We provide which are the best for clearing 70-640 test, and to get certified by Microsoft TS: Windows Server 2008 Active Directory. Configuring. The covers all the knowledge points of the real 70-640 exam. Crack your Microsoft 70-640 Exam with latest dumps, guaranteed!
Microsoft 70-640 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two domains. All domain controllers are configured as global catalog servers.
The forest root domain contains five domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table. 
You plan to create a custom attribute in Active Directory that will replicate to all of the global catalog servers.
You need to identify which domain controller must be online to perform the planned action.
Which domain controller should you identify?
- A. DC1
- B. DC2
- C. DC3
- D. DC4
- E. DC5
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 2
Your company has an Active Directory forest.
You plan to install an Enterprise certification authority (CA) on a dedicated stand-alone server.
When you attempt to add the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) role, you find that the Enterprise CA option is not available.
You need to install the AD CS role as an Enterprise CA.
What should you do first?
- A. Add the DNS Server rol
- B. Add the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS) rol
- C. Add the Web server (IIS) role and the AD CS rol
- D. Join the server to the domai
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772393%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Active Directory Certificate Services Step-by-Step Guide
http://kazmierczak.eu/itblog/2012/09/23/enterprise-ca-option-is-greyed-out-unavailable/
Enterprise CA option is greyed out / unavailable Many times, administrators ask me what to do when installing Active Directory Certificate Services they cannot choose to install Enterprise Certification Authority, because it’s unavailable as in following picture: 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Well, you need to fulfill basic requirements: Server machine has to be a member server (domain joined). You can run an Enterprise CA on the Standard, Enterprise, or Data Center Windows Edition. The difference is the number of ADCS features and components that can be enabled. To get full functionality, you need to run on Enterprise or Data Center Windows Server 2008 /R2/ Editions. It includes functionality like Role separation, Certificate manager restrictions, Delegated enrollment agent restrictions, Certificate enrollment across forests, Online Responder, Network Device Enrollment. In order to install an Enterprise CA, you must be a member of either Enterprise Admins or Domain Admins in the forest root domain (either directly or through a group nesting). If issue still persists, there is probably a problem with getting correct credentials of your account. There are many thing that can cause it (network blockage, domain settings, server configuration, and other issues). In all cases I got, this troubleshooting helped perfectly: First of all, carefully check all above requirements. Secondly, install all available patches and Service Packs with Windows Update before trying to install Enterprise CA. Check network settings on the CA Server. If there is no DNS setting, Certificate Authority Server cannot resolve and find domain. Sufficient privileges for writing the Enterprise CA configuration information in AD configuration partition are required. Determine if you are a member of the Enterprise Admins or Domain Admins in the forest root domain. Think about the account you are currently trying to install ADCS with. In fact, you may be sure, that your account is in Enterprise Admins group, but check this how CA Server “sees” your account membership by typing whoami /groups. You also need to be a member of local Administrators group. If you are not, you wouldn’t be able to run Server Manager, but still needs to be checked. View C:windowscertocm.log file. There you can find helpful details on problems with group membership. For example status of ENUM_ENTERPRISE_UNAVAIL_REASON_NO_INSTALL_RIGHTS indicates that needed memberships are not correct. Don’t forget to check event viewer on CA Server side and look for red lines. Verify that network devices or software&hardware firewalls are not blocking access from/to server and Domain Controllers. If so, Certificate Authority Server may not be communicating correctly with the domain. To check that, simply run nltest /sc_verify:DomainName Check also whether Server CA is connected to a writable Domain Controller. Enterprise Admins groups is the most powerful group and has ADCS required full control permissions, but who knows – maybe someone changed default permissions? Run adsiedit.msc on Domain Controller, connect to default context and first of all check if CN=Public Key Service,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=Your,DC=Domain,DC=Com container does exist. If so, check permissions for all subcontainers under Public Key Service if Enterprise Admins group has full control permissions. The main subcontainers to verify are Certificate Templates, OID, KRA containers. If no above tips help, disjoin the server from domain and join again. Ultimately reinstall operation system on CA Server.
NEW QUESTION 3
Your company has a main office and a branch office.
The network contains a single Active Directory domain.
The main office contains a domain controller named DC1.
You need to install a domain controller in the branch office by using an offline copy of the Active Directory database.
What should you do first?
- A. From the Ntdsutil tool, create an IFM media se
- B. From the command prompt, run djoin.exe /loadfil
- C. From Windows Server Backup, perform a system state backu
- D. From Windows PowerShell, run the get-ADDomainController cmdle
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc816722%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Installing an Additional Domain Controller by Using IFM When you install Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) by using the install from media (IFM) method, you can reduce the replication traffic that is initiated during the installation of an additional domain controller in an Active Directory domain. Reducing the replication traffic reduces the time that is necessary to install the additional domain controller. Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 include an improved version of the Ntdsutil tool that you can use to create installation media for an additional domain controller. You can use Ntdsutil.exe to create installation media for additional domain controllers that you are creating in a domain. The IFM method uses the data in the installation media to install AD DS, which eliminates the need to replicate every object from a partner domain controller. However, objects that were modified, added, or deleted since the installation media was created must be replicated. If the installation media was created recently, the amount of replication that is required is considerably less than the amount of replication that is required for a regular AD DS installation.
NEW QUESTION 4
You have a DNS zone that is stored in a custom application directory partition. You install a new domain controller.
You need to ensure that the custom application directory partition replicates to the new domain controller.
What should you use?
- A. the Active Directory Administrative Center console
- B. the Active Directory Sites and Services console
- C. the DNS Manager console
- D. the Dnscmd tool
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772069.aspx
dnscmd /enlistdirectorypartition Adds the DNS server to the specified directory partition's replica set.
NEW QUESTION 5
You are the network administrator for an organization that has all Windows Server 2008 R2 domain controllers.
You need to capture all replication errors that occur between all domain controllers.
What should you do?
- A. Use System Performance data collector set
- B. Use ntdsuti
- C. Configure event log subscription
- D. Use the ADSI Edit too
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc748890.aspx Configure Computers to Forward and Collect Events Before you can create a subscription to collect events on a computer, you must configure both the collecting computer (collector) and each computer from which events will be collected (source).
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc749183.aspx Event Subscriptions Event Viewer enables you to view events on a single remote computer. However, troubleshooting an issue might require you to examine a set of events stored in multiple logs on multiple computers. Windows Vista includes the ability to collect copies of events from multiple remote computers and store them locally. To specify which events to collect, you create an event subscription. Among other details, the subscription specifies exactly which events will be collected and in which log they will be stored locally. Once a subscription is active and events are being collected, you can view and manipulate these forwarded events as you would any other locally stored events. Using the event collecting feature requires that you configure both the forwarding and the collecting computers. The functionality depends on the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service and the Windows Event Collector (Wecsvc) service. Both of these services must be running on computers participating in the forwarding and collecting process. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc961808.aspx
NEW QUESTION 6
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. All domain controller run Windows Server 2003.
You replace all domain controllers with domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2. You raise the functional level of the domain to Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to minimize the amount of SYSVOL replication traffic on the network.
What should you do?
- A. Raise the functional level of the forest to Windows Server 2008 R2.
- B. Modify the path of the SYSVOL folder on all of the domain controller
- C. On a global catalog server, run repadmin.exe and specify the KCC paramete
- D. On the domain controller that holds the primary domain controller (PDC) emulator FSMO role, run dfsrmig.ex
Answer: D
Explanation:
Now that the domain controllers have been upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2 and the domain functional level has been upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2 we can use DFS Replication for replicating SYSVOL, instead of File Replication Service (FRS) of previous Windows Server versions. The migration takes place on a domain controller holding the PDC Emulator role.
Explanation 1: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794837.aspx Using DFS Replication for replicating SYSVOL in Windows Server 2008 DFS Replication technology significantly improves replication of SYSVOL. In Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003, and Windows Server 2003 R2, FRS is used to replicate the contents of the SYSVOL share.
When a change to a file occurs, FRS replicates the entire updated file. With DFS Replication, for files larger than 64 KB, only the updated portion of the file is replicated.
Explanation 2:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd639809.aspx
Migrating to the Prepared State
The following sections provide an overview of the procedures that you perform when you
migrate SYSVOL replication from File Replication Service (FRS) to Distributed File System
(DFS Replication).
This migration phase includes the tasks in the following list.
Running the dfsrmig /SetGlobalState 1 command on the PDC emulator to start the
migration to the Prepared state.
NEW QUESTION 7
You have a domain controller named DC1 that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. DC1 is configured as a DNS server for contoso.com.
You install the DNS server server role on a member server named server1 and then you create a standard secondary zone for contoso.com. You configure DC1 as the master server for the zone.
You need to ensure that Server1 receives zone updates from DC1.
What should you do?
- A. On DC1, modify the permissions of contoso.com zon
- B. On Server1, add a conditional forwarde
- C. Add the Server1 computer account to the DNsUpdateProxy grou
- D. On DC1, modify the zone transfer settings for the contoso.com zon
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771652.aspx
Modify Zone Transfer Settings You can use the following procedure to control whether a zone will be transferred to other servers and which servers can receive the zone transfer.
To modify zone transfer settings using the Windows interface
1. Open DNS Manager.
2. Right-click a DNS zone, and then click Properties.
3. On the Zone Transfers tab, do one of the following:
To disable zone transfers, clear the Allow zone transfers check box.
To allow zone transfers, select the Allow zone transfers check box.
4. If you allowed zone transfers, do one of the following:
To allow zone transfers to any server, click To any server.
To allow zone transfers only to the DNS servers that are listed on the Name Servers tab,
click Only to servers listed on the Name Servers tab.
To allow zone transfers only to specific DNS servers, click Only to the following servers,
and then add the IP address of one or more DNS servers.
NEW QUESTION 8
HOTSPOT
Your network contains two DNS servers named Server1 and Server2.
Server1 hosts a primary zone named contoso.com. Server2 hosts a secondary copy of the
contoso.com zone.
You need to configure how often Server2 will check for updates for the contoso.com zone. Which tab should you use?
To answer, select the appropriate tab in the answer area. 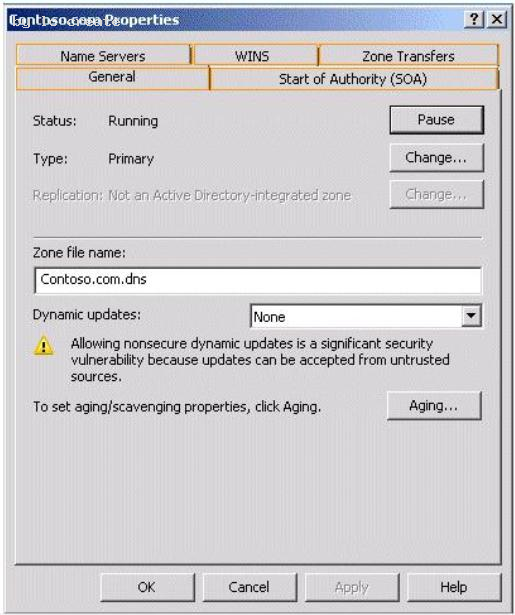
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 9
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two domains named contoso.com and child.contoso.com. The forest contains two sites named Seattle and Denver. Both sites contain users, client computers, and domain controllers from both domains.
The Seattle site contains the first domain controller deployed to the forest. The Seattle site also contains the primary domain controller (PDC) emulator for both domains. All of the domain controllers are configured as DNS servers. All DNS zones are replicated to all of the domain controllers in the forest.
The users in the Denver site report that is takes a long time to log on to their client computer when they use their user principal name (UPN). The users in the Seattle site do not experience the same issue.
You need to reduce the amount of time it takes for the Denver users to log on to their client computer by using their UPN.
What should you do?
- A. Reduce the cost of the site link between the Denver site and the Seattle sit
- B. Enable the global catalog on a domain controller in the Denver sit
- C. Enable universal group membership caching in the Denver sit
- D. Move a PDC emulator to the Denver sit
- E. Reduce the replication interval of the site link between the Denver site and the Seattle sit
- F. Add an additional domain controller to the Denver sit
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc728188.aspx
Common Global Catalog Scenarios
The following events require a global catalog server:
(...) User logon. In a forest that has more than one domain, two conditions require the global catalog during user authentication:
1. When a user principal name (UPN) is used at logon and the forest has more than one domain, a global catalog server is required to resolve the name.
2. (...)
NEW QUESTION 10
Your company has a domain controller server that runs the Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system. The server is a backup server. The server has a single 500-GB hard disk that has three partitions for the operating system, applications, and data. You perform daily backups of the server.
The hard disk fails. You replace the hard disk with a new hard disk of the same capacity. You restart the computer on the installation media. You select the Repair your computer option.
You need to restore the operating system and all files.
What should you do?
- A. Select the System Image Recovery optio
- B. Run the Imagex utility at the command promp
- C. Run the Wbadmin utility at the command promp
- D. Run the Rollback utility at the command promp
Answer: C
Explanation:
Old Answer: Run the Wbadmin utility at the command prompt. Answer: Select the System Image Recovery option.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755163.aspx Recover the Operating System or Full Server Applies To: Windows Server 2008 R2 You can recover your server operating system or full server by using Windows Recovery Environment and a backup that you created earlier with Windows Server Backup. You can access the recovery and troubleshooting tools in Windows Recovery Environment through the System Recovery Options dialog box in the Install Windows Wizard. In Windows Server 2008 R2, to launch this wizard, use the Windows Setup disc or start/restart the computer, press F8, and then select Repair Your Computer from the list of startup options.
To recover your operating system or full server using a backup created earlier and Windows Setup disc
1. Insert the Windows Setup disc that has the same architecture of the system that you are trying to recover into the CD or DVD drive and start or restart the computer. If needed, press the required key to boot from the disc. The Install Windows Wizard should appear.
2. In Install Windows, specify language settings, and then click Next.
3. Click Repair your computer.
4. Setup searches the hard disk drives for an existing Windows installation and then displays the results in System Recovery Options. If you are recovering the operating system onto separate hardware, the list should be empty (there should be no operating system on the computer). Click Next.
5. On the System Recovery Options page, click System Image Recovery. This opens the Re-image your computer page.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/dd767786.aspx Use the Wbadmin Backup Command Line Utility in Windows Server 2008 Wbadmin is the command-line counterpart to Windows Server Backup. You use Wbadmin to manage all aspects of backup configuration that you would otherwise manage in Windows Server Backup. This means that you can typically use either tool to manage backup and recovery. After you’ve installed the Backup Command-Line Tools feature, you can use Wbadmin to manage backup and recovery. Wbadmin is located in the %SystemRoot%System32 directory. As this directory is in your command path by default, you do not need to add this directory to your command path. Further information: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754015%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Wbadmin Enables you to back up and restore your operating system, volumes, files, folders, and applications from a command prompt. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Remarks The wbadmin command replaces the ntbackup command that was released with previous versions of Windows. You cannot recover backups that you created with ntbackup by using wbadmin. However, a version of ntbackup is available as a download for Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows 7 users who want to recover backups that they created using ntbackup. This downloadable version of ntbackup enables you to perform recoveries only of legacy backups, and it cannot be used on computers running Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows 7 to create new backups. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd979562%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Backup and Recovery Overview for Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2008 R2 contains features to help you create backups and, if needed, perform a recovery of your operating system, applications, and data. By using these features appropriately and implementing good operational practices, you can improve your organization's ability to recover from damaged or lost data, hardware failures, and disasters. For Windows Server 2008 R2, there are new features that expand what you can back up, where you can store backups, and how you can perform recoveries.
This table summarizes the tools you can use to perform the following backup or recovery tasks for your computers running Windows Server 2008 R2: 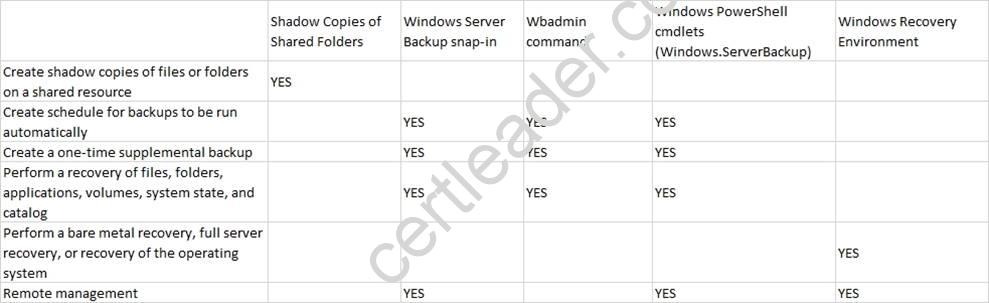
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
What is Windows Recovery Environment?
You can access the recovery and troubleshooting tools in Windows Recovery Environment through the System Recovery Options dialog box in the Install Windows Wizard. In Windows Server 2008 R2, to launch this wizard, use the Windows Setup disc or start/restart the computer, press F8, and then select Repair Your Computer from the list of startup options. Features in Windows Recovery Environment The tools in Windows Recovery Environment include: System Image Recovery. You can use this tool and a backup that you created earlier with Windows Server Backup to restore your operating system or full server. Windows Memory Diagnostic. You can use this tool (which is a memory diagnostic schedule) to check your computer's RAM. Doing this requires a restart. In addition, this tool requires a valid Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows 7 installation to function. Command Prompt. This opens a command prompt window with Administrator privileges that provides full access to your file system and volumes. In addition, certain Wbadmin commands are only available from this command window.
NEW QUESTION 11
A corporate network includes an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest that contains two domains. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2. All domain controllers are configured as DNS servers.
A standard primary zone for dev.contoso.com is stored on a member server.
You need to ensure that all domain controllers can resolve names from the dev.contoso.com zone.
What should you do?
- A. On one domain controller, create a secondary zon
- B. On the member server, create a secondary zon
- C. On each domain controller, create a secondary zon
- D. On one domain controller, create a conditional forwarde
- E. Configure the conditional forwarder to replicate to all DNS servers in the domai
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 12
Your network contains a single Active Directory domain. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2.
You deploy a new server that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. The server is not connected to the internal network.
You need to ensure that the new server is already joined to the domain when it first connects to the internal network.
What should you do?
- A. From a domain controller, run sysprep.exe and specify the /oobe paramete
- B. From the new server, run sysprep.exe and specify the /generalize paramete
- C. From a domain controller, run sysprep.exe and specify the /generalize paramete
- D. From the new server, run sysprep.exe and specify the /oobe paramete
- E. From a domain-joined computer, run djoin.exe and specify the /provision paramete
- F. From the new server, run djoin.exe and specify the /requestodj paramete
- G. From a domain-joined computer, run djoin.exe and specify the /requestodj paramete
- H. From the new server, run djoin.exe and specify the /provision paramete
Answer: C
Explanation:
Explanation 1: MS Press - Self-Paced Training Kit (Exam 70-640) (2nd Edition, July 2012) pages 217, 218 Offline Domain Join Offline domain join is also useful when a computer is deployed in a lab or other disconnected environment. When the computer is connected to the domain network and started for the first time, it will already be a member of the domain. This also helps to ensure that Group Policy settings are applied at the first startup. Four major steps are required to join a computer to the domain by using offline domain join:
1. Log on to a computer in the domain that is running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows 7 with an account that has permissions to join computers to the domain.
2. Use the DJoin command to provision a computer for offline domain join. This step prepopulates Active
Directory with the information that Active Directory needs to join the computer to the domain, and exports the information called a blob to a text file.
3. At the offline computer that you want to join the domain use DJoin to import the blob into
the Windows directory.
4. When you start or restart the computer, it will be a member of the domain.
Explanation 2:
http://technet.microsoft.com/nl-nl/library/offline-domain-join-djoin-step-by-step.aspx
Steps for performing an offline domain join
The offline domain join process includes the following steps:
1. Run the djoin.exe /provision command to create computer account metadata for the
destination computer (the computer that you want to join to the domain). As part of this
command, you must specify the name of the domain that you want the computer to join.
2. Run the djoin.exe /requestODJ command to insert the computer account metadata into
the Windows directory of the destination computer.
3. When you start the destination computer, either as a virtual machine or after a complete
operating system installation, the computer will be joined to the domain that you specify.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise. All client computers run Windows 7 Professional.
The network contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You have a custom certificate template named Sales_Temp. Sales_Temp is published to
the CA.
You need to ensure that all of the members of a group named Sales can enroll for certificates that use Sales_Temp.
Which snap-in should you use?
- A. Enterprise PKI
- B. Certification Authority
- C. Share and storage Management
- D. Certificate Templates
- E. Security Configuration Wizard
- F. Authorization Manager
- G. Group Policy Management
- H. Certificates
- I. Active Directory Administrative Center
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770794.aspx
Deploying Certificate Templates
After creating a new certificate template, the next step is to deploy the certificate template so that a certification authority (CA) can issue certificates based on it. Deployment includes publishing the certificate template to one or more CAs, defining which security principals have Enroll permissions for the certificate template, and deciding whether to configure autoenrollment for the certificate template.
To define permissions to allow a specific security principal to enroll for certificates based on a certificate template
1. Open the Certificate Templates snap-in (Certtmpl.msc).
2. In the details pane, right-click the certificate template you want to change, and then click Properties.
3. On the Security tab, ensure that Authenticated users is assigned Read permissions. This ensures that all authenticated users on the network can see the certificate templates.
4. On the Security tab, click Add. Add a global group or universal group that contains all security principals requiring Enroll permissions for the certificate template, and then click OK.
5. On the Security tab, select the newly added security group, and then assign Allow for the Read and Enroll permissions.
6. Click OK.
Permission Design
Use the following recommendations for permissions assignments:
Assign permissions only to global groups or to universal groups. It is not recommended to assign permissions to domain local groups. Domain local groups are only recognized in the domain where they exist, and assigning permissions to them can result in inconsistent application of permissions. You should not assign permissions directly to an individual user or computer account. (...)
NEW QUESTION 14
Exhibit:
Company servers run Windows Server 2008. It has a single Active Directory domain. A server called S4 has file services role installed. You install some disk for additional storage. The disks are configured as shown in the exhibit.
To support data stripping with parity, you have to create a new drive volume.
What should you do to achieve this objective?
- A. Build a new spanned volume by combining Disk0 and Disk1
- B. Create a new Raid-5 volume by adding another dis
- C. Create a new virtual volume by combining Disk 1 and Disk 2
- D. Build a new striped volume by combining Disk0 and Disk 2
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://sort.symantec.com/public/documents/sf/5.0/solaris/html/vxvm_admin/ag_ch_intro_v m17.html 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
NEW QUESTION 15
You are an administrator at ABC.com. Company has a network of 5 member servers acting as file servers. It has an Active Directory domain.
You have installed a software application on the servers. As soon as the application is installed, one of the member servers shuts down itself. To trace and rectify the problem, you create a Group Policy Object (GPO).
You need to change the domain security settings to trace the shutdowns and identify the cause of it.
What should you do to perform this task?
- A. Link the GPO to the domain and enable System Events option
- B. Link the GPO to the domain and enable Audit Object Access option
- C. Link the GPO to the Domain Controllers and enable Audit Object Access option
- D. Link the GPO to the Domain Controllers and enable Audit Process tracking option
- E. Perform all of the above actions
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms813610.aspx
Audit system events Computer ConfigurationWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsLocal PoliciesAudit Policy
Description Determines whether to audit when a user restarts or shuts down the computer;
or an event has occurred that affects either the system security or the security log.
By default, this value is set to No auditing in the Default Domain Controller Group Policy
object (GPO) and in the local policies of workstations and servers.
If you define this policy setting, you can specify whether to audit successes, audit failures,
or not to audit the event type at all. Success audits generate an audit entry when a system
event is successfully executed. Failure audits generate an audit entry when a system event
is unsuccessfully attempted. You can select No auditing by defining the policy setting and
unchecking Success and Failure.
NEW QUESTION 16
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
The domain contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You need to deploy certificates based on Version 1 templates to all of the computers in the domain. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
You create a Group Policy object (GPO) named GPOl and link the GPO to the domain.
What should you do next?
- A. In GPOl, configure Certificate Services Client - Certificate Enrollment Polic
- B. Duplicate the template
- C. In GPOl, configure Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollmen
- D. Duplicate the template
- E. In GPOl, configure Automatic Certificate Request Setting
- F. In GPOl, configure Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollmen
Answer: C
Explanation: Automatic certificate request settings Certificate enrollment is the process of requesting, receiving, and installing a certificate. By using automatic certificate settings in public key policies, you can have computers that are associated with a Group Policy object (GPO) automatically enroll for certificates. This can save you the step of explicitly enrolling for computer-related certificates for each computer. After you establish an automatic certificate request, the actual certificate requests occur the next time the computers associated with the GPO log on to the network. Incorrect: Not A: Certificate enrollment policy provides the locations of certification authorities (CAs) and the types of certificates that can be requested. Organizations that are using Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) can use Group Policy to provide certificate enrollment policy to domain members by using the Group Policy Management Console to configure the certificate enrollment policy settings. The Certificates snap-in can be used to configure certificate enrollment policy settings for individual client computers unless the Group Policy setting is configured to disable user-configured enrollment policy.
NEW QUESTION 17
You need to back up all of the group policies in a domain. The solution must minimize the size of the backup.
What should you use?
- A. the Add-WBSystemState cmdlet
- B. the Group Policy Management console
- C. the Wbadmin tool
- D. the Windows Server Backup feature
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770536.aspx
To back up a Group Policy object
1. In the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) console tree, open Group Policy Objects in the forest and domain containing the Group Policy object (GPO) to back up.
2. To back up a single GPO, right-click the GPO, and then click Back Up. To back up all GPOs in the domain, right-click Group Policy objects and click Back Up All.
NEW QUESTION 18
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains several domain controllers.All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to restore the Default Domain Controllers Policy Group Policy object (GPO) to the Windows Server 2008 R2 default settings.
What should you do?
- A. Run dcgpofix.exe /target:d
- B. Run dcgpofix.exe /target:domai
- C. Delete the link for the Default Domain Controllers Policy, and then run gpupdate.exe /syn
- D. Delete the link for the Default Domain Controllers Policy, and then run gpupdate.exe /forc
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh875588.aspx
Dcgpofix Recreates the default Group Policy Objects (GPOs) for a domain.
Syntax
DCGPOFix [/ignoreschema] [/target: {Domain | DC | Both}] [/?]
/ignoreschema Ignores the version of the Active Directory. schema when you run this command. Otherwise, the command only works on the same schema version as the Windows version in which the command was shipped.
/target {Domain | DC | Both} Specifies which GPO to restore. You can restore the Default Domain Policy GPO, the Default Domain Controllers GPO, or both.
Examples
Restore the Default Domain Controllers Policy GPO to its original state. You will lose any changes that you have made to this GPO. dcgpofix /ignoreschema /target:DC
Recommend!! Get the Full 70-640 dumps in VCE and PDF From 2passeasy, Welcome to Download: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/70-640/ (New 631 Q&As Version)