERT INTO transaction (trn_id, start_date, end_date) VALUES ('A1', , '10-DEC-2014')
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
On your Oracle 12c database, you invoked SQL *Loader to load data into the EMPLOYEES table in the HR schema by issuing the following command:
$> sqlldr hr/hr@pdb table=employees
Which two statements are true regarding the command?
- A. It succeeds with default settings if the EMPLOYEES table belonging to HR is already defined in the database.
- B. It fails because no SQL *Loader data file location is specified.
- C. It fails if the HR user does not have the CREATE ANY DIRECTORY privilege.
- D. It fails because no SQL *Loader control file location is specified.
Answer: AC
NEW QUESTION 10
Which three statements are true about multiple-row subqueries?
- A. They can contain a subquery within a subquery.
- B. They can return multiple columns as well as rows.
- C. They cannot contain a subquery within a subquery.
- D. They can return only one column but multiple rows.
- E. They can contain group functions and GROUP BY and HAVING clauses.
- F. They can contain group functions and the GROUP BY clause, but not the HAVING clause.
Answer: ABE
NEW QUESTION 11
Which three statements are true regarding the WHERE and HAVING clauses in a SQL statement? (Choose three.)
- A. WHERE and HAVING clauses cannot be used together in a SQL statement.
- B. The HAVING clause conditions can have aggregate functions.
- C. The HAVING clause conditions can use aliases for the columns.
- D. The WHERE clause is used to exclude rows before the grouping of data.
- E. The HAVING clause is used to exclude one or more aggregated results after grouping data.
Answer: ABD
NEW QUESTION 12
Evaluate the following statement. INSERT ALL
WHEN order_total < 10000 THEN INTO small_orders
WHEN order_total > 10000 AND order_total < 20000 THEN INTO medium_orders
WHEN order_total > 200000 THEN INTO large_orders
SELECT order_id, order_total, customer_id FROM orders;
Which statement is true regarding the evaluation of rows returned by the subquery in the INSERT statement?
- A. Each row is evaluated by the first WHEN clause and if the condition is false then the row would be evaluated by the subsequent when clauses.
- B. All rows are evaluated by all the three WHEN clauses.
- C. Each row is evaluated by the first WHEN clause and if the condition is true, then the row would be evaluated by the subsequent when clauses.
- D. The INSERT statement will return an error because the ELSE clause is missing.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 13
Examine the commands used to create the DEPARTMENT_DETAILS and the COURSE-DETAILS tables: SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPARTMfiNT_D£TAILS
DEPARTMENT_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY , DEPARTMEHT_NAME VARCHAR2(50) ,
HOD VARCHAP2(50));
SQL> CREATE TABLE COURSE-DETAILS (COURSE ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY , COURS_NAME VARCHAR2 (50) ,
DEPARTMEHT_ID NUMBER REFERENCES DEPARTMENT_DETAIL
You want to generate a list of all department IDs along with any course IDs that may have been assigned to them.
Which SQL statement must you use?
- A. SELECT d.departranc_id, c.cours«_id FROM cource_deatils c LEFT OUTER JOIN departmnt_details d ON (c.dapartmsnt_id=d.departtnent_id);
- B. SELECT d.department_id,
- C. course_id FROM dapartment_details d RIGHT OUTER JOIN course_dotails c ON (c.depattnient_id=d.department_id) ;
- D. SELECT d.department i
- E. ccours_id FROM department_details d RIGHT OUTER JOIN course_details c ON (d.department_id);
- F. SELECT d.department_id, c.course_id FROM department_details d LEFT OUTER JOIN course_details c ON (d.department id).- (DEPARTMENT_ID) ;
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 14
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table. (Choose two.)
You must display the maximum and minimum salaries of employees hired 1 year ago. Which two statements would provide the correct output?
- A. SELECT MIN(Salary) minsal, MAX(salary) maxsalFROM employeesWHERE hire_date < SYSDATE-365GROUP BY MIN(salary), MAX(salary);
- B. SELECT minsal, maxsalFROM (SELECT MIN(salary) minsal, MAX(salary) maxsal FROM employeesWHERE hire_date < SYSDATE-365)GROUP BY maxsal, minsal;
- C. SELECT minsal, maxsalFROM (SELECT MIN(salary) minsal, MAX(salary) maxsal FROM employeesWHERE hire_date < SYSDATE-365GROUP BY MIN(salary), MAX(salary);
- D. SELECT MIN(Salary), MAX(salary)FROM (SELECT salary FROM employeesWHERE hire_date < SYSDATE-365);
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 15
You notice a performance change in your production Oracle 12c database. You want to know which change caused this performance difference.
Which method or feature should you use?
- A. Compare Period ADDM report.
- B. AWR Compare Period report.
- C. Active Session History (ASH) report.
- D. Taking a new snapshot and comparing it with a preserved snapshot.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 16
The following are the steps for a correlated subquery, listed in random order:
The WHERE clause of the outer query is evaluated.
The candidate row is fetched from the table specified in the outer query.
This is repeated for the subsequent rows of the table, till all the rows are processed.
Rows are returned by the inner query, after being evaluated with the value from the candidate row in the outer query.
Which is the correct sequence in which the Oracle server evaluates a correlated subquery?
- A. 2, 1, 4, 3
- B. 4, 1, 2, 3
- C. 4, 2, 1, 3
- D. 2, 4, 1, 3
Answer: D
Explanation: References:
http://rajanimohanty.blogspot.co.uk/2014/01/correlated-subquery.html
NEW QUESTION 17
View the Exhibit and examine the details of PRODUCT_INFORMATION table.
PRODUCT_NAME CATEGORY_ID SUPPLIER_ID
Inkjet C/8/HQ 12
102094
Inkjet C/4 12
102090
LaserPro 600/6/BW 12
102087
LaserPro 1200/8/BW 12
102099
Inkjet B/6 12
102096
Industrial 700/ID 12
102086
Industrial 600/DQ 12
102088
Compact 400/LQ 12
102087
Compact 400/DQ 12
102088
HD 12GB /R 13
102090
HD 10GB /I 13
102071
HD 12GB @7200 /SE 13
102057
HD 18.2GB @10000 /E 13
102078
HD 18.2GB @10000 /I 13
102050
HD 18GB /SE 13
102083
HD 6GB /I 13
102072
HD 8.2GB@5400 13
102093
You have the requirement to display PRODUCT_NAME from the table where the CATEGORY_ID column has values 12 or 13, and the SUPPLIER_ID column has the value 102088. You executed the following SQL statement:
SELECT product_name FROM product_information
WHERE (category_id = 12 AND category_id = 13) AND supplier_id = 102088; Which statement is true regarding the execution of the query?
- A. It would not execute because the same column has been used in both sides of the AND logical operator to form the condition.
- B. It would not execute because the entire WHERE clause condition is not enclosed within the parentheses.
- C. It would execute and the output would display the desired result.
- D. It would execute but the output would return no rows.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 18
View the Exhibit and examine the data in the employees table.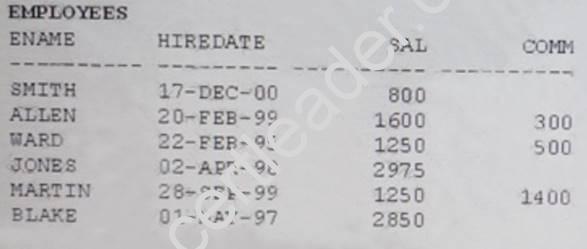
You want to generate a report showing the total compensation paid to each employee to date. You issue the following query:
What is the outcome?
- A. It executes successfully but does not give the correct output.
- B. It generates an error because the concatenation operator can be used to combine only two items.
- C. It generates an error because the usage of the round function in the expression is not valid
- D. It generates an error because the alias is not valid.
- E. It executes successfully and gives the correct output.
Answer: A
Thanks for reading the newest 1Z0-071 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Surepassexam 1Z0-071 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.surepassexam.com/1Z0-071-exam-dumps.html (187 Q&As Dumps)