Master the MCIA-Level-1 MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 content and be ready for exam day success quickly with this Testking MCIA-Level-1 test preparation. We guarantee it!We make it a reality and give you real MCIA-Level-1 questions in our MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 braindumps.Latest 100% VALID MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 Exam Questions Dumps at below page. You can use our MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 braindumps and pass your exam.
Free demo questions for MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
An organization is designing an integration solution to replicate financial transaction data from a legacy system into a data warehouse (DWH).
The DWH must contain a daily snapshot of financial transactions, to be delivered as a CSV file. Daily transaction volume exceeds tens of millions of records, with significant spikes in volume during popular shopping periods.
What is the most appropriate integration style for an integration solution that meets the organization's current requirements?
- A. API-led connectivity
- B. Batch-triggered ETL
- C. Event-driven architecture
- D. Microservice architecture
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 2
What metrics about API invocations are available for visualization in custom charts using Anypoint Analytics?
- A. Request size, request HTTP verbs, response time
- B. Request size, number of requests, JDBC Select operation result set size
- C. Request size, number of requests, JDBC Select operation response time
- D. Request size, number of requests, response size, response time
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 3
A Mule application is being designed to do the following:
Step 1: Read a SalesOrder message from a JMS queue, where each SalesOrder consists of a header and a list of SalesOrderLineltems.
Step 2: Insert the SalesOrder header and each SalesOrderLineItem into different tables in an RDBMS.
Step 3: Insert the SalesOrder header and the sum of the prices of all its SalesOrderLineltems into a table in a different RDBMS.
No SalesOrder message can be lost and the consistency of all SalesOrder-related information in both RDBMSs must be ensured at all times.
What design choice (including choice of transactions) and order of steps addresses these requirements?
- A. * 1. Read the JMS message (NOT in an XA transaction)* 2. Perform EACH DB insert in a SEPARATE DB transaction* 3. Acknowledge the JMS message
- B. * 1. Read and acknowledge the JMS message (NOT in an XA transaction)* 2. In a NEW XA transaction, perform BOTH DB inserts
- C. * 1. Read the JMS message in an XA transaction* 2. In the SAME XA transaction, perform BOTH DB inserts but do NOT acknowledge the JMS message
- D. * 1. Read the JMS message (NOT in an XA transaction)* 2. Perform BOTH DB inserts in ONE DB transaction* 3. Acknowledge the JMS message
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 4
What Anypoint Connectors support transactions?
- A. Database, JMS, VM
- B. Database, 3MS, HTTP
- C. Database, JMS, VM, SFTP
- D. Database, VM, File
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 5
An organization is creating a set of new services that are critical for their business. The project team prefers using REST for all services but is willing to use SOAP with common WS-* standards if a particular service requires it.
What requirement would drive the team to use SOAP/WS-* for a particular service?
- A. Must secure the service, requiring all consumers to submit a valid SAML token
- B. Must support message acknowledgement and retry as part of the protocol
- C. Must publish and share the service specification (including data formats) with the consumers of the service
- D. Must use XML payloads for the service and ensure that it adheres to a specific schema
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 6
What requires configuration of both a key store and a trust store for an HTTP Listener?
- A. Support for TLS mutual (two-way) authentication with HTTP clients
- B. Encryption of both HTTP request and HTTP response bodies for all HTTP clients
- C. Encryption of requests to both subdomains and API resource endpoints (https://api.customer.com/ and https://customer.com/api)
- D. Encryption of both HTTP request header and HTTP request body for all HTTP clients
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
An Order microservice and a Fulfillment microservice are being designed to communicate with their clients through message-based integration (and NOT through API invocations).
The Order microservice publishes an Order message (a kind of command message) containing the details of an order to be fulfilled. The intention is that Order messages are only consumed by one Mule application, the Fulfillment microservice.
The Fulfillment microservice consumes Order messages, fulfills the order described therein, and then publishes an OrderFulfilled message (a kind of event message). Each OrderFulfilled message can be consumed by any interested Mule application, and the Order microservice is one such Mule application.
What is the most appropriate choice of message broker(s) and message destination(s) in this scenario?
- A. Order messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ exchangeOrderFulfilled messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ queueBoth microservices interact with Anypoint MQ as the message broker, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices
- B. Order messages are sent to a JMS queueOrderFulfilled messages are sent to a JMS topicBoth microservices interact with the same JMS provider (message broker) instance, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices
- C. Order messages are sent directly to the Fulfillment microservicesOrderFulfilled messages are sent directly to the Order microserviceThe Order microservice interacts with one AMQP-compatible message broker and the Fulfillment microservice interacts with a different AMQP-compatible message broker, so that both message brokers can be chosen and scaled to best support the load of each microservice
- D. Order messages are sent to a JMS queueOrderFulfilled messages are sent to a JMS topicThe Order microservice interacts with one JMS provider (message broker) and the Fulfillment microservice interacts with a different JMS provider, so that both message brokers can be chosen and scaled to best support the load of each microservice
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 8
What is true about the network connections when a Mule application uses a JMS connector to interact with a JMS provider (message broker)?
- A. The JMS connector supports both sending and receiving of JMS messages over the protocol determined by the JMS provider
- B. The AMQP protocol can be used by the JMS connector to portably establish connections to various types of JMS providers
- C. To receive messages into the Mule application, the JMS provider initiates a network connection to the JMS connector and pushes messages along this connection
- D. To complete sending a JMS message, the JMS connector must establish a network connection with the JMS message recipient
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 9
A global organization operates datacenters in many countries. There are private network links between these datacenters because all business data (but NOT metadata) must be exchanged over these private network connections.
The organization does not currently use AWS in any way.
The strategic decision has Just been made to rigorously minimize IT operations effort and investment going forward.
What combination of deployment options of the Anypoint Platform control plane and runtime plane(s) best serves this organization at the start of this strategic journey?
- A. MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud in multiple AWS regions
- B. Anypoint Platform - Private Cloud Edition Customer-hosted runtime plane in each datacenter
- C. MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane Customer-hosted runtime plane in multiple AWS regions
- D. MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane Customer-hosted runtime plane in each datacenter
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 10
An API has been unit tested and is ready for integration testing. The API is governed by a Client ID Enforcement policy in all environments.
What must the testing team do before they can start integration testing the API in the Staging environment?
- A. They must access the API portal and create an API notebook using the Client ID and Client Secret supplied by the API portal in the Staging environment
- B. They must request access to the API instance in the Staging environment and obtain a Client ID and Client Secret to be used for testing the API
- C. They must be assigned as an API version owner of the API in the Staging environment
- D. They must request access to the Staging environment and obtain the Client ID and Client Secret for that environment to be used for testing the API
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 11
What operation can be performed through a JMX agent enabled in a Mule application?
- A. View object store entries
- B. Replay an unsuccessful message
- C. Deploy a Mule application
- D. Set a particular log4j2 log level to TRACE
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 12
What aspect of logging is only possible for Mule applications deployed to customer-hosted Mule runtimes, but NOT for Mule applications deployed to CloudHub?
- A. To send Mule application log entries to Splunk
- B. To change tog4j2 tog levels in Anypoint Runtime Manager without having to restart the Mule application
- C. To log certain messages to a custom log category
- D. To directly referenceone shared and customized log4j2.xml file from multiple Mule applications
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 13
A retailer is designing a data exchange interface to be used by its suppliers. The interface must support secure communication over the public internet. The interface must also work with a wide variety of programming languages and IT systems used by suppliers.
What are suitable interface technologies for this data exchange that are secure, cross-platform, and internet friendly, assuming that Anypoint Connectors exist for these interface technologies?
- A. EDJFACT XML over SFTP JSON/REST over HTTPS
- B. SOAP over HTTPS HOP over TLS gRPC over HTTPS
- C. XML over ActiveMQ XML over SFTP XML/REST over HTTPS
- D. CSV over FTP YAML over TLS JSON over HTTPS
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 14
An organization uses a set of customer-hosted Mule runtimes that are managed using the Mulesoft-hosted control plane.
What is a condition that can be alerted on from Anypoint Runtime Manager without any custom components or custom coding?
- A. When an SSL certificate used by one of the deployed Mule applications is about to expire
- B. When a Mule runtime on a given customer-hosted server is experiencing high memory consumption during certain periods
- C. When a Mule runtime's customer-hosted server is about to run out of disk space
- D. When the Mule runtime license installed on a Mule runtime is about to expire
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 15
Refer to the exhibit.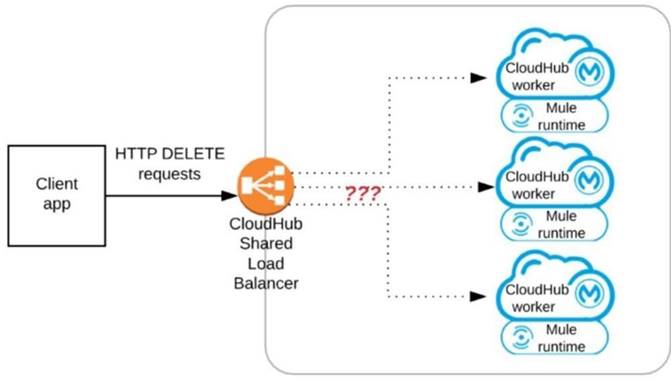
A Mule application has an HTTP Listener that accepts HTTP DELETE requests. This Mule application Is deployed to three CloudHub workers under the control of the CloudHub Shared Load Balancer.
A web client makes a sequence of requests to the Mule application's public URL.
How is this sequence of web client requests distributed among the HTTP Listeners running in the three CloudHub workers?
- A. Each request is routed to the PRIMARY CloudHub worker in the PRIMARY Availability Zone (AZ)
- B. Each request is routed to ONE ARBiTRARYCloudHub worker in the PRIMARY Availability Zone (AZ)
- C. Each request Is routed to ONE ARBiTRARY CloudHub worker out of ALL three CloudHub workers
- D. Each request is routed (scattered) to ALL three CloudHub workers at the same time
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 16
Additional nodes are being added to an existing customer-hosted Mule runtime cluster to improve performance. Mule applications deployed to this cluster are invoked by API clients through a load balancer.
What is also required to carry out this change?
- A. A new load balancer must be provisioned to allow traffic to the new nodes in a round-robin fashion
- B. External monitoring tools or log aggregators must be configured to recognize the new nodes
- C. API implementations using an object store must be adjusted to recognize the new nodes and persist to them
- D. New firewall rules must be configured to accommodate communication between API clients and the new nodes
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 17
An organization is designing the following two Mule applications that must share data via a common persistent object store instance:
- Mule application P will be deployed within their on-premises datacenter. - Mule application C will run on CloudHub in an Anypoint VPC.
The object store implementation used by CloudHub is the Anypoint Object Store v2 (OSv2).
What type of object store(s) should be used, and what design gives both Mule applications access to the same object store instance?
- A. Application C and P both use the Object Store connector to access the Anypoint Object Store v2
- B. Application C and P both use the Object Store connector to access a persistent object store
- C. Application C uses the Object Store connector to access a persistent objectApplication P accesses the persistent object store via the Object Store REST API
- D. Application P uses the Object Store connector to access a persistent object storeApplication C accesses this persistent object store via the Object Store REST API through an IPsec tunnel
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 18
An organization currently uses a multi-node Mule runtime deployment model within their datacenter, so each Mule runtime hosts several Mule applications. The organization is planning to transition to a deployment model based on Docker containers in a Kubernetes cluster. The organization has already created a standard Docker image containing a Mule runtime and all required dependencies (including a JVM), but excluding the Mule application itself.
What is an expected outcome of this transition to container-based Mule application deployments?
- A. Required redesign of Mule applications to follow microservice architecture principles
- B. Required migration to the Docker and Kubernetes-based Anypoint Platform - Private Cloud Edition
- C. Required change to the URL endpoints used by clients to send requests to the Mule applications
- D. Guaranteed consistency of execution environments across all deployments of a Mule application
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 19
A new Mule application under development must implement extensive data transformation logic. Some of the data transformation functionality is already available as external transformation services that are mature and widely used across the organization; the rest is highly specific to the new Mule application.
The organization follows a rigorous testing approach, where every service and application must be extensively acceptance tested before it is allowed to go into production.
What is the best way to implement the data transformation logic for this new Mule application while minimizing the overall testing effort?
- A. Implement and expose all transformation logic as mlaoservices using DataWeave, so it can be reused by any application component that needs it, including the new Mule application
- B. Implement transformation logic in the new Mute application using DataWeave, replicating the transformation logic of existing transformation services
- C. Extend the existing transformation services with new transformation logic and Invoke them from the new Mule application
- D. Implement transformation logic in the new Mute application using DataWeave, invoking existing transformation services when possible
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 20
A Mule application contains a Batch Job with two Batch Steps (Batch_Step_1 and Batch_Step_2). A payload with 1000 records is received by the Batch Job.
How many threads are used by the Batch Job to process records, and how does each Batch Step process records within the Batch Job?
- A. Each Batch Job uses SEVERAL THREADS for the Batch StepsEach Batch Step instance receives ONE record at a time as the payload, and BATCH STEP INSTANCES execute IN PARALLEL to process records and Batch Steps in ANY order as fast as possible
- B. Each Batch Job uses SEVERAL THREADS for the Batch StepsEach Batch Step instance receives ONE record at a time as the payload, and RECORDS are processed IN PARALLEL within and between the two Batch Steps
- C. Each Batch Job uses a SINGLE THREAD for all Batch StepsEach Batch Step instance receives ONE record at a time as the payload, and RECORDS are processed IN ORDER, first through Batch_Step_1 and then through Batch_Step_2
- D. Each Batch Job uses a SINGLE THREAD to process a configured block size of recordEach Batch Step instance receives A BLOCK OF records as the payload, and BLOCKS of records are processed IN ORDER
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 21
An integration Mule application consumes and processes a list of rows from a CSV file. Each row must be read from the CSV file, validated, and the row data sent to a JMS queue, in the exact order as in the CSV file.
If any processing step for a row fails, then a log entry must be written for that row, but processing of other rows must not be affected.
What combination of Mule components is most idiomatic (used according to their intended purpose) when implementing the above requirements?
- A. Scatter-Gather componentOn Error Continue scope
- B. VM connectorFirst Successful scopeOn Error Propagate scope
- C. Async scopeOn Error Propagate scope
- D. For Each scopeOn Error Continue scope
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 22
......
Thanks for reading the newest MCIA-Level-1 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Certshared MCIA-Level-1 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.certshared.com/exam/MCIA-Level-1/ (58 Q&As Dumps)