Your success in is our sole target and we develop all our in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. for Microsoft 70-640 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Also have 70-640 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
You install a read-only domain controller (RODC) named RODC1.
You need to ensure that a user named User1 can administer RODC1. The solution must minimize the number of permissions assigned to User1.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Active Directory Administrative Center
- B. Active Directory Users and Computers
- C. Dsadd
- D. Dsmgmt
Answer: B
Explanation:
Explanation 1:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755310.aspx
Delegating local administration of an RODC
Administrator Role Separation (ARS) is an RODC feature that you can use to delegate the
ability to administer an RODC to a user or a security group. When you delegate the ability
to log on to an RODC to a user or a security group, the user or group is not added the
Domain Admins group and therefore does not have additional rights to perform directory
service operations.
Steps and best practices for setting up ARS
You can specify a delegated RODC administrator during an RODC installation or after it.
To specify the delegated RODC administrator after installation, you can use either of the
following options:
Modify the Managed By tab of the RODC account properties in theActive Directory Users and Computerssnap-in, as shown in the following figure. You can click Change to change which security principal is the delegated RODC administrator. You can choose only one security principal. Specify a security group rather than an individual user so you can control RODC administration permissions most efficiently. This method changes the managedBy attribute of the computer object that corresponds to the RODC to the SID of the security principal that you specify. This is the recommended way to specify the delegated RODC administrator account because the information is stored in AD DS, where it can be centrally managed by domain administrators. 
Use the ntdsutil local roles command or thedsmgmtlocal roles command. You can use this command to view, add, or remove members from the Administrators group and other built-in groups on the RODC.[See also the second Explanation for more information on how to use dsmgmt.]
Using ntdsutil or dsmgmt to specify the delegated RODC administrator account is not recommendedbecause the information is stored only locally on the RODC. Therefore, when you use ntdsutil local roles to delegate an administrator for the RODC, the account that you specify does not appear on the Managed By tab of the RODC account properties. As a result, using the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in or a similar tool will not reveal that the RODC has a delegated administrator.
In addition, if you demote an RODC, any security principal that you specified by using ntdsutil local roles remains stored in the registry of the server. This can be a security concern if you demote an RODC in one domain and then promote it to be an RODC again in a different domain. In that case, the original security principal would have administrative rights on the new RODC in the different domain.
Explanation 2: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732301.aspx
Administrator Role Separation Configuration This section provides procedures for creating a local administrator role for an RODC and for adding a user to that role.
To configure Administrator Role Separation for an RODC
Click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then press ENTER.
At the command prompt, typedsmgmt.exe, and then press ENTER.
At the DSMGMT prompt, typelocal roles, and then press ENTER.
For a list of valid parameters, type ?, and then press ENTER.
By default, no local administrator role is defined on the RODC after AD DS installation. To add the local administrator role, use the Add parameter.
Type add <DOMAIN><user><administrative role>
For example, type add CONTOSOtestuser administrators
NEW QUESTION 2
Your company has two Active Directory forests named contoso.com and fabrikam.com.
The company network has three DNS servers named DNS1, DNS2, and DNS3. The DNS servers are configured as shown in the following table. 
All computers that belong to the fabrikam.com domain have DNS3 configured as the preferred DNS server. All other computers use DNS1 as the preferred DNS server.
Users from the fabrikam.com domain are unable to connect to the servers that belong to the contoso.com domain.
You need to ensure users in the fabrikam.com domain are able to resolve all contoso.com queries.
What should you do?
- A. Configure conditional forwarding on DNS1 and DNS2 to forward fabrikam.com queries to DNS3.
- B. Create a copy of the _msdcs.contoso.com zone on the DNS3 serve
- C. Create a copy of the fabrikam.com zone on the DNS1 server and the DNS2 serve
- D. Configure conditional forwarding on DNS3 to forward contoso.com queries to DNS1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc730756.aspx Understanding Forwarders A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that forwards DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders. You designate a DNS server on a network as a forwarder by configuring the other DNS servers in the network to forward the queries that they cannot resolve locally to that DNS server. By using a forwarder, you can manage name resolution for names outside your network, such as names on the Internet, and improve the efficiency of name resolution for the computers in your network. The following figure illustrates how external name queries are directed with forwarders. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Conditional forwarders A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that forwards DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, you can configure a DNS server to forward all the queries that it receives for names ending with corp.contoso.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers.
NEW QUESTION 3
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain is configured as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)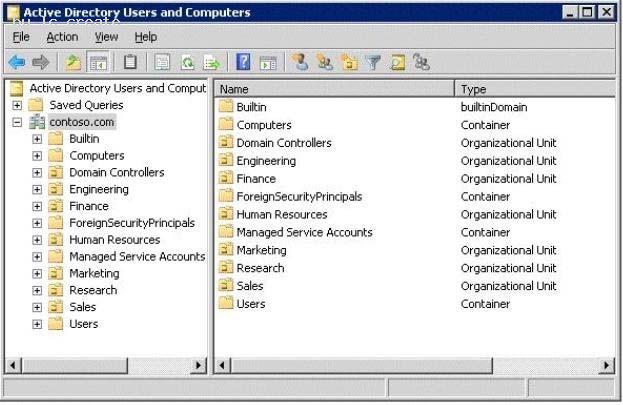
Each organizational unit (OU) contains over 500 user accounts.
The Finance OU and the Human Resources OU contain several user accounts that are members of a universal group named Group1.
You have a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the domain.
You need to prevent the GPO from being applied to the members of Group1 only.
What should you do?
- A. Modify the Group Policy permission
- B. Enable block inheritanc
- C. Configure the link orde
- D. Enable loopback processing in merge mod
- E. Enable loopback processing in replace mod
- F. Configure WMI filterin
- G. Configure Restricted Group
- H. Configure Group Policy PExplanation
- I. Link the GPO to the Finance O
- J. Link the GPO to the Human Resources O
Answer: A
Explanation:
MS Press - Self-Paced Training Kit (Exam 70-640) (2nd Edition, July 2012) page 285, 286
Using Security Filtering to Modify GPO Scope
By now, you’ve learned that you can link a GPO to a site, domain, or OU. However, you might need to apply GPOs only to certain groups of users or computers rather than to all users or computers within the scope of the GPO. Although you cannot directly link a GPO to a security group, there is a way to apply GPOs to specific security groups. The policies in a GPO apply only to users who have Allow Read and Allow Apply Group Policy permissions to the GPO.
Each GPO has an access control list (ACL) that defines permissions to the GPO. Two permissions, Allow Read and Allow Apply Group Policy, are required for a GPO to apply to a user or computer. If a GPO is scoped to a computer (for example, by its link to the computer’s OU), but the computer does not have Read and Apply Group Policy permissions, it will not download and apply the GPO. Therefore, by setting the appropriate permissions for security groups, you can filter a GPO so that its settings apply only to the computers and users you specify.
Filtering a GPO to Apply to Specific Groups
To apply a GPO to a specific security group, perform the following steps:
4. Select the GPO in the Group Policy Objects container in the console tree.
5. In the Security Filtering section, select the Authenticated Users group and click Remove.
6. Click OK to confirm the change.
7. Click Add.
8. Select the group to which you want the policy to apply and click OK.
NEW QUESTION 4
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The relevant servers in the domain are configured as shown in the following table.
You need to ensure that all device certificate requests use the MD5 hash algorithm.
What should you do?
- A. On Server2, run the Certutil too
- B. On Server1, update the CEP Encryption certificate templat
- C. On Server1, update the Exchange Enrollment Agent (Offline Request) templat
- D. On Server3, set the value of the HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftCryptographyMSCEP HashAlgorithmHashAlgorithm registry ke
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff955642.aspx
Managing Network Device Enrollment Service
Configuring NDES
NDES stores its configuration in the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCryptography
MSCEP.
To change NDES configuration, edit the NDES registry settings by using Regedit.exe or Reg.exe, then restart IIS. If necessary, create the key and value using the names and data types described in the following table.
Key name HashAlgorithm HashAlgorithm Value Data Type String Default value SHA1 Description Accepted values are SHA1 and MD5.
NEW QUESTION 5
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains one domain named contoso.com.
You discover the following event in the Event log of domain controllers: “The request for a new accountidentifier pool failed. The operation will be retried until the request succeeds. The error is “ %1 “” You need to ensure that the domain controllers can acquire new account-identifier pools successfully.
What should you do?
- A. Move the domain naming master rol
- B. Move the global catalog serve
- C. Restart the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) servic
- D. Deploy an additional global catalog serve
- E. Move the infrastructure master rol
- F. Move the PDC emulator rol
- G. Install a read-only domain controller (RODC).
- H. Move the RID master rol
- I. Move the bridgehead serve
- J. Move the schema master rol
Answer: H
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc756699.aspx
Event ID 16651 — RID Pool Request
Users, computers, and groups stored in Active Directory are collectively known as security
principals. Each security principal is assigned a unique alphanumeric string called a SID.
The SID includes a domain prefix identifier that uniquely identifies the domain and a
relative identifier (RID) that uniquely identifies the security principal within the domain. The
RID is a monotonically increasing number at the end of the SID. Each domain controller is
assigned a pool of RIDs from the global RID pool by the domain controller that holds the
RID master role (also known as flexible single master operations or FSMO) in each Active
Directory domain. The RID master (also known as the RID pool manager, RID manager, or
RID operations master) is responsible for issuing a unique RID pool to each domain
controller in its domain. By default, RID pools are obtained in increments of 500. (...) Newly
promoted domain controllers must acquire a RID pool before they can advertise their
availability to Active Directory clients or share the SYSVOL. Existing domain controllers
require additional RID allocations in order to continue creating security principals when
their current RID pool becomes depleted.
Event Details
Message
The request for a new account-identifier pool failed. The operation will be retried until the
request succeeds.
The error is " %1 "
Resolve
Check connectivity to the RID master, and check its replication status
A relative ID (RID) pool was not allocated to the local domain controller. Ensure that the
local domain controller can communicate with the domain controller that is identified as the
RID operations master.
Ensure that the RID master is online and replicating to other domain controllers.
NEW QUESTION 6
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. All DNS servers are domain controllers.
You view the properties of the DNS zone as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 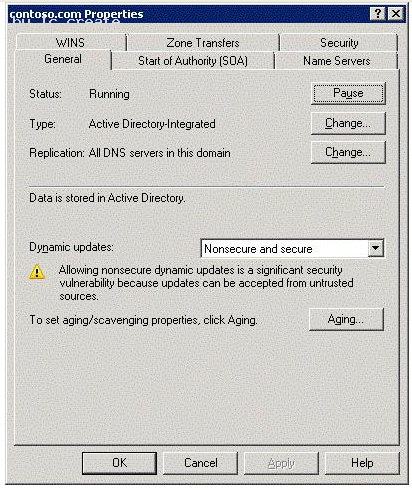
You need to ensure that DNS records can only be updated by the computer that registered the record.
What should you do first?
- A. Modify the Dynamic updates settin
- B. Create a trust ancho
- C. Modify the zone typ
- D. Modify the Advanced properties of the DNS serve
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains a single domain. The domain contains two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2 that run Windows Server 2008 R2. DC1 is configured as a global catalog server.
You need to configure DC2 as the only global catalog server in the forest. The solution must maintain DC1 in the domain. What should you do?
- A. Run the dsadd.exe command
- B. Run the nltest.exe comman
- C. Run the Set-AdDomain cmdle
- D. Run the dsmove.exe comman
- E. Run the dcpromo.exe comman
- F. Run the Move-AdDirectoryServer cmdle
- G. Use the Active Directory Schema snap-i
- H. Use the Active Directory Users and Computers consol
Answer: H
NEW QUESTION 8
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. Contoso.com contains two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2. DC1 and DC2 are configured as DNS servers and host the Active Directoryintegrated zone for contoso.com.
From DNS Manager on DC1, you enable scavenging for the contoso.com zone.
You discover stale DNS records in the zone.
You need to ensure that the stale DNS records are deleted from contoso.com.
What should you do?
- A. From DNS Manager, enable scavenging on DC1.
- B. From DNS Manager, reload the zon
- C. Run dnscmd.exe and specify the ageallrecords paramete
- D. Run dnscmd.exe and specify the startscavenging paramete
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771677.aspx
Prerequisites for aging and scavenging
Before you can use the aging and scavenging features of DNS, several conditions must be met:
Scavenging and aging must be enabled, both at the DNS server and on the zone.
NEW QUESTION 9
Your network contains two Active Directory forests named contoso.com and nwtraders.com. Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) is deployed in each forest.
You need to ensure that users from the nwtraders.com forest can access AD RMS protected content in the contoso.com forest.
What should you do?
- A. Add a trusted user domain to the AD RMS cluster in the nwtraders.com domai
- B. Create an external trust from nwtraders.com to contoso.co
- C. Add a trusted user domain to the AD RMS cluster in the contoso.com domai
- D. Create an external trust from contoso.com to nwtraders.co
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh311036.aspx
Using AD RMS trust
It is not necessary to create trust or federation relationships between the Active Directory forests of organizations to be able to share rights-protected information between separate organizations. AD RMS provides two types of trust relationships that provide this kind of rights-protected information exchange. A trusted user domain (TUD) allows the AD RMS root cluster to process requests for client licensor certificates or use licenses from users whose rights account certificates (RACs) were issued by a different AD RMS root cluster. You add a trusted user domain by importing the server licensor certificate of the AD RMS cluster to trust.
NEW QUESTION 10
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You have a management computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 7.
You need to forward the logon events of all the domain controllers in contoso.com to Computer1.
All new domain controllers must be dynamically added to the subscription.
What should you do?
- A. From Computer1, configure source-initiated event subscription
- B. From a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU), configure the Event Forwarding nod
- C. From Computer1, configure collector-initiated event subscription
- D. From a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU), configure the Event Forwarding nod
- E. From Computer1, configure source-initiated event subscription
- F. Install a server authentication certificate on Computer1. Implement autoenrollment for the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU).
- G. From Computer1, configure collector-initiated event subscription
- H. Install a server authentication certificate on Computer1. Implement autoenrollment for the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU).
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/bb870973(v=vs.85).aspx
Setting up a Source Initiated Subscription
Source-initiated subscriptions allow you to define a subscription on an event collector computer without defining the event source computers, and then multiple remote event source computers can be set up (using a group policy setting) to forward events to the event collector computer. This differs from a collector initiated subscription because in the collector initiated subscription model, the event collector must define all the event sources in the event subscription.
NEW QUESTION 11
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
The Active Directory sites are configured as shown in the Sites exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 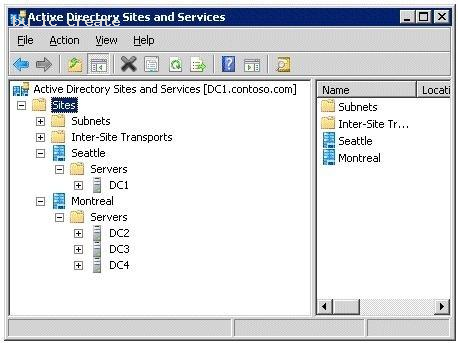
You need to ensure that DC1 and DC4 are the only servers that replicate Active Directory changes between the sites.
What should you do?
- A. Configure DC1 as a preferred bridgehead server for IP transpor
- B. Configure DC4 as a preferred bridgehead server for IP transpor
- C. From the DC4 server object, create a Connection object for DC1.
- D. From the DC1 server object, create a Connection object for DC4.
Answer: B
Explanation:
MCTS 70-640 Cert Guide: Windows Server 2008 Active Directory, Configuring (Pearson IT Certification, 2010) pages 193, 194
Bridgehead Servers
A bridgehead server is the domain controller designated by each site’s KCC to take control of intersite replication. The bridgehead server receives information replicated from other sites and replicates it to its site’s other domain controllers. It ensures that the greatest portion of replication occurs within sites rather than between them.
In most cases, the KCC automatically decides which domain controller acts as the bridgehead server.
However, you can use Active Directory Sites and Services to specify which domain controller will be the preferred bridgehead server by using the following steps:
1. In Active Directory Sites and Services, expand the site in which you want to specify the preferred bridgehead server.
2. Expand the Servers folder to locate the desired server, right-click it, and then choose Properties.
3. From the list labeled Transports available for intersite data transfer, select the protocol(s) for which you want to designate this server as a preferred bridgehead server and then click Add.
Original explanation:
Please Check Answer
Connections. The KCC creates connections that enable domain controllers to replicate with each other. A connection defines a one-way, inbound route from one domain controller, the source, to another domain controller, the destination. The KCC reuses existing connections where it can, deletes unused connections, and creates new connections if none exist that meet the current need. Bridgehead Servers. To communicate across site links, the KCC automatically designates a single server, called the bridgehead server, in each site to perform site-to-site replication. Subsequent replication occurs by replication within a site. When site links are established, authorized administrators can designate the bridgehead servers that they want to receive replication between sites. By designating a specific server to receive replication between sites, rather than using any available server, authorized administrators can specify the most beneficial conditions for the connection between sites. Bridgehead servers ensure that most replication occurs within sites rather than between sites.
http://technet.microsoft.com/library/dd277429.aspx
NEW QUESTION 12
You need to identify all failed logon attempts on the domain controllers.
What should you do?
- A. View the Netlogon.log fil
- B. View the Security tab on the domain controller computer objec
- C. Run Event Viewe
- D. Run the Security and Configuration Wizar
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/174074 Security Event Descriptions This article contains descriptions of various security-related and auditing- related events, and tips for interpreting them. These events will all appear in the Security event log and will be logged with a source of "Security." Event ID: 529 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: Unknown user name or bad password User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 530 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: Account logon time restriction violation User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 531 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: Account currently disabled User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 532 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: The specified user account has expired User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 533 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: User not allowed to logon at this computer User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 534 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: The user has not been granted the requested logon type at this machine User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 535 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: The specified account's password has expired User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 536 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: The NetLogon component is not active User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6 Event ID: 537 Type: Failure Audit Description: Logon Failure: Reason: An unexpected error occurred during logon User Name: %1 Domain: %2 Logon Type: %3 Logon Process: %4 Authentication Package: %5 Workstation Name: %6
NEW QUESTION 13
Your network contains an Active Directory domain.
You need to activate the Active Directory Recycle Bin in the domain.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Dsamain
- B. Set-ADDomain
- C. Add-WindowsFeature
- D. Ldp
Answer: D
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd379481.aspx
Enabling Active Directory Recycle Bin
After the forest functional level of your environment is set to Windows Server 2008 R2, you can enable Active Directory Recycle Bin by using the following methods: Enable-ADOptionalFeature Active Directory module cmdlet (This is the recommended
method.) Ldp.exe
NEW QUESTION 14
Your network contains a domain controller that runs Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to reset the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password on the domain controller.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Ntdsutil
- B. Dsamain
- C. Active Directory Users and Computers
- D. Local Users and Groups
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/meamcs/archive/2012/05/29/reset-the-dsrm-administrator-password.aspx
To Reset the DSRM Administrator Password
1. Click, Start, click Run, type ntdsutil, and then click OK.
2. At the Ntdsutil command prompt, type set dsrm password.
NEW QUESTION 15
Your company has a single Active Directory domain named intranet.contoso.com. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2. The domain functional level is Windows 2000 native and the forest functional level is Windows 2000.
You need to ensure the UPN suffix for contoso.com is available for user accounts.
What should you do first?
- A. Raise the intranet.contoso.com forest functional level to Windows Server 2003 or highe
- B. Raise the intranet.contoso.com domain functional level to Windows Server 2003 or highe
- C. Add the new UPN suffix to the fores
- D. Change the Primary DNS Suffix option in the Default Domain Controllers Group Policy Object (GPO) to contoso.co
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/243629
HOW TO: Add UPN Suffixes to a Forest
Adding a UPN Suffix to a Forest
Open Active Directory Domains and Trusts.
Right-click Active Directory Domains and Trusts in the Tree window pane, and then click Properties.
On the UPN Suffixes tab, type the new UPN suffix that you would like to add to the forrest. Click Add, and then click OK.
Now when you add users to the forest, you can select the new UPN suffix to complete the user's logon name.
APPLIES TO
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server
NEW QUESTION 16
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains a single domain and 10 domain controllers. All of the domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1).
The forest contains an application directory partition named dc=app1,dc=contoso,dc=com. A domain controller named DC1 has a copy of the application directory partition.
You need to configure a domain controller named DC2 to receive a copy of dc=app1,dc=contoso,dc=com.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Dsamain
- B. Ntdsutil
- C. Active Directory Sites and Services
- D. Dcpromo
Answer: C
Explanation: Active DirectorySites and Services is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in that you can use to administer the replication of directory data among all sites in an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest.
You can use the Active Directory Sites and Services snap-in to manage the site-specific objects that implement the intersite replication topology.
NEW QUESTION 17
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a domain controller named DC1. DC1 hosts a standard primary zone for contoso.com.
You discover that non-domain member computers register records in the contoso.com zone.
You need to prevent the non-domain member computers from registering records in the contoso.com zone.
All domain member computers must be allowed to register records in the contoso.com zone.
What should you do first?
- A. Configure a trust ancho
- B. Run the Security Configuration Wizard (SCW).
- C. Change the contoso.com zone to an Active Directory-integrated zon
- D. Modify the security settings of the %SystemRoot%System32Dns folde
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772746%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Active Directory-Integrated Zones DNS servers running on domain controllers can store their zones in Active Directory. In this way, it is not necessary to configure a separate DNS replication topology that uses ordinary DNS zone transfers, because all zone data is replicated automatically by means of Active Directory replication. This simplifies the process of deploying DNS and provides the following advantages: Multiple masters are created for DNS replication. Therefore: Any domain controller in the domain running the DNS server service can write updates to the Active Directory–integrated zones for the domain name for which they are authoritative. A separate DNS zone transfer topology is not needed. Secure dynamic updates are supported. Secure dynamic updates allow an administrator to control which computers update which names, and prevent unauthorized computers from overwriting existing names in DNS
NEW QUESTION 18
Domains provide which of the following functions?
- A. Creating logical boundaries
- B. Easing the administration of users, groups, computers, and other objects
- C. Providing a central database of network objects
- D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc756901%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Active Directory Logical Structure Background Information Before you design your Active Directory logical structure, it is important to understand the Active Directory logical model. Active Directory is a distributed database that stores and manages information about network resources, as well as application-specific data from directory enabled applications. Active Directory allows administrators to organize elements of a network (such as users, computers, devices, and so on) into a hierarchical containment structure. The top-level container is the forest. Within forests are domains, and within domains are organizational units. This is called the logical model because it is independent of the physical aspects of the deployment, such as the number of domain controllers required within each domain and network topology. Figure 2.2 Relationship Between Active Directory Forests, Domains, and OUs. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
P.S. Certleader now are offering 100% pass ensure 70-640 dumps! All 70-640 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.certleader.com/70-640-dumps.html (631 New Questions)