We offers . "TS: Windows Server 2008 Active Directory. Configuring", also known as 70-640 exam, is a Microsoft Certification. This set of posts, Passing the 70-640 exam with , will help you answer those questions. The covers all the knowledge points of the real exam. 100% real and revised by experts!
Check 70-640 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains a single domain and 10 domain controllers. All of the domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1).
The forest contains an application directory partition named dc=app1, dc=contoso,dc=com. A domain controller named DC1 has a copy of the application directory partition.
You need to configure a domain controller named DC2 to receive a copy of dc=app1, dc=contoso,dc=corn.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Active Directory Sites and Services
- B. Dsmod
- C. Dcpromo
- D. Dsmgmt
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732887.aspx
Dcpromo
Installs and removes Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS).
Parameter
ApplicationPartitionsToReplicate:""
Specifies the application directory partitions that dcpromo will replicate. Use the following format:
"partition1" "partition2" "partitionN"
Use * to replicate all application directory partitions.
Original explanation:
Please Check Answer
I don't think this is Dsmod. It is most likely Dcpromo.
Dsmod -- Modifies an existing object of a specific type in the directory.
NEW QUESTION 2
Your network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. Server1 is configured as an Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) 2.0 standalone server.
You plan to add a new token-signing certificate to Server1.
You import the certificate to the server as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 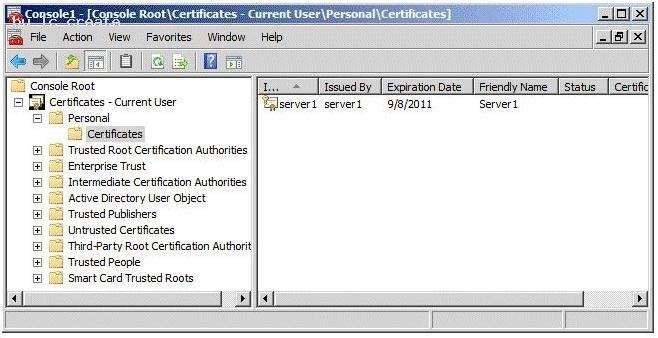
When you run the Add Token-Signing Certificate wizard, you discover that the new certificate is unavailable.
You need to ensure that you can use the new certificate for AD FS.
What should you do?
- A. From the properties of the certificate, modify the Certificate Policy OIDs settin
- B. Import the certificate to the AD FS 2.0 Windows Service personal certificate stor
- C. From the properties of the certificate, modify the Certificate purposes settin
- D. Import the certificate to the local computer personal certificate stor
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh341466.aspx
When you deploy the first federation server in a new AD FS 2.0 installation, you must obtain a token-signing certificate and install it in the local computer personal certificate store on that federation server.
NEW QUESTION 3
Your network contains an enterprise certification authority (CA) that runs Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise.
You need to ensure that users can enroll for certificates that use the IPSEC (Offline request) certificate template
Which snap-in should you use?
- A. Enterprise PKI
- B. TPM Management
- C. Certificates
- D. Active Directory Users and Computers
- E. Authorization Manager
- F. Certification Authority
- G. Group Policy Management
- H. Security Templates
- I. Certificate Templates
Answer: I
Explanation:
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en/winserversecurity/thread/962be5d1-d824-4dd8-a501-3c3a9d600083
The user should have proper permission on Certificate Templates. Please follow the steps below for troubleshooting:
1. Open MMC, add Certificate Templates snap-in.
2. Double-click IPSec (Offline Request), switch to Security tab, give the user Read and Enroll rights.
3. Close and restart IE on clients computer to test.
NEW QUESTION 4
Enable the OCSP Response Signing certificate template for the CA.
4.Your company has an Active Directory domain that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. The Sales OU contains an OU for Computers, an OU for Groups, and an OU for Users.
You perform nightly backups. An administrator deletes the Groups OU.
You need to restore the Groups OU without affecting users and computers in the Sales OU.
What should you do?
- A. Perform an authoritative restore of the Sales O
- B. Perform a non-authoritative restore of the Sales O
- C. Perform an authoritative restore of the Groups O
- D. Perform a non-authoritative restore of the Groups O
Answer: C
Explanation:
Answer: Move the ntds.dit file to the new volume by using the Files option in the Ntdsutil utility.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc816720%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Move the Directory Database and Log Files to a Local Drive You can use this procedure to move Active Directory database and log files to a local drive. When you move the files to a folder on the local domain controller, you can move them permanently or temporarily. Move the files to a temporary destination if you need to reformat the original location, or move the files to a permanent location if you have additional disk space. If you reformat the original drive, use the same procedure to move the files back after the reformat is complete. Ntdsutil.exe updates the registry when you move files locally. Even if you are moving the files only temporarily, use Ntdsutil.exe so that the registry is always current. On a domain controller that is running Windows Server 2008, you do not have to restart the domain controller in Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) to move database files. You can stop the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) service and then restart the service after you move the files to their permanent location. To move the directory database and log files to a local drive:
NEW QUESTION 5
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two sites named Seattle and Montreal. The Seattle site contains two domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table. 
The Montreal site contains a domain controller named DC3. DC3 is the only global catalog server in the forest.
You need to configure DC2 as a global catalog server.
Which object's properties should you modify? To answer, select the appropriate object in the answer area. 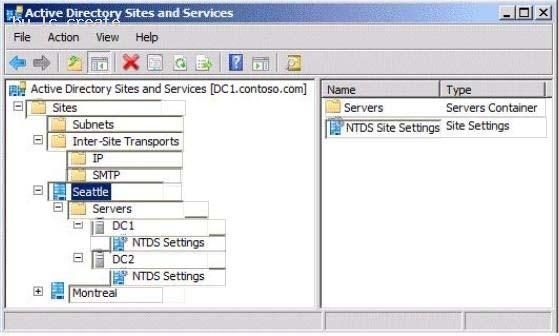
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 6
Your company has an Active Directory domain. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2. Your company uses an Enterprise Root certification authority (CA) and an Enterprise Intermediate CA.
The Enterprise Intermediate CA certificate expires.
You need to deploy a new Enterprise Intermediate CA certificate to all computers in the domain.
What should you do?
- A. Import the new certificate into the Intermediate Certification Store on the Enterprise Root CA serve
- B. Import the new certificate into the Intermediate Certification Store on the Enterprise Intermediate CA serve
- C. Import the new certificate into the Intermediate Certification Store in the Default Domain Controllers group policy objec
- D. Import the new certificate into the Intermediate Certification Store in the Default Domain group policy objec
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc962065.aspx
Certification Authority Trust Model Certification Authority Hierarchies The Windows 2000 public key infrastructure supports a hierarchical CA trust model, called the certification hierarchy, to provide scalability, ease of administration, and compatibility with a growing number of commercial third-party CA services and public key-aware products. In its simplest form, a certification hierarchy consists of a single CA. However, the hierarchy usually contains multiple CAs that have clearly defined parent-child relationships. Figure 16.5 shows some possible CA hierarchies. 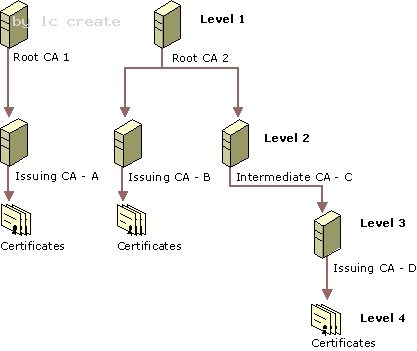
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
You can deploy multiple CA hierarchies to meet your needs. The CA at the top of the hierarchy is called a root CA . Root CAs are self-certified by using a self-signed CA certificate. Root CAs are the most trusted CAs in the organization and it is recommended that they have the highest security of all. There is no requirement that all CAs in an enterprise share a common top-level CA parent or root. Although trust for CAs depends on each domain's CA trust policy, each CA in the hierarchy can be in a different domain. Child CAs are called subordinate CAs. Subordinate CAs are certified by the parent CAs. A parent CA certifies the subordinate CA by issuing and signing the subordinate CA certificate. A subordinate CA can be either an intermediate or an issuing CA. An intermediate CA issues certificates only to subordinate CAs. An issuing CA issues certificates to users, computers, or services.
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/winserversecurity/thread/605dbf9d-2694-4783-8002-c08b9c7d4149
NEW QUESTION 7
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains several domain controllers.
You need to modify the Password Replication Policy on a read-only domain controller (RODC).
Which tool should you use?
- A. Group Policy Management
- B. Active Directory Domains and Trusts
- C. Active Directory Users and Computers
- D. Computer Management
- E. Security Configuration Wizard
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/rodc-guidance-for-administering-the-password-
replication-policy.aspx
Administering the Password Replication Policy
This topic describes the steps for viewing, configuring, and monitoring the Password Replication Policy (PRP) and password caching for read-only domain controllers (RODCs). To configure the PRP using Active Directory Users and Computers
1. Open Active Directory Users and Computers as a member of the Domain Admins group.
2. Ensure that you are connected to a writeable domain controller running Windows Server 2008 in the correct domain.
3. Click Domain Controllers, and in the details pane, right-click the RODC computer account, and then click Properties.
4. Click the Password Replication Policy tab.
5. The Password Replication Policy tab lists the accounts that, by default, are defined in the Allowed list and the Deny list on the RODC. To add other groups that should be included in either the Allowed list or the Deny list, click Add.
To add other accounts that will have credentials cached on the RODC, click Allow passwords for the account to replicate to this RODC.
To add other accounts that are not allowed to have credentials cached on the RODC, click Deny passwords for the account from replicating to this RODC.
NEW QUESTION 8
One of the remote branch offices is running a Windows Server 2008 read only domain controller (RODC). For security reasons you don't want some critical credentials like (passwords, encryption keys) to be stored on RODC.
What should you do so that these credentials are not replicated to any RODC's in the forest? (Select 2)
- A. Configure RODC filtered attribute set on the server
- B. Configure RODC filtered set on the server that holds Schema Operations Master rol
- C. Delegate local administrative permissions for an RODC to any domain user without granting that user any user rights for the domain
- D. Configure forest functional level server for Windows server 2008 to configure filtered attribute se
- E. None of the above
Answer: BD
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc753223.aspx Adding attributes to the RODC filtered attribute set The RODC filtered attribute set is a dynamic set of attributes that is not replicated to any RODCs in the forest. You can configure the RODC filtered attribute set on a schema master that runs Windows Server 2008. When the attributes are prevented from replicating to RODCs, that data cannot be exposed unnecessarily if an RODC is stolen or compromised. A malicious user who compromises an RODC can attempt to configure it in such a way that it tries to replicate attributes that are defined in the RODC filtered attribute set. If the RODC tries to replicate those attributes from a domain controller that is running Windows Server 2008, the replication request is denied. However, if the RODC tries to replicate those attributes from a domain controller that is running Windows Server 2003, the replication request could succeed. Therefore, as a security precaution, ensure that forest functional level is Windows Server 2008 if you plan to configure the RODC filtered attribute set. When the forest functional level is Windows Server 2008, an RODC that is compromised cannot be exploited in this manner because domain controllers that are running Windows Server 2003 are not allowed in the forest.
NEW QUESTION 9
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You need to ensure that when computers are joined manually to the domain by using the System Properties, the computer account of the computers is created automatically in an organizational unit (OU) named NewComputers.
Which command should you run?
- A. dsmgmt.exe
- B. redircmp.exe
- C. csvde.exe
- D. computerdefaults.exe
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 10
Your network contains an Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) cluster.
You have several custom policy templates. The custom policy templates are updated
frequently.
Some users report that it takes as many as 30 days to receive the updated policy
templates.
You need to ensure that users receive the updated custom policy templates within seven
days.
What should you do?
- A. Modify the registry on the AD RMS server
- B. Modify the registry on the users' computer
- C. Change the schedule of the AD RMS Rights Policy Template Management (Manual) scheduled tas
- D. Change the schedule of the AD RMS Rights Policy Template Management (Automated) scheduled tas
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771971.aspx
Configuring the AD RMS client
The automated scheduled task will not query the AD RMS template distribution pipeline each time that this scheduled task runs. Instead, it checks updateFrequency DWORD value registry entry. This registry entry specifies the time interval (in days) after which the client should update its rights policy templates. By default the registry key is not present on the client computer. In this scenario, the client checks for new, deleted, or modified rights policy templates every 30 days. To configure an interval other than 30 days, create a registry entry at the following location: HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftMSDRM
TemplateManagement. In this registry key, you can also configure the updateIfLastUpdatedBeforeTime, which forces the client computer to update its rights policy templates.
NEW QUESTION 11
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named fabrikam.com. The forest contains the following domains:
. Fabrikam.com
Eu.fabrikam.com
Na.fabrikam.com
Eu.contoso.com
Na.contoso.com
You need to configure the forest to ensure that the administrators of any of the domains can specify a user principal name (UPN) suffix o contoso.com when they create user accounts from Active Directory Users and Computers.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Active Directory Users and Computers
- B. Active Directory Administrative Center
- C. Active Directory Domains and Trusts
- D. Set-ADAccountControl
Answer: C
Explanation: To add UPN suffixes
1. Open Active Directory Domains and Trusts. To open Active Directory Domains and Trusts, click Start , click Administrative Tools , and then click Active Directory Domains and Trusts .
2. In the console tree, right-click Active Directory Domains and Trusts , and then click Properties .
3. On the UPN Suffixes tab, type an alternative UPN suffix for the forest, and then click Add .
NEW QUESTION 12
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two member servers named Server1 and Server2. Server1 and Server2 have the DNS Server server role installed.
Server1 hosts a standard primary zone for contoso.com. Server2 is configured as a secondary name server for contoso.com.
You experience issues with the copy of the zone on Server2,
You verify that both copies of the zone have the same serial number.
You need to transfer a complete copy of the zone from Server1 to Server2.
What should you do on Server2?
- A. From DNS Manager, right-click contoso.com and click Transfer from Maste
- B. From Services, right-click DNS Server and click Refres
- C. From Services, right-click DNS Server and click Restar
- D. From DNS Manager, right-click contoso.com and click Reloa
- E. From DNS Manager, right-click contoso.com and click Transfer a new copy of zone from Maste
Answer: E
Explanation:
MS Press - Self-Paced Training Kit (Exam 70-642) (2nd Edition, 2011) page 212
Manually Updating a Secondary Zone
By right-clicking a secondary zone in the DNS Manager console tree, you can use the shortcut menu to perform the following secondary zone update operations:
Reload - This operation reloads the secondary zone from the local storage.
Transfer From Master - The server hosting the local secondary zone determines whether the serial number in the secondary zone’s SOA resource record has expired and then pulls a zone transfer from the master server. Transfer New Copy Of Zone From Master - This operation performs a zone transfer from the secondary zone’s master server regardless of the serial number in the secondary zone’s SOA resource record.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your company has an Active Directory domain. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2.
Your company uses an Enterprise Root certificate authority (CA).
You need to ensure that revoked certificate information is highly available.
What should you do?
- A. Implement an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responder by using an Internet Security and Acceleration Server arra
- B. Publish the trusted certificate authorities list to the domain by using a Group Policy Object (GPO).
- C. Implement an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responder by using Network Load Balancin
- D. Create a new Group Policy Object (GPO) that allows users to trust peer certificate
- E. Link the GPO to the domai
Answer: C
Explanation:
Answer: Implement an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responder by using Network Load Balancing.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731027%28v=ws.10%29.aspx AD CS: Online Certificate Status Protocol Support Certificate revocation is a necessary part of the process of managing certificates issued by certification authorities (CAs). The most common means of communicating certificate status is by distributing certificate revocation lists (CRLs). In the Windows Server. 2008 operating system, public key infrastructures (PKIs) where the use of conventional CRLs is not an optimal solution, an Online Responder based on the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) can be used to manage and distribute revocation status information. What does OCSP support do? The use of Online Responders that distribute OCSP responses, along with the use of CRLs, is one of two common methods for conveying information about the validity of certificates. Unlike CRLs, which are distributed periodically and contain information about all certificates that have been revoked or suspended, an Online Responder receives and responds only to requests from clients for information about the status of a single certificate. The amount of data retrieved per request remains constant no matter how many revoked certificates there might be. In many circumstances, Online Responders can process certificate status requests more efficiently than by using CRLs.
Adding one or more Online Responders can significantly enhance the flexibility and scalability of an organization's PKI.
Further information: http://blogs.technet.com/b/askds/archive/2009/08/20/implementing-an-ocsp-responder-part-v-highavailability.aspx Implementing an OCSP Responder: Part V High Availability There are two major pieces in implementing the High Availability Configuration. The first step is to add the OCSP Responders to what is called an Array. When OCSP Responders are configured in an Array, the configuration of the OCSP responders can be easily maintained, so that all Responders in the Array have the same configuration. The configuration of the Array Controller is used as the baseline configuration that is then applied to other members of the Array. The second piece is to load balance the OCSP Responders. Load balancing of the OCSP responders is what actually provides fault tolerance.
NEW QUESTION 14
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains a server named Server1.Server1 runs Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to mount an Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) snapshot from Server1.
What should you do?
- A. Run ldp.exe and use the Bind optio
- B. Run diskpart.exe and use the Attach optio
- C. Run dsdbutil.exe and use the snapshot optio
- D. Run imagex.exe and specify the /mount paramete
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc753151%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Dsdbutil Performs database maintenance of the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) store, facilitates configuration of Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) communication ports, and views AD LDS instances that are installed on a computer. Commands snapshot Manages snapshots. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731620%28v=ws.10%29.aspx snapshot Manages snapshots of the volumes that contain the Active Directory database and log files, which you can view on a domain controller without starting in Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM). You can also run the snapshot subcommand on an Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) server. This is a subcommand of Ntdsutil and Dsdbutil. Ntdsutil and Dsdbutil are command-line tools that are built into Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. Syntax activate instance %s [create] [delete %s] [unmount %s] [list all] [list mounted ] [mount %s] [quit] Parameters Mount %s Mounts a snapshot with GUID %s. You can refer to an index number of any mounted snapshot instead of its GUID.
NEW QUESTION 15
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. All servers run
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise. All client computers run Windows 7 Professional.
The network contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You need to approve a pending certificate request.
Which snap-in should you use?
- A. Active Directory Administrative Center
- B. Authorization Manager
- C. Certificate Templates
- D. Certificates
- E. Certification Authority
- F. Enterprise PKI
- G. Group Policy Management
- H. Security Configuration Wizard
- I. Share and Storage Management
Answer: E
Explanation:
Explanation 1: http://technet.microsoft.com/de-de/library/ff849263.aspx To issue a pending certificate request:
1. Log on to your root CA by using an account that is a certificate manager.
2. Start the Certification Authority snap-in.
3. In the console tree, expand your root CA, and click Pending Certificates.
4. In the details pane, right-click the pending CA certificate, and click Issue.
NEW QUESTION 16
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008. The functional level of the domain is Windows Server 2003. All client computers run Windows 7.
You install Windows Server 2008 R2 on a server named Server1.
You need to perform an offline domain join of Server1.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- A. From Server1, run djoin.ex
- B. From Server1, run netdom.ex
- C. From a Windows 7 computer, run djoin.ex
- D. Upgrade one domain controller to Windows Server 2008 R2.
- E. Raise the functional level of the domain to Windows Server 2008.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
MS Press - Self-Paced Training Kit (Exam 70-640) (2nd Edition, July 2012) pages 217, 218
Offline Domain Join
Offline domain join is also useful when a computer is deployed in a lab or other disconnected environment.
When the computer is connected to the domain network and started for the first time, it will already be a member of the domain. This also helps to ensure that Group Policy settings are applied at the first startup.
Four major steps are required to join a computer to the domain by using offline domain join:
1. Log on to a computer in the domain that is running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows 7 with an account that has permissions to join computers to the domain.
2. Use the DJoin command to provision a computer for offline domain join. This step prepopulates Active Directory with the information that Active Directory needs to join the computer to the domain, and exports the information called a blob to a text file.
3. At the offline computer that you want to join the domain use DJoin to import the blob into the Windows directory.
4. When you start or restart the computer, it will be a member of the domain.
NEW QUESTION 17
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a domain controller named DC1. DC1 has the DNS Server server role installed and hosts an Active Directory-integrated zone for contoso.com. The no-refresh interval is set to three days and the refresh interval is set to 10 days.
The Advanced DNS settings of DC1 are shown in the Advanced DNS Settings exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 
You open the properties of a static record named Server1 as shown in the Server1 Record exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 
You discover that the scavenging process ran today, but the record for Server1 was not deleted.
You run dnscmd.exe and specify the ageallrecords parameter.
You need to identify when the record for Server1 will be deleted from the zone.
In how many days will the record be deleted?
- A. 7
- B. 10
- C. 17
- D. 20
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 18
You have an existing Active Directory site named Site1. You create a new Active Directory site and name it Site2.
You need to configure Active Directory replication between Site1 and Site2. You install a new domain controller.
You create the site link between Site1 and Site2.
What should you do next?
- A. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to assign a new IP subnet to Site2. Move the new domain controller object to Site2.
- B. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to configure a new site link bridge objec
- C. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to decrease the site link cost between Site1 and Site2.
- D. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to configure the new domain controller as a preferred bridgehead server for Site1.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsysm/article.php/624411/Intersite-eplication.htm Inter-site Replication The process of creating a custom site link has five basic steps:
1. Create the site link.
2. Configure the site link's associated attributes.
3. Create site link bridges.
4. Configure connection objects. (This step is optional.)
5. Designate a preferred bridgehead server. (This step is optional)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc759160%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Replication between sites
Thanks for reading the newest 70-640 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM 2passeasy 70-640 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/70-640/ (631 Q&As Dumps)