It is more faster and easier to pass the Oracle 1z0-1085-20 exam by using Precise Oracle Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations 2020 Associate questuins and answers. Immediate access to the Replace 1z0-1085-20 Exam and find the same core area 1z0-1085-20 questions with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Oracle 1z0-1085-20 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two are enabled by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Fault Domains?
- A. Protect against unexpected hardware or power supply failures
- B. To meet requirements for legal jurisdictions
- C. To mitigate the risk of large scale events such as earthquakes
- D. Build replicated systems for disaster recovery
- E. Protect against planned hardware maintenance
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains provide anti-affinity: they let you distribute your instances so that the instances are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. A hardware failure or Compute hardware maintenance event that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. In addition, the physical hardware in a fault domain has independent and redundant power supplies, which prevents a failure in the power supply hardware within one fault domain from affecting other fault domains.
To control the placement of your compute instances, bare metal DB system instances, or virtual machine DB system instances, you can optionally specify the fault domain for a new instance or instance pool at launch time. If you don't specify the fault domain, the system selects one for you. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure makes a best-effort anti-affinity placement across different fault domains, while optimizing for available capacity in the availability domain. To change the fault domain for an instance, terminate it and launch a new instance in the preferred fault domain.
Use fault domains to do the following things:
Protect against unexpected hardware failures or power supply failures. Protect against planned outages because of Compute hardware maintenance.
We can use fault domains to do the following things:
1) Protect against unexpected hardware failures or power supply failures.
2) Protect against planned outages because of Compute hardware maintenance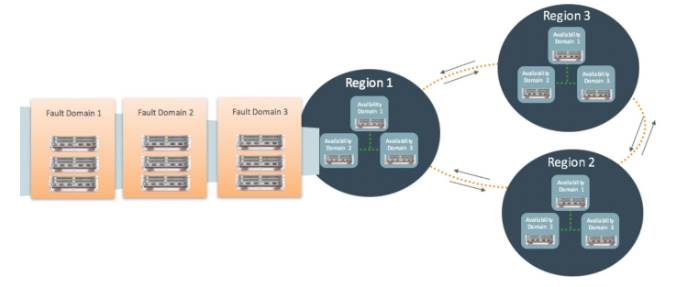
NEW QUESTION 2
You want to migrate mission-critical Oracle E- Business Suite application to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) with full control and access to the underlying infrastructure.
Which option meets this requirement?
- A. Replace E-Business Suite with an Oracle SaaS application
- B. OCI Exadata DB Systems and OCI compute instances
- C. OCI Exadata DB Systems and Oracle Functions
- D. Oracle Exadata Cloud at customer, Storage Gateway and API Gateway
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 3
What is the frequency of OCI usage report generation?
- A. Weekly
- B. Monthly
- C. Annually
- D. Daily
Answer: D
Explanation:
A usage report is a comma-separated value (CSV) file that can be used to get a detailed breakdown of resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for audit or invoice reconciliation.
The usage report is automatically generated daily, and is stored in an Oracle-owned Object Storage bucket. It contains one row per each Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resource (such as instance, Object Storage bucket, VNIC) per hour along with consumption information, metadata, and tags. Usage reports generally contain 24 hours of usage data, although occasionally a usage report may contain late-arriving data that is older than 24 hours.
Usage reports are retained for one year.
NEW QUESTION 4
A new customer has logged into Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) as an administrator for the first time. The admin would like to deploy infrastructure. What is the first step they must take in order to accomplish this task?
- A. File a service request for access to each additional region.
- B. Use API endpoints to create resources in the desired region.
- C. Subscribe to the desired region.
- D. Navigate to the desired region and begin creating resources.
Answer: C
Explanation:
When you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Oracle creates a tenancy for you in one region. This is
your home region. Your home region is where your IAM resources are defined. When you subscribe to another region, your IAM resources are available in the new region, however, the master definitions reside in your home region and can only be changed there.
When you subscribe your tenancy to a new region, all the policies from your home region are enforced in the new region. If you want to limit access for groups of users to specific regions, you can write policies to grant access to specific regions only.
NEW QUESTION 5
Which CANNOT be used with My Oracle Support (MOS)?
- A. Add or change a tenancy administrator
- B. Request a Service Limit increase
- C. Reset the password or unlock the account for the tenancy administrator
- D. Troubleshoot your resources in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Trial account
Answer: D
Explanation:
Open a support service request with MOS option is available to paid accounts. Customers using only Always Free resources are not eligible for Oracle Support. Limited support is available to Free Tier accounts with Free Trial credits. After you use all of your credits or after your trial period ends (whichever comes first), you must upgrade to a paid account to access Oracle Support. If you choose not to upgrade and continue to use Always Free Services, you will not be eligible to raise a service request in My Oracle Support.
In addition to support for technical issues, use My Oracle Support if you need to:
· Reset the password or unlock the account for the tenancy administrator
· Add or change a tenancy administrator
· Request a service limit increase
NEW QUESTION 6
What service is NOT available as part of Oracle Cloud Free Tier?
- A. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring
- B. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Exadata DB Systems
- C. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Autonomous Data Warehouse
- D. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute
Answer: B
Explanation:
For more information on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier refer below official documentation https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/FreeTier/freetier.htm?Highlight=Free%20Tier Exadata DB Systems aren't a part of the free tier:
NEW QUESTION 7
Which capability enables you to search, purchase, and start using software in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy?
- A. OCI Marketplace
- B. OCI OS Management
- C. OCI Resource Manager
- D. OCI Registry
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Marketplace is an online store that offers solutions specifically for customers of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. In the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Marketplace catalog, you can find listings for two types of solutions from Oracle and trusted partners: images and stacks. These listing types include different categories of applications. Also, some listings are free and others require payment.
Images are templates of virtual hard drives that determine the operating system and software to run on an instance. You can deploy image listings on an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute instance. Marketplace also offers stack listings. Stacks represent definitions of groups of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources that you can act on as a group. Each stack has a configuration consisting of one or more declarative configuration files. With an image or a stack, you have a customized, more streamlined way of getting started with a publisher's software.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service can send you an alert when you might exceed your spending threshold?
- A. Budgets
- B. Monitoring
- C. Streaming
- D. Events
Answer: A
Explanation:
Budgets can be used to set thresholds for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure spending. You can set alerts on your budget to let you know when you might exceed your budget, and you can view all of your budgets and spending from one single place in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console.
NEW QUESTION 9
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service can you use to assess user security of your Oracle databases?
- A. Oracle Data Safe
- B. Oracle Data Guard
- C. Audit Vault and Database Firewall option for Oracle Database Enterprise Edition
- D. Audit Service
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Data Safe is a unified control center for your Oracle databases which helps you understand the sensitivity of your data, evaluate risks to data, mask sensitive data, implement and monitor security controls, assess user security, monitor user activity, and address data security compliance requirements.
Whether you’re using an Autonomous Database or an Oracle DB system, Oracle Data Safe delivers essential
data security capabilities as a service on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
NEW QUESTION 10
Which describes a key benefit of using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. With OCI, you can only run Java based workloads on bare metal.
- B. With OCI, you can run only cloud-native workloads.
- C. Only bare metal workloads are supported on OCI.
- D. OCI offers consistent performance with a predictable pricing model.
Answer: D
Explanation:
https://www.oracle.com/in/cloud/pricing.html
- OCI offers consistent performance with a predictable pricing model - is the best suited answer.
- Only bare metal workloads are supported in OCI - False, since you can work with VMs etc too
- With OCI, you can run cloud native workloads - False, since you can work with on-premise by connecting it to OCI too.
- With OCI, you can only run Java based workloads on bare metal - False since Java is not the only programming language supported by OCI.
NEW QUESTION 11
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is complement with which three industry standard?
- A. USA E-WALLED
- B. PRACE UK
- C. HIPPA
- D. PCI-DSS
- E. IG Toolkit-UK
Answer: CDE
Explanation:
https://www.oracle.com/cloud/cloud-infrastructure-compliance/
NEW QUESTION 12
Which feature is not component of Oracle cloud Infrastructure identity and Access management service?
- A. federation
- B. User Credential
- C. Network Security Group
- D. Policies
Answer: C
Explanation:
Components of IAM RESOURCE
The cloud objects that your company's employees create and use when interacting with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. For example: compute instances, block storage volumes, virtual cloud networks (VCNs), subnets, route tables, etc.
USER
An individual employee or system that needs to manage or use your company's Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Users might need to launch instances, manage remote disks, work with your virtual cloud network, etc. End users of your application are not typically IAM users. Users have one or more IAM credentials
(see User Credentials).
GROUP
A collection of users who all need the same type of access to a particular set of resources or compartment. DYNAMIC GROUP
A special type of group that contains resources (such as compute instances) that match rules that you define (thus the membership can change dynamically as matching resources are created or deleted). These instances act as "principal" actors and can make API calls to services according to policies that you write for the dynamic group. NETWORK SOURCE
A group of IP addresses that are allowed to access resources in your tenancy. The IP addresses can be public IP addresses or IP addresses from a VCN within your tenancy. After you create the network source, you use policy to restrict access to only requests that originate from the IPs in the network source.
COMPARTMENT
A collection of related resources. Compartments are a fundamental component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for organizing and isolating your cloud resources. You use them to clearly separate resources for the purposes of measuring usage and billing, access (through the use of policies), and isolation (separating the resources for one project or business unit from another). A common approach is to create a compartment for each major part of your organization. For more information, see Setting Up Your Tenancy.
TENANCY
The root compartment that contains all of your organization's Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Oracle automatically creates your company's tenancy for you. Directly within the tenancy are your IAM entities (users, groups, compartments, and some policies; you can also put policies into compartments inside the tenancy). You place the other types of cloud resources (e.g., instances, virtual networks, block storage volumes, etc.) inside the compartments that you create.
POLICY
A document that specifies who can access which resources, and how. Access is granted at the group and compartment level, which means you can write a policy that gives a group a specific type of access within a specific compartment, or to the tenancy itself. If you give a group access to the tenancy, the group automatically gets the same type of access to all the compartments inside the tenancy. For more information, see Example Scenario and How Policies Work. The word "policy" is used by people in different ways: to mean an individual statement written in the policy language; to mean a collection of statements in a single, named "policy" document (which has an Oracle Cloud ID (OCID) assigned to it); and to mean the overall body of policies your organization uses to control access to resources.
HOME REGION
The region where your IAM resources reside. All IAM resources are global and available across all regions, but the master set of definitions reside in a single region, the home region. You must make changes to your IAM resources in your home region. The changes will be automatically propagated to all regions. For more information, see Managing Regions.
FEDERATION
A relationship that an administrator configures between an identity provider and a service provider. When you federate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with an identity provider, you manage users and groups in the identity provider. You manage authorization in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's IAM service. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancies are federated with Oracle Identity Cloud Service by default.
NEW QUESTION 13
Which feature is NOT a component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Identity and Access management service?
- A. User Credentials
- B. Network Security Group
- C. Federation
- D. Policies
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 14
You are setting up a proof of concept (POC) and need to quickly establish a secure between an on-premises data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Which OCI service should you implement?
- A. VCN Peering
- B. FastConnect
- C. Internet Gateway
- D. IPSec VPN
Answer: D
Explanation:
You can set up a single IPSec VPN with a simple layout that you might use for a proof of concept (POC).
NEW QUESTION 15
Which service level agreement type is NOT offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service?
- A. Data Plane
- B. Performance
- C. Application Plane
- D. Control Plane
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle offers several different service level agreements as defined in this section (Service Level Agreements).Service level agreements range from least restrictive (data plane) to more restrictive (control plane) to most restrictive (performance).
NEW QUESTION 16
Which statement about Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) shared security model is true?
- A. You are responsible for managing security controls within the physical OCI network.
- B. You are not responsible for any aspect of security in OCI.
- C. You are responsible for securing all data that you place in OCI
- D. You are responsible for securing the hypervisor within OCI Compute service.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers best-in-class security technology and operational processes to secure its enterprise cloud services. However, for you to securely run your workloads in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you must be aware of your security and compliance responsibilities. By design, Oracle provides security of cloud infrastructure and operations (cloud operator access controls, infrastructure security patching, and so on), and you are responsible for securely configuring your cloud resources. Security in the cloud is a shared responsibility between you and Oracle.
In a shared, multi-tenant compute environment, Oracle is responsible for the security of the underlying cloud infrastructure (such as data-center facilities, and hardware and software systems) and you are responsible for securing your workloads and configuring your services (such as compute, network, storage, and database) securely.
In a fully isolated, single-tenant, bare metal server with no Oracle software on it, your responsibility increases as you bring the entire software stack (operating systems and above) on which you deploy your applications. In this environment, you are responsible for securing your workloads, and configuring your services (compute, network, storage, database) securely, and ensuring that the software components that you run on the bare metal servers are configured, deployed, and managed securely.
More specifically, your and Oracle's responsibilities can be divided into the following areas:
Identity and Access Management (IAM): As with all Oracle cloud services, you should protect your cloud access credentials and set up individual user accounts. You are responsible for managing and reviewing access for your own employee accounts and for all activities that occur under your tenancy. Oracle is responsible for providing effective IAM services such as identity management, authentication, authorization, and auditing.
Workload Security: You are responsible for protecting and securing the operating system and application layers of your compute instances from attacks and compromises. This protection includes patching applications and operating systems, operating system configuration, and protection against malware and network attacks. Oracle is responsible for providing secure images that are hardened and have the latest patches. Also, Oracle makes it simple for you to bring the same third-party security solutions that you use today.
Data Classification and Compliance: You are responsible for correctly classifying and labeling your data and meeting any compliance obligations. Also, you are responsible for auditing your solutions to ensure that they meet your compliance obligations.
Host Infrastructure Security: You are responsible for securely configuring and managing your compute (virtua hosts, containers), storage (object, local storage, block volumes), and platform (database configuration) services. Oracle has a shared responsibility with you to ensure that the service is optimally configured and secured. This responsibility includes hypervisor security and the configuration of the permissions and network access controls required to ensure that hosts can communicate correctly and that devices are able to attach or mount the correct storage devices.
Network Security: You are responsible for securely configuring network elements such as virtual networking, load balancing, DNS, and gateways. Oracle is responsible for providing a secure network infrastructure.
Client and Endpoint Protection: Your enterprise uses various hardware and software systems, such as mobile devices and browsers, to access your cloud resources. You are responsible for securing all clients and endpoints that you allow to access Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services.
Physical Security: Oracle is responsible for protecting the global infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. This infrastructure consists of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services.
NEW QUESTION 17
Which is NOT considered a security resource within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure?
- A. Network Security Group
- B. Web Application Firewall
- C. File Storage Service
- D. Security Lists
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service provides a durable, scalable, secure, enterprise-grade netwo file system. You can connect to a File Storage service file system from any bare metal, virtual machine, or container instance in your Virtual Cloud Network (VCN).
You can control the access of the file system from FSS by applying some security rules and others but the services it self not related to security but it related to shared storage
NEW QUESTION 18
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service leverages Terraform to configure infrastructure as code?
- A. Resource Manager
- B. Events
- C. Compartment Explorer
- D. Oracle Functions
Answer: A
Explanation:
Resource Manager is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service that allows you to automate the process of
provisioning your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Using Terraform, Resource Manager helps you install, configure, and manage resources through the "infrastructure-as-code" model.
A Terraform configuration codifies your infrastructure in declarative configuration files. Resource Manager allows you to share and manage infrastructure configurations and state files across multiple teams and platforms. This infrastructure management can't be done with local Terraform installations and Oracle Terraform modules alone. For more information about the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Terraform provider, see Terraform Provider. For a general introduction to Terraform and the "infrastructure-as-code" model, see https://www.terraform.io.
NEW QUESTION 19
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service is best suited for running serverless apps?
- A. Oracle Functions
- B. Virtual Cloud Network
- C. Streaming
- D. Audit
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Functions is a fully managed, multi-tenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a-Service platform. It is built on enterprise-grade Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Use Oracle Functions (sometimes abbreviated to just Functions) when you want to focus on writing code to meet business needs.
The serverless and elastic architecture of Oracle Functions means there's no infrastructure administration or software administration for you to perform. You don't provision or maintain compute instances, and operating system software patches and upgrades are applied automatically. Oracle Functions simply ensures your app is highly-available, scalable, secure, and monitored. With Oracle Functions, you can write code in Java, Python, Node, Go, and Ruby (and for advanced use cases, bring your own Dockerfile, and Graal VM). You can then deploy your code, call it directly or trigger it in response to events, and get billed only for the resources consumed during the execution.
Oracle Functions is based on Fn Project. Fn Project is an open source, container native, serverless platform that can be run anywhere - any cloud or on-premises. Fn Project is easy to use, extensible, and performant. You can download and install the open source distribution of Fn Project, develop and test a function locally, and then use the same tooling to deploy that function to Oracle Functions.
You can access Oracle Functions using the Console, a CLI, and a REST API. You can invoke the functions you deploy to Oracle Functions using the CLI or by making signed HTTP requests.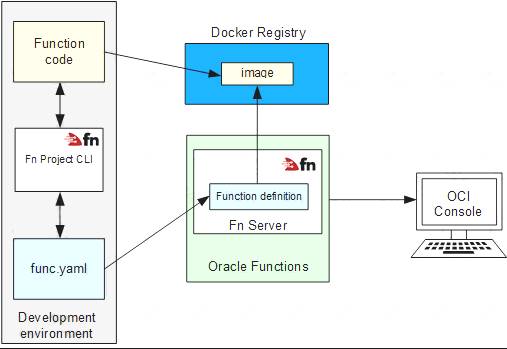
NEW QUESTION 20
Your company has deployed a business critical application in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. What should you do to ensure that your application has the highest level of resilience and availability?
- A. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Subnets
- B. Deploy the application across multiple Virtual Cloud Networks
- C. Deploy the application across multiple Regions and Availability Domains
- D. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Fault Domains
Answer: C
Explanation:
To design a high availability architecture, three key elements should be considered— redundancy, monitoring, and failover:
1) Redundancy means that multiple components can perform the same task. The problem of a single point of failure is eliminated because redundant components can take over a task performed by a component that has failed.
2) Monitoring means checking whether or not a component is working properly.
3) Failover is the process by which a secondary component becomes primary when the primary component fails.
The best practices introduced here focus on these three key elements. Although high availability can be achieved at many different levels, including the application level and the cloud infrastructure level, here we will focus on the cloud infrastructure level.
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area composed of one or more availability domains, each composed of three fault domains. High availability is ensured by a redundancy of fault domains within the availability domains.
An availability domain is one or more data centers located within a region. Availability domains are isolated from each other, fault tolerant, and unlikely to fail simultaneously. Because availability domains do not share physical infrastructure, such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network, a failure that impacts one availability domain is unlikely to impact the availability of others.
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains let you distribute your instances so that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, an unexpected hardware failure or a Compute hardware maintenance that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. You can optionally specify the fault domain for a new instance at launch time, or you can let the system select one for you.
All the availability domains in a region are connected to each other by a low-latency, high bandwidth network. This predictable, encrypted interconnection between availability domains provides the building blocks for both high availability and disaster recovery.
NEW QUESTION 21
......
P.S. Dumpscollection.com now are offering 100% pass ensure 1z0-1085-20 dumps! All 1z0-1085-20 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.dumpscollection.net/dumps/1z0-1085-20/ (83 New Questions)