Exam Code: 200-101 (), Exam Name: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2), Certification Provider: Cisco Certifitcation, Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 200-101 Exam.
Check 200-101 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Refer to the exhibit.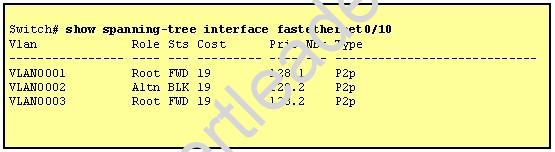
Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
- A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
- B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
- C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
- D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Explanation: These four parameters are examined in order to make root bridge , root port , designated port. Other switch has lowest Sending Bridge ID or Sending Port ID so vlan 2 is not the root port.
*1. A lower Root Bridge ID
*2. A lower path cost to the Root
*3. A lower Sending Bridge ID
*4. A lower Sending Port ID
NEW QUESTION 2
What command visualizes the general NetFlow data on the command line?
- A. show ip flow export
- B. show ip flow top-talkers
- C. show ip cache flow
- D. show mls sampling
- E. show mls netflow ip
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 3
Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (Choose two.)
- A. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
- B. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing table.
- C. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
- D. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
- E. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables, using automatic updates.
- F. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
- G. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
Answer: BG
Explanation: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24090&seqNum=6 http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24090
NEW QUESTION 4
Which port state is introduced by Rapid-PVST?
- A. learning
- B. listening
- C. discarding
- D. forwarding
Answer: C
Explanation: Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example
Reference 1: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/products_configuration_example 09186a00807b0670.shtml
Reference 2: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cf a.shtml
PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But PVST+ has only 3 port states (discarding, learning and forwarding) while STP has 5 port states (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding and disabled). So discarding is a new port state in PVST+.
Background Information
802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) has a drawback of slow convergence. Cisco Catalyst switches support three types of STPs, which are PVST+, rapid-PVST+ and MST. PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D standard and includes Cisco proprietary extensions such as BackboneFast, UplinkFast, and PortFast. Rapid-PVST+ is based on IEEE 802.1w standard and has a faster convergence than 802.1D. RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) natively includes most of the Cisco proprietary enhancements to the 802.1D Spanning Tree, such as BackboneFast and UplinkFast. Rapid-PVST+ has these unique features:
Uses Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) version 2 which is backward compatible with the 802.1D STP, which uses BPDU version 0.
All the switches generate BPDUs and send out on all the ports every 2 seconds, whereas in 802.1D STP only the root bridge sends the configuration BPDUs.
Port Roles—Root port, designated port, alternate port and backup port. Port States—Discarding, Learning, and Forwarding.
Port Types—Edge Port (PortFast), Point-to-Point and Shared port.
Rapid-PVST uses RSTP to provide faster convergence. When any RSTP port receives legacy 802.1D BPDU, it falls back to legacy STP and the inherent fast convergence benefits of 802.1w are lost when it interacts with legacy bridges.
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.
Given the output from the show ip eigrp topology command, which router is the feasible successor?
A)
B)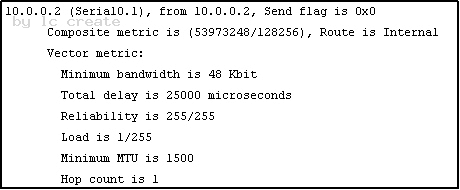
C)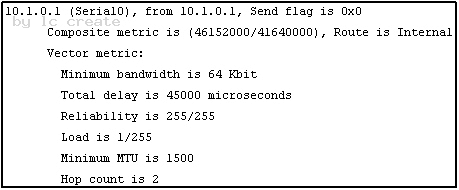
D)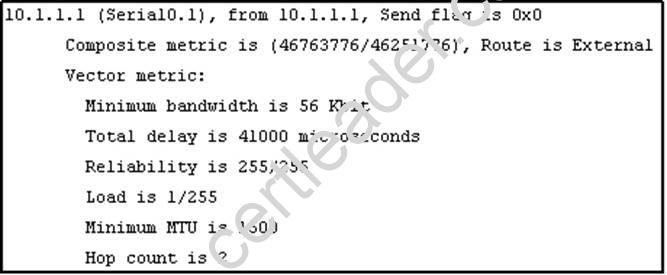
- A. Exhibit A
- B. Exhibit B
- C. Exhibit C
- D. Exhibit D
Answer: B
Explanation: http://networklessons.com/eigrp/eigrp-neighbor-and-topology-table-explained/
To be the feasible successor, the Advertised Distance (AD) of that route must be less than the Feasible Distance (FD) of the successor. From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255 we learn that the FD of the successor is 41152000.
Now we will mention about the answers, in the “Composite metric is (…/…)” statement the first parameter is the FD while the second parameter is the AD of that route. So we need to find out which route has the second parameter (AD) less than 41152000 -> only answer B satisfies this requirement with an AD of 128256.
NEW QUESTION 6
What is a valid HSRP virtual MAC address?
- A. 0000.5E00.01A3
- B. 0007.B400.AE01
- C. 0000.0C07.AC15
- D. 0007.5E00.B301
Answer: C
Explanation: Hot Standby Router Protocol Features and Functionality http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk362/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094a91. shtml
HSRP Addressing
In most cases when you configure routers to be part of an HSRP group, they listen for the HSRP MAC address for that group as well as their own burned-in MAC address. The exception is routers whose Ethernet controllers only recognize a single MAC address (for example, the Lance controller on the Cisco 2500 and Cisco 4500 routers). These routers use the HSRP MAC address when they are the Active router, and their burned-in address when they are not.
HSRP uses the following MAC address on all media except Token Ring: 0000.0c07.ac** (where ** is the HSRP group number)
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.
The network is converged. After link-state advertisements are received from Router_A, what information will Router_E contain in its routing table for the subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96?
- A. O 208.149.23.64 [110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:07, FastEthernet 0/0 O 208.149.23.96 [110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:16, FastEthernet 0/0
- B. O 208.149.23.64 [110/1] via 190.172.23.10, 00:00:07, Serial 1/0 O 208.149.23.96 [110/3] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:16, FastEthernet 0/0
- C. O 208.149.23.64 [110/13] via 190.172.23.10, 00:00:07, Serial 1/0 O 208.149.23.96 [110/13] via 190.172.23.10, 00:00:16, Serial 1/0 O 208.149.23.96 [110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:16, FastEthernet 0/0
- D. O 208.149.23.64 [110/3] via 190.172.23.10, 00:00:07, Serial 1/0 O 208.149.23.96 [110/3] via 190.172.23.10, 00:00:16, Serial 1/0
Answer: A
Explanation: Router_E learns two subnets subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96 via Router_A through FastEthernet interface. The interface cost is calculated with the formula 108
/Bandwidth. For FastEthernet it is 108 / 100 Mbps = 108 / 100,000,000 = 1. Therefore the cost is12(learned from Router_A)+ 1=13for both subnets - B is not correct.
The cost through T1 link is much higher than through T3 link (T1 cost = 108 / 1.544 Mbps = 64; T3 cost = 108 / 45 Mbps = 2) so surely OSPF will choose the path through T3 link -> Router_E will choose the path from Router_A through FastEthernet0/0, not Serial1/0 - C & D are not correct.
In fact, we can quickly eliminate answers B, C and D because they contain at least one subnet learned from Serial1/0 - they are surely incorrect.
NEW QUESTION 8
Refer to the exhibit.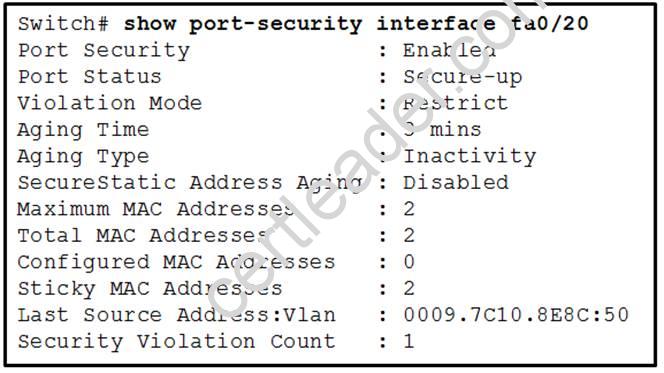
What three actions will the switch take when a frame with an unknown source MAC address arrives at the interface? (Select three.)
- A. Send an SNMP trap.
- B. Send a syslog message.
- C. Increment the Security Violation counter.
- D. Forward the traffic.
- E. Write the MAC address to the startup-config.
- F. Shut down the port.
Answer: ABC
Explanation: Switchport Security Concepts and Configuration
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1722561
Switchport Security Violations
The second piece of switchport port-security that must be understood is a security violation including what it is what causes it and what the different violation modes that exist. A switchport violation occurs in one of two situations:
When the maximum number of secure MAC addresses has been reached (by default, the maximum number of secure MAC addresses per switchport is limited to 1)
An address learned or configured on one secure interface is seen on another secure interface in the same VLAN
The action that the device takes when one of these violations occurs can be configured: Protect—This mode permits traffic from known MAC addresses to continue to be forwarded while dropping traffic from unknown MAC addresses when over the allowed MAC address limit. When configured with this mode, no notification action is taken when traffic is dropped.
Restrict—This mode permits traffic from known MAC addresses to continue to be forwarded while dropping traffic from unknown MAC addresses when over the allowed MAC address limit. When configured with this mode, a syslog message is logged, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is sent, and a violation counter is incremented when traffic is dropped.
Shutdown—This mode is the default violation mode; when in this mode, the switch will automatically force the switchport into an error disabled (err-disable) state when a violation occurs. While in this state, the switchport forwards no traffic. The switchport can be brought out of this error disabled state by issuing the errdisable recovery cause CLI command or by disabling and re-enabling the switchport.
Shutdown VLAN—This mode mimics the behavior of the shutdown mode but limits the error disabled state the specific violating VLAN.
NEW QUESTION 9
What are two characteristics of a switch that is configured as a VTP client? (Choose two.)
- A. If a switch that is configured to operate in client mode cannot access a VTP server, then the switch reverts to transparent mode.
- B. On switches that are configured to operate in client mode, VLANs can be created, deleted, or renamed locally.
- C. The local VLAN configuration is updated only when an update that has a higher configuration revision number is received.
- D. VTP advertisements are not forwarded to neighboring switches that are configured in VTP transparent mode.
- E. VTP client is the default VTP mode.
- F. When switches in VTP client mode are rebooted, they send a VTP advertisement request to the VTP servers.
Answer: CF
Explanation: VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
http://archive.networknewz.com/2004/0317.html
VTP Modes
Server Mode Once VTP is configured on a Cisco switch, the default mode used is Server Mode. In any given VTP management domain, at least one switch must be in Server Mode. When in Server Mode, a switch can be used to add, delete, and modify VLANs, and this information will be passed to all other switches in the VTP management domain.
Client Mode When a switch is configured to use VTP Client Mode, it is simply the recipient of any VLANs added, deleted, or modified by a switch in Server Mode within the same management domain. A switch in VTP client mode cannot make any changes to VLAN information.
Transparent Mode A switch in VTP Transparent Mode will pass VTP updates received by switches in Server Mode to other switches in the VTP management domain, but will not actually process the contents of these messages. When individual VLANs are added, deleted, or modified on a switch running in transparent mode, the changes are local to that particular switch only, and are not passed to other switches in the VTP management domain.
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the exhibit.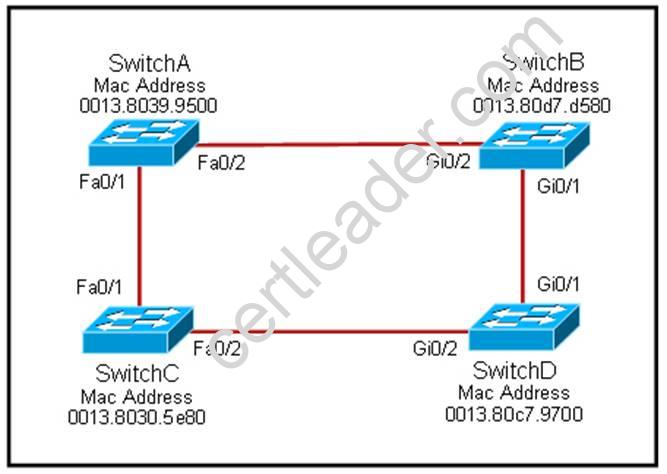
Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three.)
- A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
- B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
- C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
- D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
- E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
- F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: ABF
Explanation: The question says "no other configuration changes have been made" so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. SwitchC has lowest MAC address so, it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports (DP). Because SwitchC is the root bridge the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports (RP) -> B and F are correct.
SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, "cost" is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
Link speed Cost SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the "cost to the root bridge" of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
- A. Bandwidth
- B. Bandwidth and Delay
- C. Bandwidth, Delay, and MTU
- D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay, and Load
Answer: A
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094e9e.sht ml#t6
OSPF Cost
The cost (also called metric) of an interface in OSPF is an indication of the overhead required to send packets across a certain interface. The cost of an interface is inversely proportional to the bandwidth of that interface. A higher bandwidth indicates a lower cost. There is more overhead (higher cost) and time delays involved in crossing a 56k serial line than crossing a 10M Ethernet line. The formula used to calculate the cost is:
Cost= 10000 0000/bandwidth in bps
For example, it will cost 10 EXP8/10 EXP7 = 10 to cross a 10M Ethernet line and will cost
10 EXP8/1544000 =64 to cross a T1 line. By default, the cost of an interface is calculated based on the bandwidth; you can force the cost of an interface with the ip ospf cost
<value> interface sub configuration mode command.
NEW QUESTION 12
Which Layer 2 protocol encapsulation type supports synchronous and asynchronous circuits and has built-in security mechanisms?
- A. HDLC
- B. PPP
- C. X.25
- D. Frame Relay
Answer: B
Explanation: High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) - HDLC is the default encapsulation type on point-to- point, dedicated links, and circuit-switched connections. It is used typically when communicating between two Cisco devices. It is a bit-oriented synchronous data link layer protocol.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) - Provides router-to-router and host-to network connections over synchronous and asynchronous circuits. PPP was designed to work with several network layer protocols, such as IP, and IPX. PPP also has built in security mechanisms such as PAP and CHAP X.25/Link Access Procedure, Balanced (LAPB) - ITU-T standard that defines how connections between DTE and DCE are maintained for remote terminal access and computer communications in public data networks. X.25 specifies LAPB, a data line layer protocol. X.25 is a predecessor to Frame Relay.
Frame Relay - Industry standard, switched data link layer protocol that handles multiple virtual circuits. It is a next-generation to X.25 that is streamlined to eliminate some of the time-consuming processes (such as error correction and flow control) that were employed in X.25.
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit.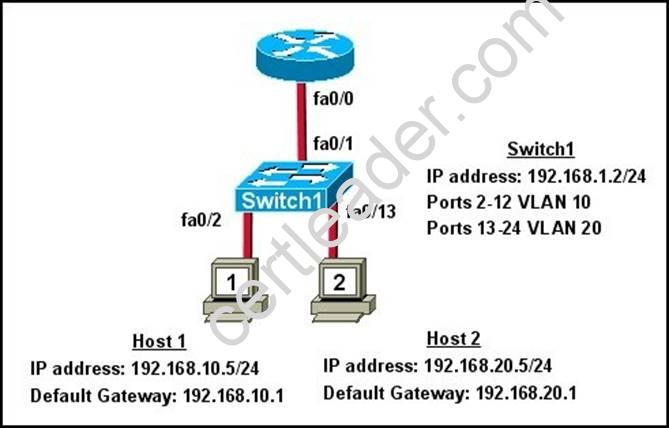
What commands must be configured on the 2950 switch and the router to allow communication between host 1 and host 2? (Choose two.)
- A. Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0Router(config-if)# no shut down
- B. Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)# no shut down Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.1 Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.2Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 20Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
- C. Router(config)# router eigrp 100 Router(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0Router(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
- D. Switch1(config)# vlan database Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp domain XYZ Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp server
- E. Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
- F. Switch1(config)# interface vlan 1 Switch1(config-if)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
Answer: BE
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk815/technologies_configuration_example09186a 00800949fd.shtml
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/servlet/JiveServlet/download/5669-2461/Router%20on%20a%20Stick.pdf.
NEW QUESTION 14
Refer to the exhibit.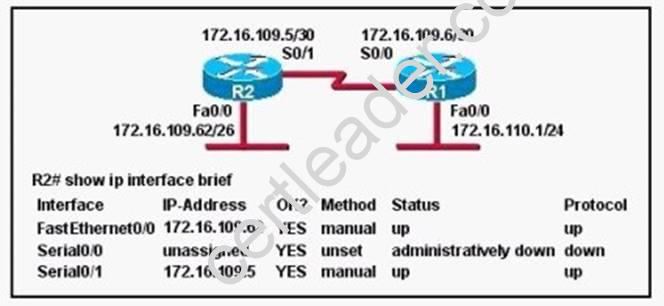
Assuming that the entire network topology is shown, what is the operational status of the interfaces of R2 as indicated by the command output shown?
- A. One interface has a problem.
- B. Two interfaces have problems.
- C. The interfaces are functioning correctly.
- D. The operational status of the interfaces cannot be determined from the output shown.
Answer: C
Explanation: R2 has setup with two interface s0/1 and fa0/0 and both are interfaces configured with IP address and up. "show ip interface brief" showing the status of R2 interfaces.
NEW QUESTION 15
What occurs on a Frame Relay network when the CIR is exceeded?
- A. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible.
- B. All UDP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
- C. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
- D. All traffic exceeding the CIR is marked discard eligible.
Answer: D
Explanation: Committed information rate (CIR): The minimum guaranteed data transfer rate agreed to by the Frame Relay switch. Frames that are sent in excess of the CIR are marked as discard eligible (DE) which means they can be dropped if the congestion occurs within the Frame Relay network.
Note: In the Frame Relay frame format, there is a bit called Discard eligible (DE) bit that is used to identify frames that are first to be dropped when the CIR is exceeded.
NEW QUESTION 16
Which command allows you to verify the encapsulation type (CISCO or IETF) for a Frame Relay link?
- A. show frame-relay lmi
- B. show frame-relay map
- C. show frame-relay pvc
- D. show interfaces serial
Answer: B
Explanation: map will show frame relay encapsulation (cisco or ietf) http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/wan/command/reference/wrffr4.html#wp102934 3
"show frame-relay map" will show frame relay encapsulation type (CISCO or IETF)
NEW QUESTION 17
What is the purpose of LCP?
- A. to perform authentication
- B. to negotiate control options
- C. to encapsulate multiple protocols
- D. to specify asynchronous versus synchronous
Answer: B
Explanation: Link Control Protocol
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1661.txt
In order to be sufficiently versatile to be portable to a wide variety of environments, PPP provides a Link
Control Protocol (LCP). The LCP is used to automatically agree upon the encapsulation format options, handle varying limits on sizes of packets, detect a looped-back link and other common misconfiguration errors, and terminate the link. Other optional facilities provided are authentication of the identity of its peer on the link, and determination when a link is functioning properly and when it is failing.
NEW QUESTION 18
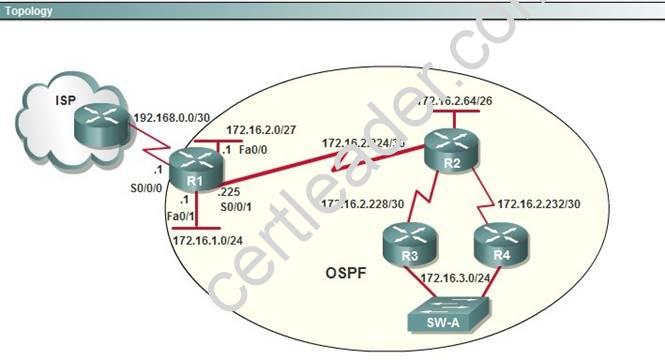
After the network has converged, what type of messaging, if any, occurs between R3 and R4?
- A. No messages are exchanged.
- B. Hellos are sent every 10 seconds.
- C. The full database from each router is sent every 30 seconds.
- D. The routing table from each router is sent every 60 seconds.
Answer: B
Explanation: HELLO messages are used to maintain adjacent neighbors so even when the network is converged, hellos are still exchanged. On broadcast and point-to-point links, the default is 10 seconds, on NBMA the default is 30 seconds.
NEW QUESTION 19
Refer to the exhibit.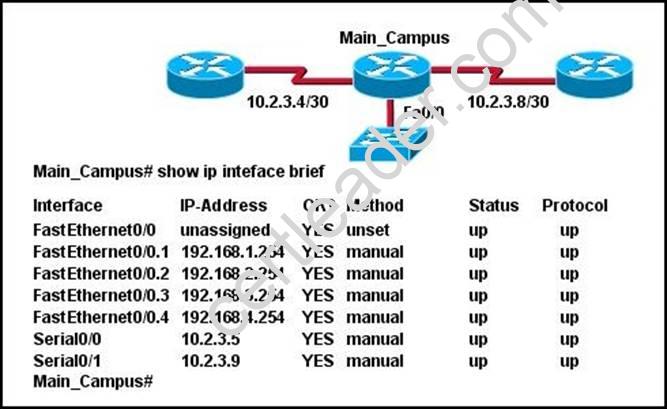
What information about the interfaces on the Main_Campus router is true?
- A. The LAN interfaces are configured on different subnets.
- B. Interface FastEthernet 0/0 is configured as a trunk.
- C. The Layer 2 protocol of interface Serial 0/1 is NOT operational.
- D. The router is a modular router with five FastEthernet interfaces.
- E. Interface FastEthernet 0/0 is administratively deactivated.
Answer: B
Explanation: Interface fa0/0 breaks into sub-interfaces and Main_Campus router is connected with switch via fa0/0 .Subinterfaces configured with different subnet mask so the seem switch has multiple vlans and allows communication between these VLAN's. For routing and inter- vlan we need to configure a trunk port. So B will be the correct answer.
Thanks for reading the newest 200-101 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Certleader 200-101 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.certleader.com/200-101-dumps.html (149 Q&As Dumps)