We provide real Professional-Cloud-Architect exam questions and answers braindumps in two formats. Download PDF & Practice Tests. Pass Google Professional-Cloud-Architect Exam quickly & easily. The Professional-Cloud-Architect PDF type is available for reading and printing. You can print more and practice many times. With the help of our Google Professional-Cloud-Architect dumps pdf and vce product and material, you can easily pass the Professional-Cloud-Architect exam.
Free Professional-Cloud-Architect Demo Online For Google Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
The development team has provided you with a Kubernetes Deployment file. You have no infrastructure yet and need to deploy the application. What should you do?
- A. Use gcloud to create a Kubernetes cluste
- B. Use Deployment Manager to create the deployment.
- C. Use gcloud to create a Kubernetes cluste
- D. Use kubect1 to create the deployment.
- E. Use kubect1 to create a Kubernetes cluste
- F. Use Deployment Manager to create the deployment.
- G. Use kubect1 to create a Kubernetes cluste
- H. Use kubect1 to create the deployment.
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/creating-a-cluster
NEW QUESTION 2
Your company just finished a rapid lift and shift to Google Compute Engine for your compute needs. You have another 9 months to design and deploy a more cloud-native solution. Specifically, you want a system that is no-ops and auto-scaling. Which two compute products should you choose? Choose 2 answers
- A. Compute Engine with containers
- B. Google Kubernetes Engine with containers
- C. Google App Engine Standard Environment
- D. Compute Engine with custom instance types
- E. Compute Engine with managed instance groups
Answer: BC
Explanation:
B: With Container Engine, Google will automatically deploy your cluster for you, update, patch, secure the nodes.
Kubernetes Engine's cluster autoscaler automatically resizes clusters based on the demands of the workloads you want to run.
C: Solutions like Datastore, BigQuery, AppEngine, etc are truly NoOps.
App Engine by default scales the number of instances running up and down to match the load, thus providing consistent performance for your app at all times while minimizing idle instances and thus reducing cost.
Note: At a high level, NoOps means that there is no infrastructure to build out and manage during usage of the platform. Typically, the compromise you make with NoOps is that you lose control of the underlying infrastructure.
References:
https://www.quora.com/How-well-does-Google-Container-Engine-support-Google-Cloud-Platform%E2%80%9
NEW QUESTION 3
For this question refer to the TerramEarth case study
Operational parameters such as oil pressure are adjustable on each of TerramEarth's vehicles to increase their efficiency, depending on their environmental conditions. Your primary goal is to increase the operating efficiency of all 20 million cellular and unconnected vehicles in the field How can you accomplish this goal?
- A. Have your engineers inspect the data for patterns, and then create an algorithm with rules that make operational adjustments automatically.
- B. Capture all operating data, train machine learning models that identify ideal operations, and run locally to make operational adjustments automatically.
- C. Implement a Google Cloud Dataflow streaming job with a sliding window, and use Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) to make operational adjustments automatically.
- D. Capture all operating data, train machine learning models that identify ideal operations, and host in Google Cloud Machine Learning (ML) Platform to make operational adjustments automatically.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 4
Your company has multiple on-premises systems that serve as sources for reporting. The data has not been maintained well and has become degraded over time. You want to use Google-recommended practices to detect anomalies in your company data. What should you do?
- A. Upload your files into Cloud Storag
- B. Use Cloud Datalab to explore and clean your data.
- C. Upload your files into Cloud Storag
- D. Use Cloud Dataprep to explore and clean your data.
- E. Connect Cloud Datalab to your on-premises system
- F. Use Cloud Datalab to explore and clean your data.
- G. Connect Cloud Dataprep to your on-premises system
- H. Use Cloud Dataprep to explore and clean your data.
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/dataprep/
NEW QUESTION 5
You need to design a solution for global load balancing based on the URL path being requested. You need to ensure operations reliability and end-to-end in-transit encryption based on Google best practices.
What should you do?
- A. Create a cross-region load balancer with URL Maps.
- B. Create an HTTPS load balancer with URL maps.
- C. Create appropriate instance groups and instance
- D. Configure SSL proxy load balancing.
- E. Create a global forwarding rul
- F. Configure SSL proxy balancing.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Reference https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/https/url-map
NEW QUESTION 6
The operations manager asks you for a list of recommended practices that she should consider when migrating a J2EE application to the cloud. Which three practices should you recommend? Choose 3 answers
- A. Port the application code to run on Google App Engine.
- B. Integrate Cloud Dataflow into the application to capture real-time metrics.
- C. Instrument the application with a monitoring tool like Stackdriver Debugger.
- D. Select an automation framework to reliably provision the cloud infrastructure.
- E. Deploy a continuous integration tool with automated testing in a staging environment.
- F. Migrate from MySQL to a managed NoSQL database like Google Cloud Datastore or Bigtable.
Answer: AEF
Explanation:
References: https://cloud.google.com/appengine/docs/standard/java/tools/uploadinganapp https://cloud.google.com/appengine/docs/standard/java/building-app/cloud-sql
NEW QUESTION 7
Your company is forecasting a sharp increase in the number and size of Apache Spark and Hadoop jobs being run on your local datacenter You want to utilize the cloud to help you scale this upcoming demand with the least amount of operations work and code change. Which product should you use?
- A. Google Cloud Dataflow
- B. Google Cloud Dataproc
- C. Google Compute Engine
- D. Google Container Engine
Answer: B
Explanation:
Google Cloud Dataproc is a fast, easy-to-use, low-cost and fully managed service that lets you run the Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop ecosystem on Google Cloud Platform. Cloud Dataproc provisions big or small clusters rapidly, supports many popular job types, and is integrated with other Google Cloud Platform services, such as Google Cloud Storage and Stackdriver Logging, thus helping you reduce TCO.
References: https://cloud.google.com/dataproc/docs/resources/faq
NEW QUESTION 8
You are migrating your on-premises solution to Google Cloud in several phases. You will use Cloud VPN to maintain a connection between your on-premises systems and Google Cloud until the migration is completed.
You want to make sure all your on-premises systems remain reachable during this period. How should you organize your networking in Google Cloud?
- A. Use the same IP range on Google Cloud as you use on-premises
- B. Use the same IP range on Google Cloud as you use on-premises for your primary IP range and use a secondary range that does not overlap with the range you use on-premises
- C. Use an IP range on Google Cloud that does not overlap with the range you use on-premises
- D. Use an IP range on Google Cloud that does not overlap with the range you use on-premises for your primary IP range and use a secondary range with the same IP range as you use on-premises
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
Your customer support tool logs all email and chat conversations to Cloud Bigtable for retention and analysis. What is the recommended approach for sanitizing this data of personally identifiable information or payment card information before initial storage?
- A. Hash all data using SHA256
- B. Encrypt all data using elliptic curve cryptography
- C. De-identify the data with the Cloud Data Loss Prevention API
- D. Use regular expressions to find and redact phone numbers, email addresses, and credit card numbers
Answer: A
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/solutions/pci-dss-compliance-ingcp#
NEW QUESTION 10
You have an outage in your Compute Engine managed instance group: all instance keep restarting after 5 seconds. You have a health check configured, but autoscaling is disabled. Your colleague, who is a Linux expert, offered to look into the issue. You need to make sure that he can access the VMs. What should you do?
- A. Grant your colleague the IAM role of project Viewer
- B. Perform a rolling restart on the instance group
- C. Disable the health check for the instance grou
- D. Add his SSH key to the project-wide SSH keys
- E. Disable autoscaling for the instance grou
- F. Add his SSH key to the project-wide SSH Keys
Answer: C
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/instance-groups/autohealing-instances-in-migs
Health checks used for autohealing should be conservative so they don't preemptively delete and recreate your instances. When an autohealer health check is too aggressive, the autohealer might mistake busy instances for failed instances and unnecessarily restart them, reducing availability
NEW QUESTION 11
A development team at your company has created a dockerized HTTPS web application. You need to deploy the application on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and make sure that the application scales automatically.
How should you deploy to GKE?
- A. Use the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and enable cluster autoscalin
- B. Use an Ingress resource to loadbalance the HTTPS traffic.
- C. Use the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and enable cluster autoscaling on the Kubernetes cluste
- D. Use a Service resource of type LoadBalancer to load-balance the HTTPS traffic.
- E. Enable autoscaling on the Compute Engine instance grou
- F. Use an Ingress resource to load balance the HTTPS traffic.
- G. Enable autoscaling on the Compute Engine instance grou
- H. Use a Service resource of type LoadBalancer to load-balance the HTTPS traffic.
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/tutorials/http-balancer https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/network-overview#ext-lb
NEW QUESTION 12
You are designing a large distributed application with 30 microservices. Each of your distributed microservices needs to connect to a database back-end. You want to store the credentials securely. Where should you store the credentials?
- A. In the source code
- B. In an environment variable
- C. In a secret management system
- D. In a config file that has restricted access through ACLs
Answer: C
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/docs/authentication/production#providing_credentials_to_your_application
NEW QUESTION 13
Your web application has several VM instances running within a VPC. You want to restrict communications between instances to only the paths and ports you authorize, but you don’t want to rely on static IP addresses or subnets because the app can autoscale. How should you restrict communications?
- A. Use separate VPCs to restrict traffic
- B. Use firewall rules based on network tags attached to the compute instances
- C. Use Cloud DNS and only allow connections from authorized hostnames
- D. Use service accounts and configure the web application particular service accounts to have access
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 14
Your organization has a 3-tier web application deployed in the same network on Google Cloud Platform. Each tier (web, API, and database) scales independently of the others Network traffic should flow through the web to the API tier and then on to the database tier. Traffic should not flow between the web and the database tier. How should you configure the network?
- A. Add each tier to a different subnetwork.
- B. Set up software based firewalls on individual VMs.
- C. Add tags to each tier and set up routes to allow the desired traffic flow.
- D. Add tags to each tier and set up firewall rules to allow the desired traffic flow.
Answer: D
Explanation:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/building-three-tier-architectures-with-security-groups/
Google Cloud Platform(GCP) enforces firewall rules through rules and tags. GCP rules and tags can be defined once and used across all regions.
References: https://cloud.google.com/docs/compare/openstack/ https://aws.amazon.com/it/blogs/aws/building-three-tier-architectures-with-security-groups/
NEW QUESTION 15
You are designing a mobile chat application. You want to ensure people cannot spoof chat messages, by providing a message were sent by a specific user.
What should you do
- A. Tag messages client side with the originating user identifier and the destination user.
- B. Encrypt the message client side using block-based encryption with a shared key.
- C. Use public key infrastructure (PKI) to encrypt the message client side using the originating user's private key.
- D. Use a trusted certificate authority to enable SSL connectivity between the client application and the server.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 16
Your customer is moving their corporate applications to Google Cloud Platform. The security team wants detailed visibility of all projects in the organization. You provision the Google Cloud Resource Manager and set up yourself as the org admin. What Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (Cloud IAM) roles should you give to the security team'?
- A. Org viewer, project owner
- B. Org viewer, project viewer
- C. Org admin, project browser
- D. Project owner, network admin
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/using-iam-securely
NEW QUESTION 17
A news teed web service has the following code running on Google App Engine. During peak load, users report that they can see news articles they already viewed. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
- A. The session variable is local to just a single instance.
- B. The session variable is being overwritten in Cloud Datastore.
- C. The URL of the API needs to be modified to prevent caching.
- D. The HTTP Expires header needs to be set to -1 to stop caching.
Answer: A
Explanation:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3164280/google-app-engine-cache-list-in-session-variable?rq=1
NEW QUESTION 18
You deploy your custom Java application to Google App Engine. It fails to deploy and gives you the following stack trace.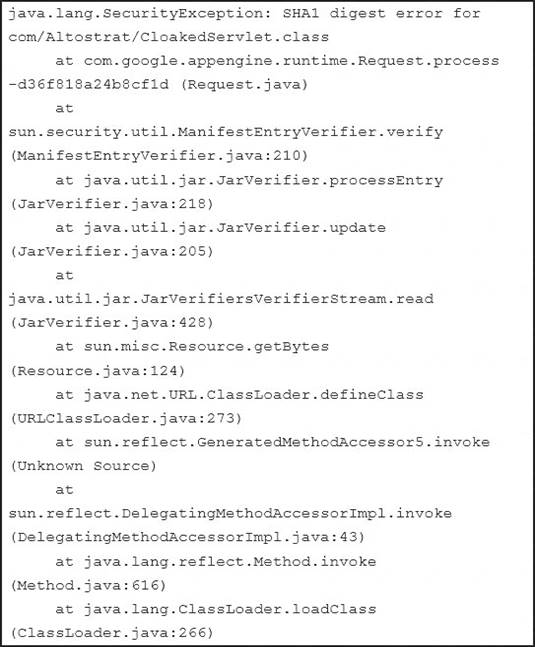
What should you do?
- A. Upload missing JAR files and redeploy your application.
- B. Digitally sign all of your JAR files and redeploy your application
- C. Recompile the CLoakedServlet class using and MD5 hash instead of SHA1
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 19
You have deployed an application to Kubernetes Engine, and are using the Cloud SQL proxy container to make the Cloud SQL database available to the services running on Kubernetes. You are notified that the application is reporting database connection issues. Your company policies require a post-mortem. What
should you do?
- A. Use gcloud sql instances restart.
- B. Validate that the Service Account used by the Cloud SQL proxy container still has the Cloud Build Editor role.
- C. In the GCP Console, navigate to Stackdriver Loggin
- D. Consult logs for Kubernetes Engine and Cloud SQL.
- E. In the GCP Console, navigate to Cloud SQ
- F. Restore the latest backu
- G. Use kubect1 to restart all pods.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 20
You have been engaged by your client to lead the migration of their application infrastructure to GCP. One of their current problems is that the on-premises high performance SAN is requiring frequent and expensive upgrades to keep up with the variety of workloads that are identified as follows: 20TB of log archives retained for legal reasons; 500 GB of VM boot/data volumes and templates; 500 GB of image thumbnails; 200 GB of customer session state data that allows customers to restart sessions even if off-line for several days.
Which of the following best reflects your recommendations for a cost-effective storage allocation?
- A. Local SSD for customer session state dat
- B. Lifecycle-managed Cloud Storage for log archives, thumbnails, and VM boot/data volumes.
- C. Memcache backed by Cloud Datastore for the customer session state dat
- D. Lifecycle- managed Cloud Storage for log archives, thumbnails, and VM boot/data volumes.
- E. Memcache backed by Cloud SQL for customer session state dat
- F. Assorted local SSD-backed instances for VM boot/data volume
- G. Cloud Storage for log archives and thumbnails.
- H. Memcache backed by Persistent Disk SSD storage for customer session state dat
- I. Assorted local SSDbacked instances for VM boot/data volume
- J. Cloud Storage for log archives and thumbnails.
Answer: D
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/disks
NEW QUESTION 21
......
Thanks for reading the newest Professional-Cloud-Architect exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM 2passeasy Professional-Cloud-Architect dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/Professional-Cloud-Architect/ (170 Q&As Dumps)