for Microsoft certification, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated . 100% PASS 70-640 TS: Windows Server 2008 Active Directory. Configuring exam Today!
Microsoft 70-640 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
Your company has a server that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. The server runs an instance of ActiveDirectory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS).
You need to replicate the AD LDS instance on a test computer that is located on the network.
What should you do?
- A. Run the repadmin /kcc <servername> command on the test compute
- B. Create a naming context by running the Dsmgmt command on the test compute
- C. Create a new directory partition by running the Dsmgmt command on the test compute
- D. Create and install a replica by running the AD LDS Setup wizard on the test compute
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771946.aspx
Create a Replica AD LDS Instance
To create an AD LDS instance and join it to an existing configuration set, use the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Set Wizard to create a replica AD LDS instance. To create a replica AD LDS instance
1. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Setup Wizard.
2. On the Welcome to the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Setup Wizard page, click Next.
3. On the Setup Options page, click A replica of an existing instance, and then click Next.
4. Finish creating the new instance by following the wizard instructions.
NEW QUESTION 2
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains a domain
controller named DC1 that runs windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1).
You need to implement a central store for domain policy templates.
What should you do?
To answer, select the source content that should be copied to the destination folder in the
answer area. 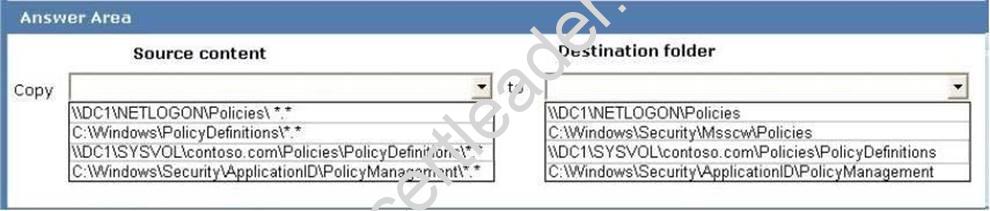
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 3
Your network contains a single Active Directory domain. The domain contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You need to ensure that the encryption keys for e-mail certificates can be recovered from the CA database.
You modify the e-mail certificate template to support key archival.
What should you do next?
- A. Issue the key recovery agent certificate templat
- B. Run certutil.exe -recoverke
- C. Run certreq.exe-polic
- D. Modify the location of the Authority Information Access (AIA) distribution poin
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770588.aspx
Identify a Key Recovery Agent
A key recovery agent is a person who is authorized to recover a certificate on behalf of an end user. Because the role of key recovery agents can involve sensitive data, only highly trusted individuals should be assigned to this role.
To identify a key recovery agent, you must configure the Key Recovery Agent certificate template to allow the person assigned to this role to enroll for a key recovery agent certificate.
NEW QUESTION 4
Your company has two offices. The offices are located in Miami and London.
The network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two child domains named miami.contoso.com and london.contoso.com. The domain contains 50 domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site.
The forest contains a custom attribute named SecurityAccessCode.
You recently configured a domain controller named DC22 as a global catalog server.
You need to verify that SecurityAccessCode is configured to replicate to DC22.
What should you do?
- A. Run the dsadd.exe command
- B. Run the nltest.exe comman
- C. Run the Set-AdDomain cmdle
- D. Run the dsmove.exe comman
- E. Run the dcpromo.exe comman
- F. Run the Move-AdDirectoryServer cmdle
- G. Use the Active Directory Schema snap-i
- H. Use the Active Directory Users and Computers consol
Answer: G
NEW QUESTION 5
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You have an organizational unit (OU) named Sales and an OU named Engineering.
You have a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the domain. The GPO is used to deploy a number of software packages.
You need to ensure that the GPO is applied only to client computers that have sufficient free disk space.
What should you do?
- A. Modify the Group Policy permission
- B. Enable block inheritanc
- C. Configure the link orde
- D. Enable loopback processing in merge mod
- E. Enable loopback processing in replace mod
- F. Configure WMI filterin
- G. Configure Restricted Group
- H. Configure Group Policy PExplanation
- I. Link the GPO to the Sales O
- J. Link the GPO to the Engineering O
Answer: F
NEW QUESTION 6
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You need to audit changes to a service account. The solution must ensure that the audit logs contain the before and after values of all the changes.
Which security policy setting should you configure?
- A. Audit Sensitive Privilege Use
- B. Audit User Account Management
- C. Audit Directory Service Changes
- D. Audit Other Account Management Events
Answer: C
Explanation:
Explanation 1: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd772641.aspx
Audit Directory Service Changes This security policy setting determines whether the operating system generates audit events when changes are made to objects in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). Explanation 2: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731607.aspx AD DS Auditing Step-by-Step Guide This guide includes a description of the new Active Directory. Domain Services (AD DS) auditing feature in Windows Server. 2008. With the new auditing feature, you can log events that show old and new values; for example, you can show that Joe's favorite drink changed from single latte to triple-shot latte.
NEW QUESTION 7
Your company has an Active Directory domain named ad.contoso.com. The domain has two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2. Both domain controllers have the DNS server role installed.
You install a new DNS server named DNS1.contoso.com on the perimeter network. You configure DC1 to forward all unresolved name requests to DNS1.contoso.com.
You discover that the DNS forwarding option is unavailable on DC2.
You need to configure DNS forwarding on the DC2 server to point to the DNS1.contoso.com server.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Choose two.)
- A. Clear the DNS cache on DC2.
- B. Configure conditional forwarding on DC2.
- C. Configure the Listen On address on DC2.
- D. Delete the Root zone on DC2.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Answer: Delete the Root zone on DC2. Configure conditional forwarding on DC2.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx Configure a DNS Server to Use Forwarders A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also configure your server to forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders. http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/winserverNIS/thread/0ca38ece-d76e-42f0-85d5-a342f9e169f5/ Deleting .root dns zone in 2008 DNS
Q: We have 2 domain controllers and .root zone is created in the DNS. Due to which the external name resolution is not possible. I had tried to add conditional forwarders but i get an error saying that conditional forwarders cannot be created on root DNS servers. A 1: If you have a "root" zone created in your DNS, and you no longer want that configuration, you can just simply delete that zone. There is no reason to have a root "." zone hosted unless you want to make sure that the DNS server is authoritative for all queries and not allow the DNS server to go elsewhere for name resolution.
If you delete this zone, the DNS server will be able to use its root hints, or fowarders to resolve queries for zones its not authoritative for. A 2: That was from the old 2000 days where DCPROMO would create it if it detected no internet access while promoting the first DC. Jut remove it, and the Forwarders option reappear.
Further information: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/298148
How To Remove the Root Zone (Dot Zone)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731879%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Reviewing DNS Concepts Delegation For a DNS server to answer queries about any name, it must have a direct or indirect path to every zone in the namespace. These paths are created by means of delegation. A delegation is a record in a parent zone that lists a name server that is authoritative for the zone in the next level of the hierarchy. Delegations make it possible for servers in one zone to refer clients to servers in other zones. The following illustration shows one example of delegation. 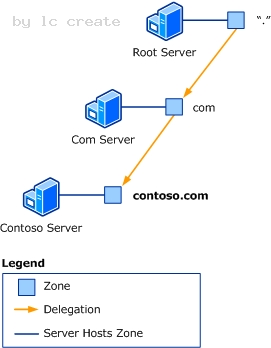
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
The DNS root server hosts the root zone represented as a dot ( . ). The root zone contains a delegation to a zone in the next level of the hierarchy, the com zone. The delegation in the root zone tells the DNS root server that, to find the com zone, it must contact the Com server. Likewise, the delegation in the com zone tells the Com server that, to find the contoso.com zone, it must contact the Contoso server. Note: A delegation uses two types of records. The name server (NS) resource record provides the name of an authoritative server. Host (A) and host (AAAA) resource records provide IP version 4 (IPv4) and IP version 6 (IPv6) addresses of an authoritative server. This system of zones and delegations creates a hierarchical tree that represents the DNS namespace. Each zone represents a layer in the hierarchy, and each delegation represents a branch of the tree. By using the hierarchy of zones and delegations, a DNS root server can find any name in the DNS namespace. The root zone includes delegations that lead directly or indirectly to all other zones in the hierarchy. Any server that can query the DNS root server can use the information in the delegations to find any name in the namespace.
NEW QUESTION 8
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2.
The network contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You need to ensure that all of the members of a group named Managers can view the event log entries for Certificate Services.
Which snap-in should you use?
- A. Active Directory Administrative Center
- B. Authorization Manager
- C. Certificate Templates
- D. Certificates
- E. Certification Authority
- F. Enterprise PKI
- G. Group Policy Management
- H. Security Configuration Wizard
- I. Share and Storage Management
Answer: G
Explanation: We can make the Group1 group a member of theEvent Log Readers Group
, giving them read access to all event logs, thus including the Certificate Services events.
We can do that by usingGroup Policy Management.
Explanation 1:
It's a bit hard to find some good, clear Explanation for this. There's nothing wrong with doing it
yourself, so here's what I did in VMWare, using a domain controller and a member server.
Click along if you want!
In VMWare I have setup a domain controller, DC01 and a member server MEM01, both
belonging to the contoso.com domain. I have placed MEM01 in an OU named Events. I
have created a global security group, named TESTGROUP, and I want to make it a member of the built-in Event Log Readers group on MEM01.
Start the Group Policy Management console on DC01.
Right-click the Events OU and choose "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it
here..."
I named the GPO "EventLog_TESTGROUP"
Right-click the "EventLog_TESTGROUP" GPO and choose "Edit..."
Go to Computer Configuration Policies Windows Settings Security Settings and
select "Restricted Groups"
Right-click "Restricted Groups" and choose "Add Group..."
Now there are two ways to do this. We can select TESTGROUP and make it a
member of the Event Log Readers group, or we can select the Event Log Readers
group and add TESTGROUP as a member. Let's do the second one. Click the
Browse button and go find the Event Log Readers group. Click OK.
Click the Browse button next to "Members of this group", search for the
TESTGROUP group and add it.
Click OK.
10. On MEM01 open a command prompt and rungpupdate /force.
Check the Event Log Readers group properties and see that the TESTGROUP
group is now a member.
Explanation 2: http://blogs.technet.com/b/janelewis/archive/2010/04/30/giving-non-administrators-permission-to-read-event-logs-windows-2003-and-windows-2008.aspx
Giving Non Administrators permission to read Event Logs Windows 2003 and Windows 2008
So if you want to give Non-Administrator users access remotely to Event logs if the Servers or Domain Controllers they are accessing are Windows 2003 follow the steps below.
(...)
Windows 2008 is much easier as long as you are giving the users and groups in question read access to all event logs. If that is the case just add them to the Built inEvent Log Readers group.
NEW QUESTION 9
CORRECT TEXT
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com.
You need to use Group Policies to deploy the line-of-business applications shown in the following table. 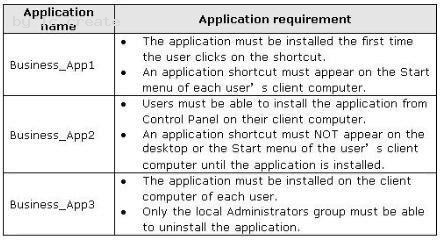
What should you do?
To answer, drag the appropriate deployment method to the correct application in the answer area.
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 10
Your network contains a single Active Directory domain. The domain contains five read-only domain controllers (RODCs) and five writable domain controllers. All servers run Windows Server 2008.
You plan to install a new RODC that runs Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to ensure that you can add the new RODC to the domain. You want to achieve this goal by using the minimum amount of administrative effort.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- A. From Active Directory Domains and Trusts, raise the functional level of the domai
- B. At the command prompt, run adprep.exe /forestpre
- C. From Active Directory Users and Computers, pre-stage the RODC computer accoun
- D. At the command prompt, run adprep.exe /domainpre
- E. At the command prompt, run adprep.exe /rodcpre
Answer: CD
Explanation: C:
* During the first stage of the installation, the wizard records all the data about the RODC that will be stored in the distributed Active Directory database, including the read-only domain controller account name and the site in which it will be placed. This stage must be performed by a member of the Domain Admins group.
* To create an RODC account by using the Windows interface Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers. Double-click the domain container, then you can either right-click the Domain Controllers container or click the Domain Controllers container, and then click Action. Click Pre-create Read-only Domain Controller account
NEW QUESTION 11
DRAG DROP
A server named DC1 has the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role and the Active DirectoryLightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) role installed.
An AD LDS instance named LDS1 stores its data on the C: drive.
You need to relocate the LDS1 instance to the D: drive.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?(To answer, move the three appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.) 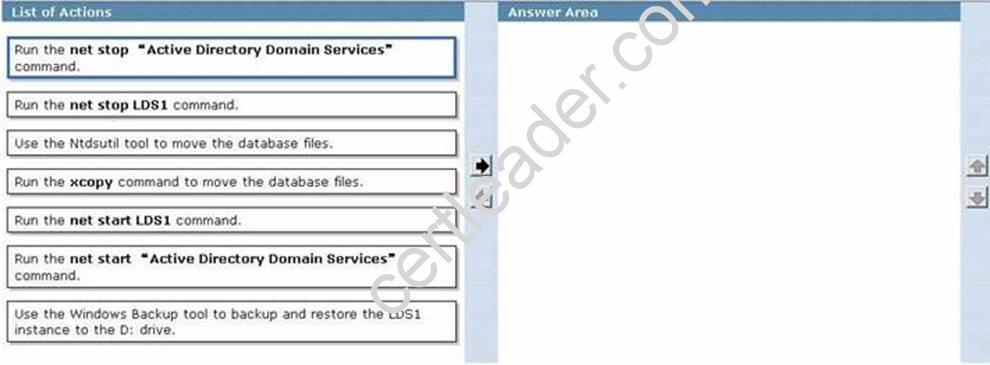
Answer:
Explanation: 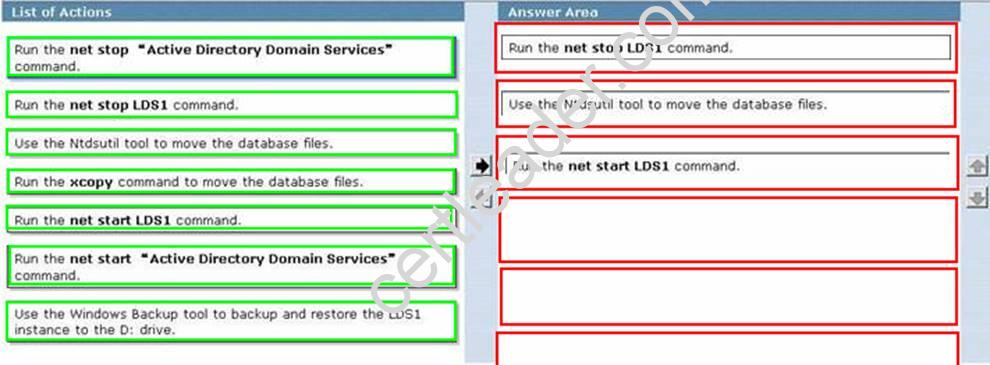
NEW QUESTION 12
A corporate network includes an Active Directory-integrated zone. All DNS servers that host the zone are domain controllers.
You add multiple DNS records to the zone.
You need to ensure that the new records are available on all DNS servers as soon as possible.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Ldp
- B. Repadmin
- C. Ntdsutil
- D. Nslookup
- E. Active Directory Sites And Services console
- F. Active Directory Domains And Trusts console
- G. Dnslint
- H. Dnscmd
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc811569.aspx
Forcing Replication
Sometimes it becomes necessary to forcefully replicate objects and entire partitions
between domain controllers that may or may not have replication agreements.
Force a replication event with all partners
The repadmin /syncall command synchronizes a specified domain controller with all
replication partners.
Syntax
repadmin /syncall <DC> [<NamingContext>] [<Flags>]
Parameters
<DC>
Specifies the host name of the domain controller to synchronize with all replication
partners.
<NamingContext>
Specifies the distinguished name of the directory partition.
<Flags>
Performs specific actions during the replication.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2008 R2.
The DNS zone for contoso.com is Active Directory-integrated.
You deploy a read-only domain controller (RODC) named RODC1. You install the DNS
Server server role on RODC1.
You discover that RODC1 does not have any DNS application directory partitions.
You need to ensure that RODC1 has a copy of the DNS application directory partition of contoso.com.
What should you do? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose two.)
- A. From DNS Manager, right-click RODC1 and click Create Default Application Directory Partition
- B. Run ntdsutil.ex
- C. From the Partition Management context, run the create nc comman
- D. Run dnscmd.exe and specify the /createbuiltindirectorypartitions paramete
- E. Run ntdsutil.ex
- F. From the Partition Management context, run the add nc replica comman
- G. Run dnscmd.exe and specify the /enlistdirectorypartition paramete
Answer: DE
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc742490.aspx
RODC Post-Installation Configuration
If you install DNS server after the AD DS installation, you must also enlist the RODC in the DNS application directory partitions. The RODC is not enlisted automatically in the DNS application directory partitions by design because it is a privileged operation. If the RODC were allowed to enlist itself, it would have permissions to add or remove other DNS servers that are enlisted in the application directory partitions.
To enlist a DNS server in a DNS application directory partition
1. Open an elevated command prompt.
2. At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
dnscmd<ServerName> /EnlistDirectoryPartition <FQDN>
For example, to enlist RODC01 in the domain-wide DNS application directory partition in a
domain named child.contoso.com, type the following command:
dnscmd RODC01 /EnlistDirectoryPartition DomainDNSZones.child.contoso.com
You might encounter the following error when you run this command:
Command failed: ERROR_DS_COULDNT_CONTACT_FSMO 8367 0x20AF
If this error appears, use NTDSUTIL to add the RODC for the partition to be replicated:
1. ntdsutil
2. partition management
3. connections
4. Connect to a writeable domain controller (not an RODC): connect to server <WriteableDC>.Child.contoso.com
5. quit
6. To enlist this server in the replication scope for this zone, run the following command: add NC Replica DC=DomainDNSZones,DC=Child,DC=Contoso,DC=Com <rodc Server>.Child.
contoso.com
Original explanation:
Please Check but I think this should be A and C and not A and D.
I have changed it to A and C.
Reason: Once the application directory partition is created, contoso.com should replicate to it.
Dnscmd /enlistdirectorypartition --- Adds the DNS server to the specified directory partition's replica set.
Dnscmd /createbuiltindirectorypartitions Creates a DNS application directory partition. When DNS is installed, an application directory partition for the service is created at the forest and domain levels. Use this command to create DNS application directory partitions that were deleted or never created. With no parameter, this command creates a built-in DNS directory partition for the domain.
To create the default DNS application directory partitions
Using the Windows interface
Open DNS.
In the console tree, right-click the applicable DNS server.
Where?
DNS/applicable DNS server
Click Create Default Application Directory Partitions.
Follow the instructions to create the DNS application directory partitions.
NEW QUESTION 14
DRAG DROP
You manage an Active Directory forest named contoso.com.
The forest contains an empty root domain named contoso.com and a child domain named child.contoso.com.
All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2008.
You need to raise the functional level of the forest to Windows Server 2008 R2. You must achieve this goal by using the minimum amount of administrative effort.
What should you do?
To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order. 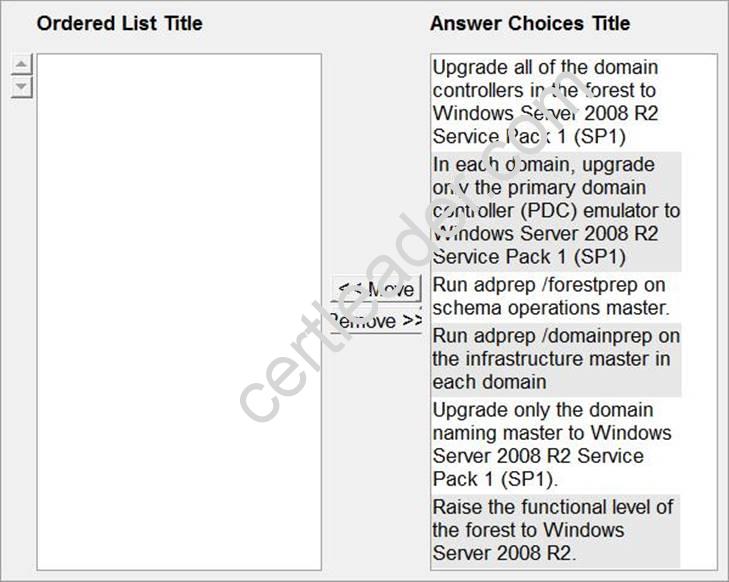
Answer:
Explanation: 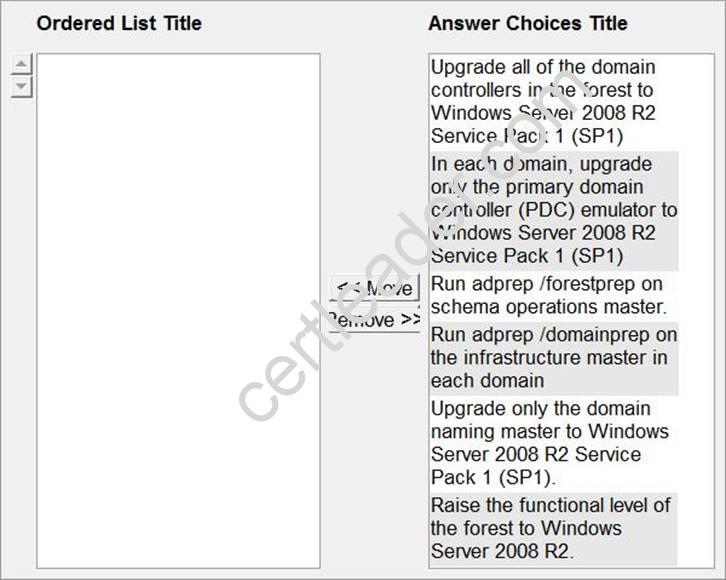
NEW QUESTION 15
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains 20 domain controllers. You need to identify which domain controllers are global catalog servers. Which tool should you use?
- A. Dcdiag
- B. Get-ADComputer
- C. Net computer
- D. Netsh
Answer: D
Explanation: The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Netdom command.
On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type CMD in the Open box, and then click
OK.
In the Command Prompt window, type netdom query /domain:<domain> fsmo (where
<domain> is the name of YOUR domain).
Note: netsh is also known as the command prompt.
NEW QUESTION 16
Contoso, Ltd. has an Active Directory domain named ad.contoso.com. Fabrikam, Inc. has an Active Directory domain named intranet.fabrikam.com. Fabrikam's security policy prohibits the transfer of internal DNS zone data outside the Fabrikam network.
You need to ensure that the Contoso users are able to resolve names from the intranet.fabrikam.com domain.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new stub zone for the intranet.fabrikam.com domai
- B. Configure conditional forwarding for the intranet.fabrikam.com domai
- C. Create a standard secondary zone for the intranet.fabrikam.com domai
- D. Create an Active DirectoryCintegrated zone for the intranet.fabrikam.com domai
Answer: B
Explanation:
Answer: Configure conditional forwarding for the intranet.fabrikam.com domain.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc730756.aspx Understanding Forwarders A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that forwards DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders. You designate a DNS server on a network as a forwarder by configuring the other DNS servers in the network to forward the queries that they cannot resolve locally to that DNS server. By using a forwarder, you can manage name resolution for names outside your network, such as names on the Internet, and improve the efficiency of name resolution for the computers in your network. The following figure illustrates how external name queries are directed with forwarders. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Conditional forwarders
A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that forwards DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, you can configure a DNS server to forward all the queries that it receives for names ending with corp.contoso.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers. Further information: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794735%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Assign a Conditional Forwarder for a Domain Name http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx Configure a DNS Server to Use Forwarders
NEW QUESTION 17
Your network contains a single Active Directory domain. Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) is deployed on the network.
A user named User1 is a member of only the AD RMS Enterprise Administrators group. You need to ensure that User1 can change the service connection point (SCP) for the AD RMS installation.The solution must minimize the administrative rights of User1.
To which group should you add User1?
- A. AD RMS Auditors
- B. AD RMS Service Group
- C. Domain Admins
- D. Schema Admins
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/710.the-ad-rms-service-connection-point.aspx The AD RMS Service Connection Point The Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) Service Connection Point (SCP) is an object in Active Directory that holds the web address of the AD RMS certification cluster. AD RMS-enabled applications use the SCP to discover the AD RMS service; it is the first connection point for users to discover the AD RMS web services. The AD RMS SCP can be registered automatically during AD RMS installation, or it can be registered after installation has completed. To register the SCP you must be a member of the local AD RMS Enterprise Administrators group and the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) Enterprise Admins group, or you must have been given the appropriate authority.
NEW QUESTION 18
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. OU1 contains all managed service accounts in the domain.
You need to prevent the managed service accounts from being deleted accidentally from OU1.
Which cmdlet should you use?
- A. Set-ADUser
- B. Set-ADOrganizationalUnit
- C. Set-ADServiceAccount
- D. Set-ADObject
Answer: D
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh852326.aspx Set-ADObject Modifies an Active Directory object.
Parameter -ProtectedFromAccidentalDeletion <Boolean>Specifies whether to prevent the object from
being deleted. When this property is set to true, you cannot delete the corresponding object without changing the value of the property. Possible values for this parameter include: $false or 0 $true or 1 The following example shows how to set this parameter to true. -ProtectedFromAccidentalDeletion $true
Thanks for reading the newest 70-640 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM 2passeasy 70-640 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/70-640/ (631 Q&As Dumps)