It is impossible to pass Cisco 200-101 exam without any help in the short term. Come to us soon and find the most advanced, correct and guaranteed . You will get a surprising result by our .
Online 200-101 free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two options are valid WAN connectivity methods? (Choose two.)
- A. PPP
- B. WAP
- C. DSL
- D. L2TPv3
- E. Ethernet
Answer: AC
Explanation: On each WAN connection, data is encapsulated into frames before itcrosses the WAN link. The following are typical WAN protocols:1. High-level Data Link Control (HDLC): The Cisco default encapsulation type onpoint-to-point connections, dedicated links, and circuit- switches connections.2. PPP: Provides router-to-router and host-to-network connections over synchronous andasynchronous circuits. PPP was designed to work with several network layer protocols,including IP.3. Frame-relay: A successor to X.25. This protocol is an industry-standard, switchesdata-link layer protocol that handles multiple virtual circuits
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wide_area_network
NEW QUESTION 2
Refer to the exhibit.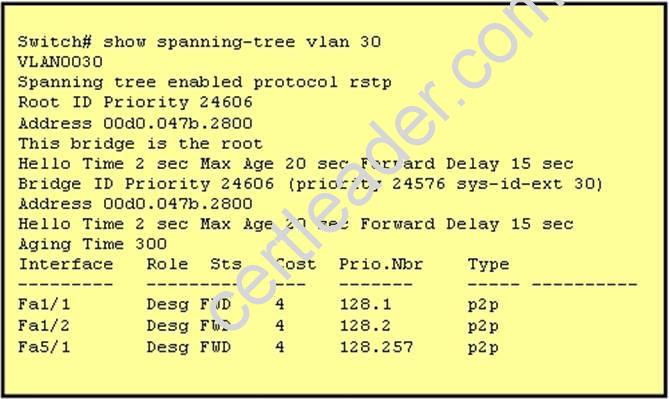
The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
- A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning, or forwarding.
- B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
- C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
- D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
- E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
- F. This switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Answer: ACE
Explanation: From the output, we see that all ports are in Designated role (forwarding state) -> A and E are correct.
The command “show spanning-tree vlan 30 only shows us information about VLAN 30. We don’t know how many VLAN exists in this switch -> B is not correct.
The bridge priority of this switch is 24606 which is lower than the default value bridge priority 32768 -> C is correct.
All three interfaces on this switch have the connection type “p2p”, which means Point-to-
point environment – not a shared media -> D is not correct.
The only thing we can specify is this switch is the root bridge for VLAN 3o but we can not guarantee it is also the root bridge for other VLANs -> F is not correct.
NEW QUESTION 3
What can be done to secure the virtual terminal interfaces on a router? (Choose two.)
- A. Administratively shut down the interface.
- B. Physically secure the interface.
- C. Create an access list and apply it to the virtual terminal interfaces with the access-group command.
- D. Configure a virtual terminal password and login process.
- E. Enter an access list and apply it to the virtual terminal interfaces using the access-class command.
Answer: DE
Explanation: It is a waste to administratively shut down the interface. Moreover, someone can still access the virtual terminal interfaces via other interfaces -> A is not correct.
We can not physically secure a virtual interface because it is “virtual” -> B is not correct. To apply an access list to a virtual terminal interface we must use the “access-class” command. The “access-group” command is only used to apply an access list to a physical interface -> C is not correct; E is correct.
The most simple way to secure the virtual terminal interface is to configure a username & password to prevent unauthorized login -> D is correct.
NEW QUESTION 4
CORRECT TEXT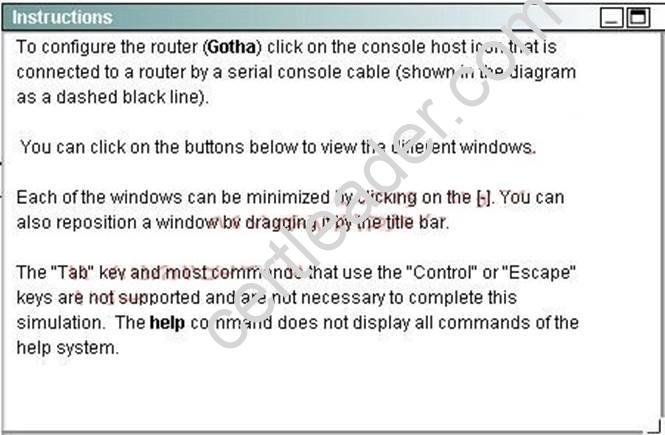
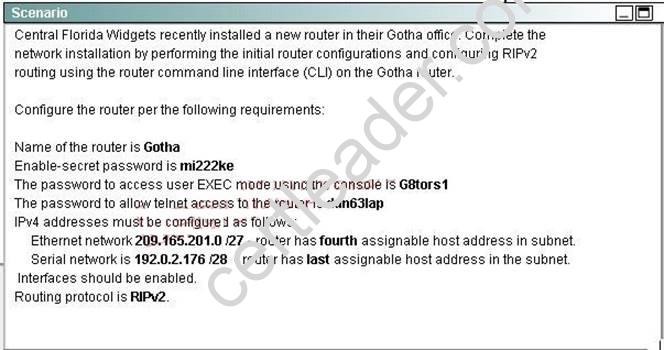
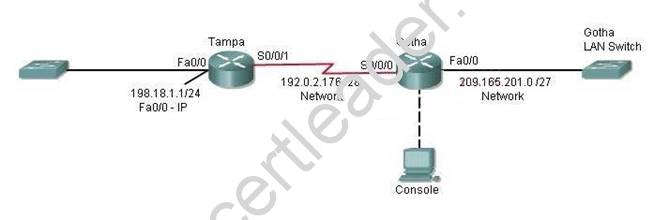
Attention:
In practical examinations, please note the following, the actual information will prevail.
1. Name of the router is xxx
2. Enable secret password is xxx
3. Password In access user EXEC mode using the console is xxx
4. The password to allow telnet access to the router is xxx
5. IP information
Answer:
Explanation: Router#config terminal
Router(config)#hostname Gotha
Gotha(config)#enable secret mi222ke
Gotha(config)#line console 0
Gotha(config-line)#password G8tors1
Gotha(config-line)#exit
Gotha(config)#line vty 0 4
Gotha(config-line)#password dun63lap
Gotha(config-line)#login
Gotha(config-line)#exit
Gotha(config)#interface fa0/0
Gotha(config-if)#no shutdown
Gotha(config-if)#ip address 209.165.201.4 255.255.255.224
Gotha(config)#interface s0/0/0
Gotha(config-if)#ip address 192.0.2.190 255.255.255.240
Gotha(config-if)#no shutdown
Gotha(config-if)#exit
Gotha(config)#router rip
Gotha(config-router)#version 2
Gotha(config-router)#network 209.165.201.0
Gotha(config-router)#network 192.0.2.176
Gotha(config-router)#end
Gotha#copy running-config startup-config
NEW QUESTION 5
What are three benefits of GLBP? (Choose three.)
- A. GLBP supports up to eight virtual forwarders per GLBP group.
- B. GLBP supports clear text and MD5 password authentication between GLBP group members.
- C. GLBP is an open source standardized protocol that can be used with multiple vendors.
- D. GLBP supports up to 1024 virtual routers.
- E. GLBP can load share traffic across a maximum of four routers.
- F. GLBP elects two AVGs and two standby AVGs for redundancy.
Answer: BDE
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2s/feature/guide/fs_glbp2.html
Load Sharing
You can configure GLBP in such a way that traffic from LAN clients can be shared by
multiple routers, thereby sharing the traffic load more equitably among available routers. Multiple Virtual Routers GLBP supports up to 1024 virtual routers (GLBP groups) on each physical interface of a router, and up to four virtual forwarders per group.
Preemption
The redundancy scheme of GLBP enables you to preempt an active virtual gateway with a higher priority backup virtual gateway that has become available. Forwarder preemption works in a similar way, except that forwarder preemption uses weighting instead of priority and is enabled by default.
Authentication
You can use a simple text password authentication scheme between GLBP group members to detect configuration errors. A router within a GLBP group with a different authentication string than other routers will be ignored by other group members.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx- s/unicast/configuration/guide/l3_glbp.html
GLBP Authentication
GLBP has three authentication types: MD5 authentication
Plain text authentication No authentication
MD5 authentication provides greater security than plain text authentication. MD5 authentication allows each GLBP group member to use a secret key to generate a keyed MD5 hash that is part of the outgoing packet. At the receiving end, a keyed hash of an incoming packet is generated. If the hash within the incoming packet does not match the generated hash, the packet is ignored. The key for the MD5 hash can either be given directly in the configuration using a key string or supplied indirectly through a key chain. You can also choose to use a simple password in plain text to authenticate GLBP packets, or choose no authentication for GLBP.
NEW QUESTION 6
What is the result of issuing the frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 broadcast command?
- A. defines the destination IP address that is used in all broadcast packets on DCLI 202
- B. defines the source IP address that is used in all broadcast packets on DCLI 202
- C. defines the DLCI on which packets from the 192.168.1.2 IP address are received
- D. defines the DLCI that is used for all packets that are sent to the 192.168.1.2 IP address
Answer: D
Explanation: Frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 command statically defines a mapping between a network layer address and a DLCI. The broadcast option allows multicast and broadcast packets to flow across the link.
The command frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 broadcast means to mapping the distal IP 192.168.1.2 202 to the local DLCI . When the “broadcast” keyword is included, it turns Frame Relay network as a broadcast network, which can forward broadcasts. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/wan/command/reference/wan_f2.html#wp1012264
NEW QUESTION 7
What OSPF command, when configured, will include all interfaces into area 0?
- A. network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
- B. network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
- C. network 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0 area 0
- D. network all-interfaces area 0
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 8
What does a router do if it has no EIGRP feasible successor route to a destination network and the successor route to that destination network is in active status?
- A. It routes all traffic that is addressed to the destination network to the interface indicated in the routing table.
- B. It sends a copy of its neighbor table to all adjacent routers.
- C. It sends a multicast query packet to all adjacent neighbors requesting available routing paths to the destination network.
- D. It broadcasts Hello packets to all routers in the network to re-establish neighbor adjacencies.
Answer: C
Explanation: Feasible Successors
A destination entry is moved from the topology table to the routing table when there is a feasible successor. All minimum cost paths to the destination form a set. From this set, the neighbors that have an advertised metric less than the current routing table metric are considered feasible successors.
Feasible successors are viewed by a router as neighbors that are downstream with respect to the destination.
These neighbors and the associated metrics are placed in the forwarding table.
When a neighbor changes the metric it has been advertising or a topology change occurs in the network, the set of feasible successors may have to be re-evaluated. However, this is not categorized as a route recomputation.
Route States
A topology table entry for a destination can have one of two states. A route is considered in the Passive state when a router is not performing a route recomputation. The route is in Active state when a router is undergoing a route recomputation. If there are always feasible successors, a route never has to go into Active state and avoids a route recomputation.
When there are no feasible successors, a route goes into Active state and a route recomputation occurs. A route recomputation commences with a router sending a query packet to all neighbors. Neighboring routers can either reply if they have feasible successors for the destination or optionally return a query indicating that they are performing a route recomputation. While in Active state, a router cannot change the next- hop neighbor it is using to forward packets. Once all replies are received for a given query, the destination can transition to Passive state and a new successor can be selected.
When a link to a neighbor that is the only feasible successor goes down, all routes through that neighbor commence a route recomputation and enter the Active state.
NEW QUESTION 9
DRAG DROP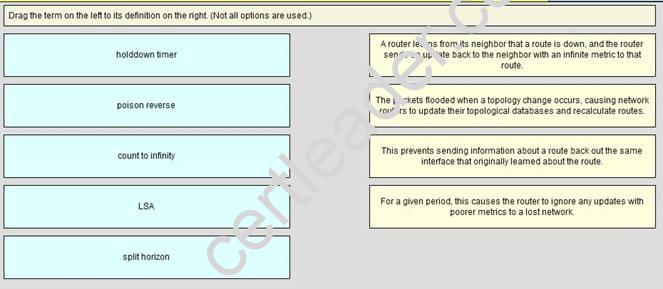
Answer:
Explanation: poison reverse: A router learns from its neighbor that a route is down and the router sends an update back to the neighbor with an infinite metric to that route
LSA: The packets flooded when a topology change occurs, causing network routers to update their topological databases and recalculate routes
split horizon: This prevents sending information about a routeback out the same interface that originally learned about the route
holddown timer: For a given period, this causes the router to ignore any updates with poorer metrics to a lost network
NEW QUESTION 10
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
- A. a backup route, stored in the routing table
- B. a primary route, stored in the routing table
- C. a backup route, stored in the topology table
- D. a primary route, stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml
Feasible Successors
A destination entry is moved from the topology table to the routing table when there is a feasible successor. All minimum cost paths to the destination form a set. From this set, the neighbors that have an advertised metric less than the current routing table metric are considered feasible successors.
Feasible successors are viewed by a router as neighbors that are downstream with respect to the destination.
These neighbors and the associated metrics are placed in the forwarding table.
When a neighbor changes the metric it has been advertising or a topology change occurs in the network, the set of feasible successors may have to be re-evaluated. However, this is not categorized as a route recomputation.
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance (AD) is less than the Feasible Distance (FD) of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but, stored in the topology table.
NEW QUESTION 11
What are two enhancements that OSPFv3 supports over OSPFv2? (Choose two.)
- A. It requires the use of ARP.
- B. It can support multiple IPv6 subnets on a single link.
- C. It supports up to 2 instances of OSPFv3 over a common link.
- D. It routes over links rather than over networks.
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 12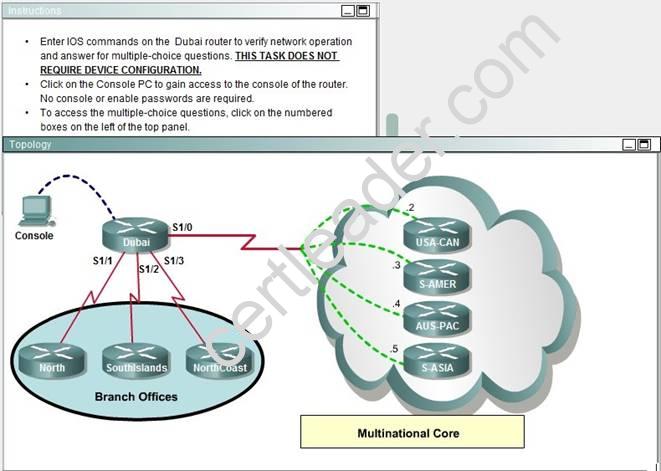


If required, what password should be configured on the DeepSouth router in the branch office to allow a connection to be established with the MidEast router?
- A. No password is required.
- B. Enable
- C. Secret
- D. Telnet
- E. Console
Answer: B
Explanation: In the diagram, DeepSouth is connected to Dubai’s S1/2 interface and is configured as follows:
Interface Serial1/2
IP address 192.168.0.5 255.255.255.252
Encapsulalation PPP ; Encapsulation for this interface is PPP Check out the following Cisco Link:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk713/tk507/technologies_configuration_example09186a 0080094333.shtml#configuringausernamedifferentfromtheroutersname
Here is a snipit of an example:
Network Diagram
If Router 1 initiates a call to Router 2, Router 2 would challenge Router 1, but Router 1 would not challenge Router 2. This occurs because theppp authentication chap callin command is configured on Router 1. This is an example of a unidirectional authentication. In this setup, theppp chap hostname alias-r1command is configured on Router 1. Router 1 uses "alias-r1" as its hostname for CHAP authentication instead of "r1." The Router 2 dialer map name should match Router 1's ppp chap hostname; otherwise, two B channels are established, one for each direction.
NEW QUESTION 13
CORRECT TEXT
Lab - Access List Simulation
A network associate is adding security to the configuration of the Corp1 router. The user on host C should be able to use a web browser to access financial information from the Finance Web Server. No other hosts from the LAN nor the Core should be able to use a web browser to access this server. Since there are multiple resources for the corporation at this location including other resources on the Finance Web Server, all other traffic should be allowed.
The task is to create and apply a numbered access-list with no more than three statements that will allow ONLY host C web access to the Finance Web Server. No other hosts will have web access to the Finance Web Server. All other traffic is permitted.
Access to the router CLI can be gained by clicking on the appropriate host. All passwords have been temporarily set to “cisco”.
The Core connection uses an IP address of 198.18.196.65
The computers in the Hosts LAN have been assigned addresses of 192.168.33.1 –92.168.33.254
Host A 192.168.33.1
Host B 192.168.33.2
Host C 192.168.33.3
Host D 192.168.33.4
The servers in the Server LAN have been assigned addresses of 172.22.242.17 – 172.22.242.30
The Finance Web Server is assigned an IP address of 172.22.242.23. The Public Web Server is assigned an IP address of 172.22.242.17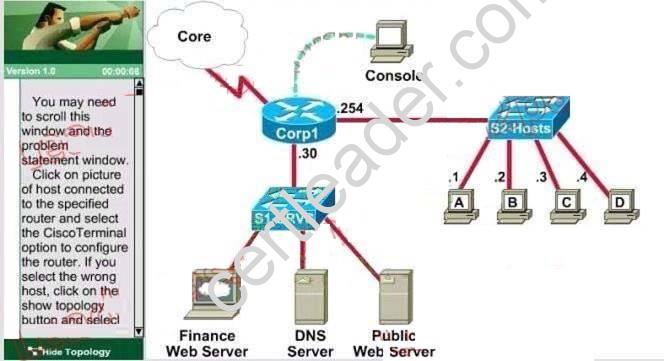
Answer:
Explanation: Our access-list needs to allow host C – 192.168.33.3 to the Finance Web Server 172.22.242.23 via web (port80)
Corp1(config)#access-list 100 permit tcp host 192.168.33.3 host 172.22.242.23 eq 80
Deny other hosts access to the Finance Web Server via web
Corp1(config)#access-list 100 deny tcp any host 172.22.242.23 eq 80
All other traffic is permitted
Corp1(config)#access-list 100 permit ip any any
Apply this access-list to Fa0/1 interface (outbound direction)
Corp1(config)#interface fa0/1
Corp1(config-if)#ip access-group 100 out Explanation :
Select the console on Corp1 router Configuring ACL
Corp1>enable Corp1#configure terminal
Comment: To permit only Host C (192. 168. 33. 3){source addr} to access finance server address (172.
22.242. 23){destination addr} on port number 80 (web) Corp1(config)# access-list 100 permit tcp host 192.168.33.3 host 172.22.242.23 eq 80
Comment: To deny any source to access finance server address (172. 22. 242. 23)
{destination addr} on port number 80 (web)
Corp1(config)# access-list 100 deny tcp any host 172.22.242.23 eq 80
Comment: To permit ip protocol from any source to access any destination because of the implicit deny any any statement at the end of ACL.
Corp1(config)# access-list 100 permit ip any any Applying the ACL on the Interface
Comment: Check show ip interface brief command to identify the interface type and number by checking the IP address configured.
Corp1(config)#interface fa 0/1
If the ip address configured already is incorrect as well as the subnet mask. this should be corrected in order ACL to work type this commands at interface mode :
no ip address 192. x. x. x 255. x. x. x (removes incorrect configured ip address and subnet mask) Configure
Correct IP Address and subnet mask :
ip address 172. 22. 242. 30 255. 255. 255. 240 ( range of address specified going to server is given as 172.
22. 242. 17 172. 22. 242. 30 )
Comment: Place the ACL to check for packets going outside the interface towards the finance web server.
Corp1(config-if)#ip access-group 100 out Corp1(config-if)#end
Important: To save your running config to startup before exit. Corp1#copy running-config startup-config
Verifying the Configuration :
Step1: Show ip interface brief command identifies the interface on which to apply access list . Step2: Click on each host A, B, C & D . Host opens a web browser page , Select address box of the web browser and type the ip address of finance web server(172. 22. 242. 23) to test whether it permits /deny access to the finance web Server.
NEW QUESTION 14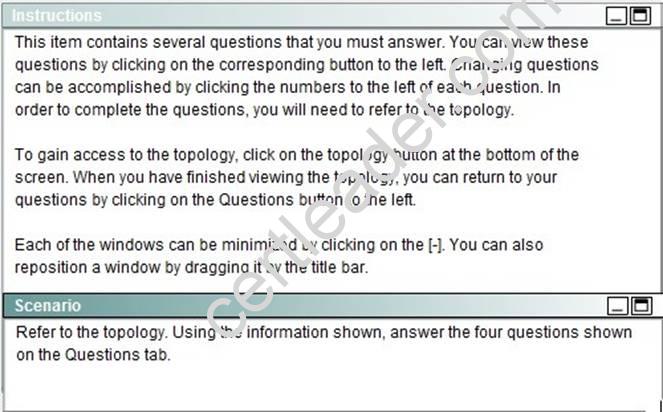
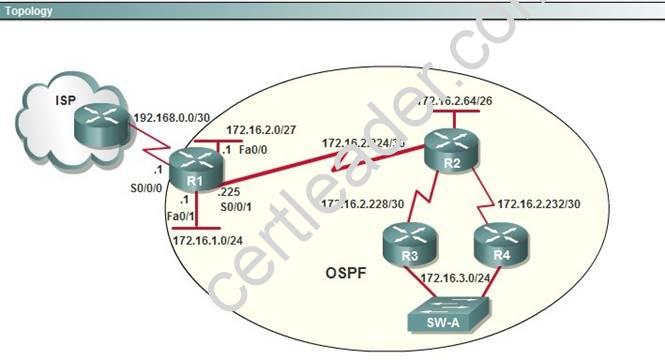
OSPF is configured using default classful addressing. With all routers and interfaces operational, how many networks will be in the routing table of R1 that are indicated to be learned by OSPF?
- A. 2
- B. 3
- C. 4
- D. 5
- E. 6
- F. 7
Answer: C
Explanation: It already knows about its directly connected ones, only those not directly connected are “Learned by OSPF”.
OSPF as a link state routing protocol (deals with LSAs rather than routes) does not auto summarize (doesn't support "auto-summary").So learned route by OSPF are followed 172.16.2.64/26
172.16.2.228/30
172.16.2.232/30
172.16.3.0/24
Topic 5, WAN Technologies
NEW QUESTION 15
Which statement is true, as relates to classful or classless routing?
- A. Classful routing protocols send the subnet mask in routing updates.
- B. RIPv1 and OSPF are classless routing protocols.
- C. Automatic summarization at classful boundaries can cause problems on discontiguous subnets.
- D. EIGRP and OSPF are classful routing protocols and summarize routes by default.
Answer: C
Explanation: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=174107&seqNum=3
RIPv1, RIPv2, IGRP, and EIGRP all auto-summarize classful boundaries by default (OSPF does not).To make discontiguous networks work, meaning you don't want classful boundries to summarize, you need to turn off auto-summary.
NEW QUESTION 16
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency.
The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
- A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
- B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
- C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
- D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation: Implementing EIGRP
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1171169&seqNum=3
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 0 10.10.10.2 Fa0/0 12 00:00:39 1282 5000 0 3
NEW QUESTION 17
In GLBP, which router will respond to client ARP requests?
- A. The active virtual gateway will reply with one of four possible virtual MAC addresses.
- B. All GLBP member routers will reply in round-robin fashion.
- C. The active virtual gateway will reply with its own hardware MAC address.
- D. The GLBP member routers will reply with one of four possible burned in hardware addresses.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 18
Refer to the exhibit.
Which three EIGRP routes will be present in the router R4's routing table? (Choose three.)
- A. 172.16.1.0/24
- B. 10.1.10.0/30
- C. 10.0.0.0/8
- D. 10.1.11.0/30
- E. 172.16.0.0/16
- F. 192.168.1.0/24
Answer: CEF
NEW QUESTION 19
Which feature does PPP use to encapsulate multiple protocols?
- A. NCP
- B. LCP
- C. IPCP
- D. IPXP
Answer: A
Explanation: Network Core Protocol (NCP) is the component that encapsulates and configures multiple network layer protocols.
Thanks for reading the newest 200-101 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Certifytools 200-101 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.certifytools.com/200-101-exam.html (149 Q&As Dumps)