Exambible NSE7_LED-7.0 Questions are updated and all NSE7_LED-7.0 answers are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our NSE7_LED-7.0 exam prep kits you will be ready for the real NSE7_LED-7.0 exam without a problem. We have Avant-garde Fortinet NSE7_LED-7.0 dumps study guide. PASSED NSE7_LED-7.0 First attempt! Here What I Did.
Fortinet NSE7_LED-7.0 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
Refer to the exhibit
A device connected to port2 on FortiSwitch cannot access the network The port is assigned a security policy to enforce 802 1X authentication While troubleshooting the issue, the administrator obtains the debug output shown in the exhibit
Which two scenarios are likely to cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- A. The device is not configured for 802 IX authentication.
- B. The device has been quarantined for 3600 seconds.
- C. The device has been assigned the guest VLAN
- D. The device does not support 802 1X authentication
Answer: AD
Explanation:
According to the exhibit, the debug output shows that the device connected to port2 on FortiSwitch is sending an EAPOL-Start message, which is the first step of the 802.1X authentication process. However, the output also shows that the device is not sending any EAP-Response messages, which are required to complete the authentication process. Therefore, option A is true because the device is not configured for 802.1X authentication, which means that it does not have the correct credentials or settings to authenticate with the RADIUS server. Option D is also true because the device does not support 802.1X authentication, which means that it does not have the capability or software to perform 802.1X authentication. Option B is false because the device has not been quarantined for 3600 seconds, but rather has a session timeout of 3600 seconds, which is the default value for 802.1X sessions. Option C is false because the device has not been assigned the guest VLAN, but rather has been assigned the default VLAN, which is VLAN 1.
NEW QUESTION 2
Where can FortiGate learn the FortiManager IP address or FQDN for zero-touch provisioning'?
- A. From an LDAP server using a simple bind operation
- B. From a TFTP server
- C. From a DHCP server using options 240 and 241
- D. From a DNS server using A or AAAA records
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, “FortiGate can learn the FortiManager IP address or FQDN for zero-touch provisioning from a DNS server using A or AAAA records. The DNS server must be configured to resolve the hostname fortimanager.fortinet.com to the IP address or FQDN of the FortiManager device.” Therefore, option D is true because it describes the method for FortiGate to learn the FortiManager IP address or FQDN for zero-touch provisioning. Option A is false because LDAP is not used for zero-touch provisioning. Option B is false because TFTP is not used for zero-touch provisioning. Option C is false because DHCP options 240 and 241 are not used for zero-touch provisioning.
NEW QUESTION 3
Which EAP method requires the use of a digital certificate on both the server end and the client end?
- A. EAP-TTLS
- B. PEAP
- C. EAP-GTC
- D. EAP-TLS
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, “EAP-TLS is the most secure EAP method. It requires a digital certificate on both the server end and the client end. The server and client authenticate each other using
their certificates.” Therefore, option D is true because it describes the EAP method that requires the use of a digital certificate on both the server end and the client end. Option A is false because EAP-TTLS only requires a digital certificate on the server end, not the client end. Option B is false because PEAP also only requires a digital certificate on the server end, not the client end. Option C is false because EAP-GTC does not require a digital certificate on either the server end or the client end.
NEW QUESTION 4
An administrator is testing the connectivity for a new VLAN The devices in the VLAN are connected to a FortiSwitch device that is managed by FortiGate Quarantine is disabled on FortiGate
While testing the administrator noticed that devices can ping FortiGate and FortiGate can ping the devices The administrator also noticed that inter-VLAN communication works However intra-VLAN communication does not work
Which scenario is likely to cause this issue?
- A. Access VLAN is enabled on the VLAN
- B. The native VLAN configured on the ports is incorrect
- C. The FortiSwitch MAC address table is missing entries
- D. The FortiGate ARP table is missing entries
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the scenario, the devices in the VLAN are connected to a FortiSwitch device that is managed by FortiGate. Quarantine is disabled on FortiGate, which means that the devices are not blocked by any security policy. The devices can ping FortiGate and FortiGate can ping the devices, which means that the IP connectivity is working. Inter-VLAN communication works, which means that the routing between VLANs is working. However, intra-VLAN communication does not work, which means that the switching within the VLAN is not working. Therefore, option C is true because the FortiSwitch MAC address table is missing entries, which means that the FortiSwitch does not know how to forward frames to the destination MAC addresses within the VLAN. Option A is false because access VLAN is enabled on the VLAN, which means that the VLAN ID is added to the frames on ingress and removed on egress. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication. Option B is false because the native VLAN configured on the ports is incorrect, which means that the frames on the native VLAN are not tagged with a VLAN ID. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication. Option D is false because the FortiGate ARP table is missing entries, which means that FortiGate does not know how to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. This does not affect intra-VLAN communication.
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.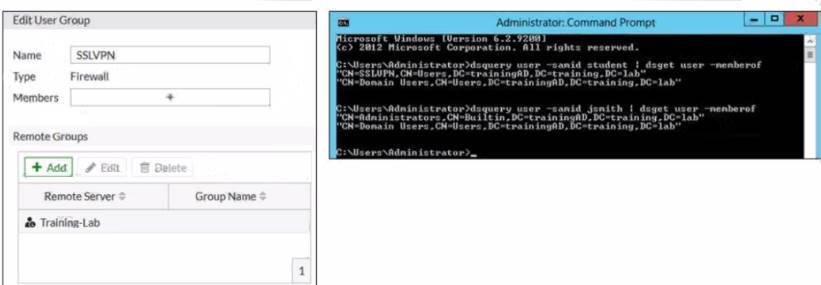
Examine the FortiGate user group configuration and the Windows AD LDAP group membership information shown in the exhibit
FortiGate is configured to authenticate SSL VPN users against Windows AD using LDAP The administrator configured the SSL VPN user group for SSL VPN users However the administrator noticed that both the student and j smith users can connect to SSL VPN
Which change can the administrator make on FortiGate to restrict the SSL VPN service to the student user only?
- A. In the SSL VPN user group configuration set Group Nam© to CN-SSLVPN, CN="users, DC-trainingAD, DC-training, DC-lab
- B. In the SSL VPN user group configuration, change Name to cn=sslvpn, CN=users, DC=trainingAD, Detraining, DC-lab.
- C. In the SSL VPN user group configuration set Group Name to ::;=Domain users.CN-Users/DC=trainingAD, DC-training, DC=lab.
- D. In the SSL VPN user group configuration change Type to Fortinet Single Sign-On (FSSO)
Answer: A
Explanation:
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, “The Group Name is the name of the LDAP group that you want to use for authentication. The name must match exactly the name of the LDAP group on the LDAP server.” Therefore, option A is true because it will set the Group Name to match the LDAP group that contains only the student user. Option B is false because changing the Name will not affect the authentication process, as it is only a local identifier for the user group on FortiGate. Option C is false because setting the Group Name to Domain Users will include all users in the domain, not just the student user. Option D is false because changing the Type to FSSO will require a different configuration method and will not solve the problem.
NEW QUESTION 6
What is the purpose of enabling Windows Active Directory Domain Authentication on FortiAuthenticator?
- A. It enables FortiAuthenticator to use Windows administrator credentials to perform an LDAP lookup for a user search
- B. It enables FortiAuthenticator to use a Windows CA certificate when authenticating RADIUS users
- C. It enables FortiAuthenticator to import users from Windows AD
- D. It enables FortiAuthenticator to register itself as a Windows trusted device to proxy authentication using Kerberos
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the FortiAuthenticator Administration Guide2, “Windows Active Directory domain authentication enables FortiAuthenticator to join a Windows Active Directory domain as a machine entity and proxy authentication requests using Kerberos.” Therefore, option D is true because it describes the purpose of enabling Windows Active Directory domain authentication on FortiAuthenticator. Option A is false because FortiAuthenticator does not need Windows administrator credentials to perform an LDAP lookup for a user search. Option B is false because FortiAuthenticator does not use a Windows CA certificate when authenticating RADIUS users, but rather its own CA certificate. Option C is false because FortiAuthenticator does not import users from Windows AD, but rather synchronizes them using LDAP or FSSO.
NEW QUESTION 7
A wireless network in a school provides guest access using a captive portal to allow unregistered users to self-register and access the network The administrator is requested to update the existing configuration to provide captive portal authentication through a secure connection (HTTPS)
Which two changes must the administrator make to enforce HTTPS authentication"? (Choose two >
- A. Create a new SSID with the HTTPS captive portal URL
- B. Enable HTTP redirect in the user authentication settings
- C. Disable HTTP administrative access on the guest SSID to enforce HTTPS connection
- D. Update the captive portal URL to use HTTPS on FortiGate and FortiAuthenticator
Answer: BD
Explanation:
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, “To enable HTTPS authentication, you must enable HTTP redirect in the user authentication settings. This redirects HTTP requests to HTTPS. You must also update the captive portal URL to use HTTPS on both FortiGate and FortiAuthenticator.” Therefore, options B and D are true because they describe the changes that the administrator must make to enforce HTTPS authentication for the captive portal. Option A is false because creating a new SSID with the HTTPS captive portal URL is not required, as the existing SSID can be updated with the new URL. Option C is false because disabling HTTP
administrative access on the guest SSID will not enforce HTTPS connection, but rather block HTTP connection.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which CLI command should an administrator use to view the certificate verification process in real time?
- A. diagnose debug application foauthd -1
- B. diagnose debug application radiusd -1
- C. diagnose debug application authd -1
- D. diagnose debug application fnbamd -1
Answer: A
Explanation:
According to the FortiOS CLI Reference Guide, “The diagnose debug application foauthd command enables debugging of certificate verification process in real time.” Therefore, option A is true because it describes the CLI command that an administrator should use to view the certificate verification process in real time. Option B is false because diagnose debug application radiusd -1 enables debugging of RADIUS authentication process, not certificate verification process. Option C is false because diagnose debug application authd -1 enables debugging of authentication daemon process, not certificate verification process. Option D is false because diagnose debug application fnbamd -1 enables debugging of FSSO daemon process, not certificate verification process.
NEW QUESTION 9
Exhibit.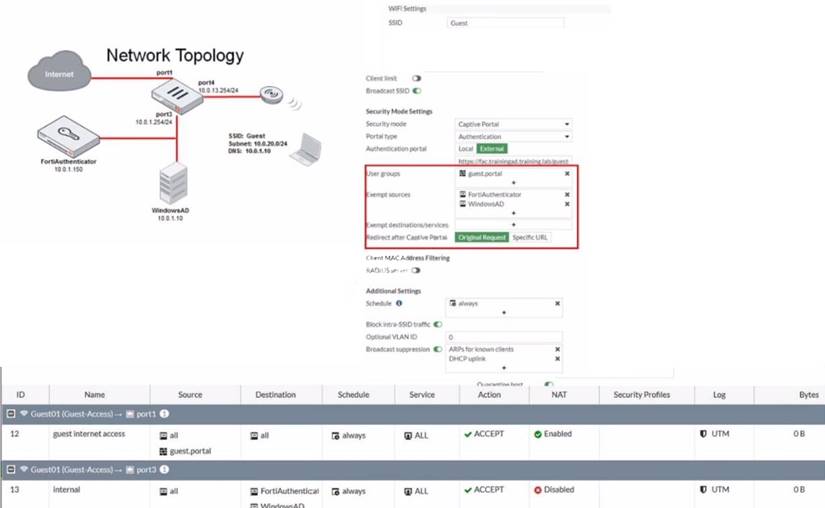
Refer to the exhibit showing a network topology and SSID settings.
FortiGate is configured to use an external captive portal However wireless users are not able to see the captive portal login page
Which configuration change should the administrator make to fix the problem?
- A. Enable NAT in the firewall policy with the ID 13.
- B. Add the FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD address objects as exempt destinations services
- C. Enable the captive-portal-exempt option in the firewall policy with the ID 12
- D. Remove the guest.portal user group in the firewall policy with the ID 12
Answer: B
Explanation:
According to the exhibit, the network topology and SSID settings show that FortiGate is configured to use an external captive portal hosted on FortiAuthenticator, which is connected to a Windows AD server for user authentication. However, wireless users are not able to see the captive portal login page, which means that they are not redirected to the external captive portal URL. Therefore, option B is true because adding the FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD address objects as exempt destinations services will allow the wireless users to access the external captive portal URL without being blocked by the firewall policy. Option A is false because enabling NAT in the firewall policy with the ID 13 will not affect the redirection to the external captive portal URL, but rather the source IP address of the wireless traffic. Option C is false because enabling the captive-portal-exempt option in the firewall policy with the ID 12will bypass the captive portal authentication for the wireless users, which is not the desired outcome. Option D is false because removing the guest.portal user group in the firewall policy with the ID 12 will prevent the wireless users from being authenticated by FortiGate, which is required for accessing the external captive portal.
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the exhibits.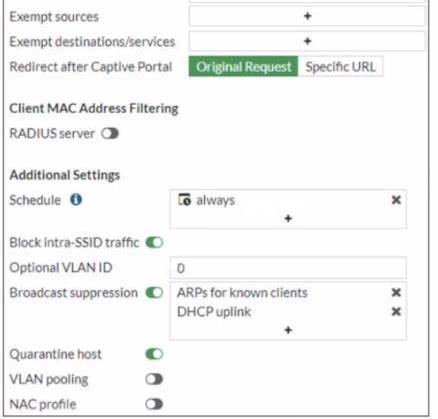
Firewall Policy
Examine the firewall policy configuration and SSID settings
An administrator has configured a guest wireless network on FortiGate using the external captive portal The administrator has verified that the external captive portal URL is correct However wireless users are not able to see the captive portal login page
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit and the SSID settings which configuration change should the administrator make to fix the problem?
- A. Disable the user group from the SSID configuration
- B. Enable the captivs-portal-exempt option in the firewall policy with the ID 11.
- C. Apply a guest.portal user group in the firewall policy with the ID 11.
- D. Include the wireless client subnet range in the Exempt Source section
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the FortiGate Administration Guide, “To use an external captive portal, you must configure a user group that uses the external captive portal as the authentication method and apply it to a firewall policy.” Therefore, option C is true because it will allow the wireless users to be redirected to the external captive portal URL when they try to access the Internet. Option A is false because disabling the user group from the SSID configuration will prevent the wireless users from being authenticated by the FortiGate device. Option B is false because enabling the captive-portal-exempt option in the firewall policy will bypass the captive portal authentication for the wireless users, which is not the desired outcome. Option D is false because including the wireless client subnet range in the Exempt Source section will also bypass the captive portal authentication for the wireless users, which is not the desired outcome.
NEW QUESTION 11
You are investigating a report of poor wireless performance in a network that you manage. The issue is related to an AP interface in the 5 GHz range You are monitoring the channel utilization over time.
What is the recommended maximum utilization value that an interface should not exceed?
- A. 85%
- B. 95%
- C. 75%
- D. 65%
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the FortiAP Configuration Guide, “Channel utilization measures how busy a channel is over a given period of time. It includes both Wi-Fi and non-Wi-Fi interference sources. A high channel utilization indicates a congested channel and can result in poor wireless performance. The recommended maximum utilization value that an interface should not exceed is 65%.” Therefore, option D is true because it gives the recommended maximum utilization value for an interface in the 5 GHz range. Options A, B, and C are false because they give higher utilization values that can cause poor wireless performance.
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiap/7.0.0/configuration-guide/734537/wireless-radio-settings#channel-uti
NEW QUESTION 12
......
P.S. Easily pass NSE7_LED-7.0 Exam with 37 Q&As DumpSolutions.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest DumpSolutions.com NSE7_LED-7.0 Dumps: https://www.dumpsolutions.com/NSE7_LED-7.0-dumps/ (37 New Questions)